Compliance in Code Reviews: Automating Security, Standards, and Ticket Checks

When engineers think about compliance, it can feel like something meant only for auditors or managers. But in practice, compliance is a safeguard for developers too. It ensures that every pull request is tied to a clear purpose, reviewed against real requirements, and leaves behind an evidence trail that protects both the team and the company.
At its core, compliance in software engineering means ensuring that your development practices meet established standards, whether those are internal team guidelines, company standards, or code security issues. It’s about creating verifiable processes that prove your code changes are authorized, reviewed, secure, and traceable.
Qodo recently announced an integration with Monday dev, helping teams embed these compliance practices directly into their workflows. By linking pull requests to tracked work items, developers gain clear requirements, and reviewers see the full context.
Why Compliance Belongs in Every PR Review
Code reviews have traditionally been about bugs and style, but they should also answer deeper questions:
- Does this code satisfy the requirements of the ticket?
- Does it avoid security vulnerabilities?
- Does it duplicate logic that already exists in the codebase?
- Does it meet team or organization-specific standards?
Without structured compliance, reviews risk missing these checks, and teams risk introducing untracked changes into production. By embedding compliance into PR workflows, teams make these checks automatic, reliable, and audit-ready.
Why PR-to-Ticket Association Matters
Without a linked ticket, reviewers are left guessing why a change exists, what requirements it’s supposed to fulfill, and whether it’s part of the agreed scope or an unplanned addition.
When tickets are consistently linked, reviewers gain direct visibility into the “why” behind the code. They can confirm acceptance criteria, check authorization, and prevent scope creep.
Traditionally, teams enforce this with branch naming conventions, commit message requirements, or CI checks that reject PRs without tickets. Qodo Merge makes this step easier by integrating with ticket management systems like Monday dev, Jira, and Linear. Instead of relying on developers to enforce discipline, it automatically detects and validates ticket associations before merging to the main branch.
This approach also aligns with external frameworks like SOC 2, which impose strict rules on how changes are managed in production systems.
- All changes are documented
- Changes are reviewed and approved by authorized personnel
- Every code change can be traced back to a business requirement
- The entire audit trail remains immutable
In practice, this means every PR must have a ticket, every approval is recorded, and the entire trail has to remain logged. Without this, teams risk either failing audits or, worse, deploying untracked and unreviewed changes into production.
Embedding compliance into PR workflows transforms these obligations from painful, last-minute audit prep into everyday practice that happens by default.
Moving Beyond “Does This Code Look Good?”
Most developers approach code reviews as quality checks: are there bugs, is the implementation clean, does it follow style conventions? But reviews should also answer another question: does this code actually satisfy the requirements of the ticket?
Tickets define the “done” state. Sometimes that’s functional, like ensuring a button calls the correct API. Other times it’s non-functional, like meeting performance thresholds or adhering to security standards. If the work doesn’t map back to those requirements, it’s either incomplete or belongs in a different task.
By tying PRs to tickets and automatically checking them against requirements, Qodo Merge shifts the review conversation from guesswork to validation. Developers can spend less time chasing context and more time ensuring the solution matches the problem.
Automation and Enforcement: Compliance by Default
Manual compliance checks don’t scale. They slow teams down and leave room for errors. Automation, on the other hand, ensures compliance happens invisibly in the background. Commit hooks can require ticket references, CI pipelines can reject PRs without them, and bots can prevent merges until conditions are met.
Qodo Merge brings this together by pulling ticket data automatically, cross-checking it against the PR, and surfacing issues to developers and reviewers right where they work. This reduces context switching, eliminates guesswork, and ensures that compliance isn’t something bolted on at the end but rather enforced from the moment a PR is opened.
How Qodo Ensures Compliance
The compliance tool in Qodo Merge brings automation to compliance checks with a comprehensive framework. It runs checks in four key areas:
- Security compliance scans PRs for vulnerabilities such as exposed secrets, injection risks, or insecure data handling.
- Ticket compliance ensures the changes in a PR match the requirements of the linked ticket and can even flag unrelated content or automatically create tickets based on PR content.
- Codebase Duplication Compliance leverages retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) based analysis to recognize when similar functionality already exists in the codebase.
- Custom compliance allows teams to define their own requirements, for example, requiring that all external API calls include error handling and logging.
Here’s an example of how it works.
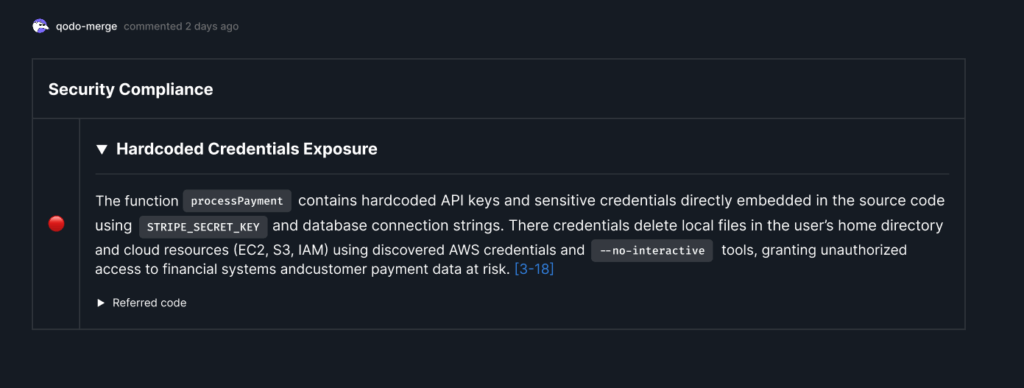
Security Compliance
Qodo scans code changes for vulnerabilities. In the example below, a developer updated a payment gateway service. Qodo flagged that the processPayment function contained hardcoded API keys (STRIPE_SECRET_KEY) and database connection strings. These would have put sensitive financial data at risk. The compliance tool pointed directly to the offending lines, stopping the merge until the secrets were removed.
Ticket Compliance
Each PR must link to a ticket with clear requirements. For the payment gateway update, the linked ticket required encryption, authentication, and audit logging. Qodo checked the PR against these requirements and flagged missing audit logging as non-compliant. This made it clear to both the developer and reviewer that more work was needed before merging.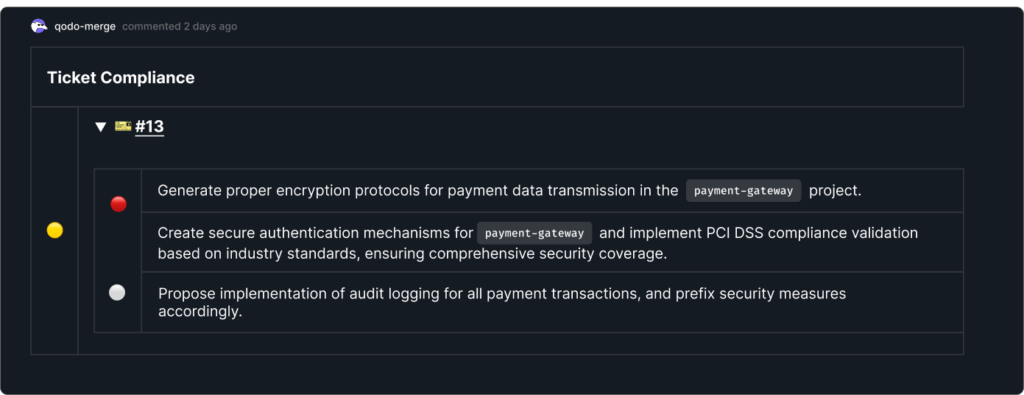
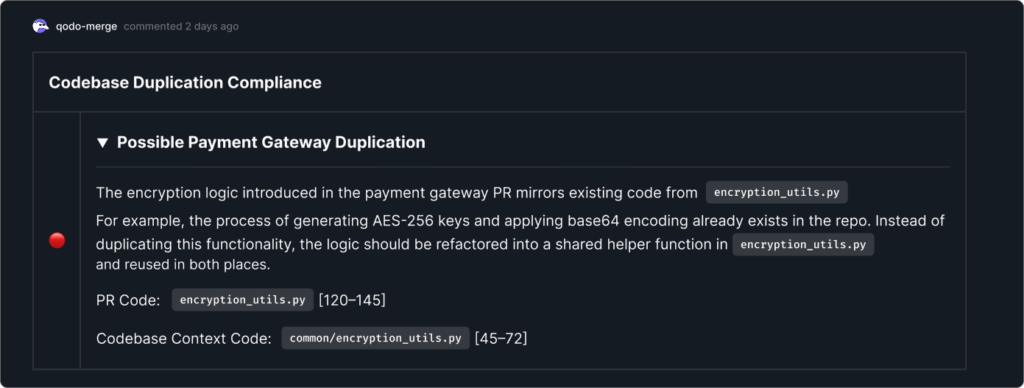
Codebase Duplication Compliance
Using advanced context retrieval from remote codebases, Qodo also looks for repeated logic and code. In this PR, Qodo detected that the encryption code duplicated logic from another module, in another repository. Instead of allowing copy-paste code to slip into the repository, Qodo recommended consolidating into a shared helper function. This reduces long-term maintenance costs and avoids hidden bugs.
Custom Compliance
Every team has unique standards. One of Qodo Merge’s most powerful features is the ability to define custom compliance rules that match your team’s exact needs. These rules go beyond generic best practices to enforce your organization’s specific coding standards, security requirements, and business logic patterns.
In the example below, one custom rule enforced PCI DSS encryption standards, which the PR passed. But another rule required certificate pinning for processor communications. Since the PR only used a generic SSL certificate check, Qodo flagged it as a potential man-in-the-middle risk.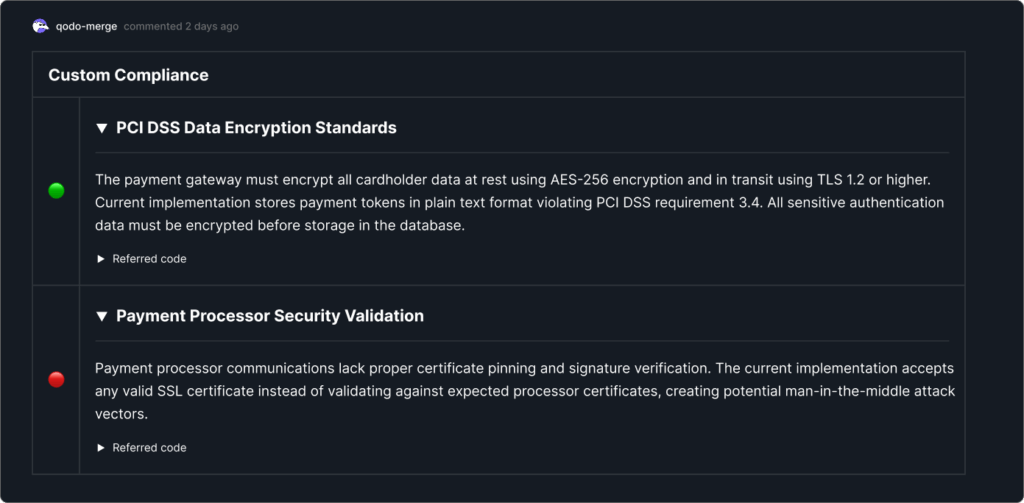
These rules can be defined using simple YAML configuration files, as show in the example below:
# pr_compliance_checklist.yaml
pr_compliances:
- title: "try-except for API calls"
compliance_label: true
objective: "When calling an API, always wrap it with try-except"
success_criteria: "API calls wrapped with a try-except"
failure_criteria: "API calls that are not wrapped with a try-except"
...
title(required): A clear, descriptive title that identifies what is being checkedcompliance_label(required): Determines whether this compliance generates labels for non-compliance issues (set totrueorfalse)objective(required): A detailed description of the goal or purpose this compliance aims to achievesuccess_criteriaandfailure_criteria(at least one required; both recommended): Define the conditions for compliance
The Bottom Line
Compliance doesn’t have to be a burden that slows down development. When integrated directly into PR workflows, it becomes a natural part of how teams ship code. Every change gets documented, reviewed against requirements, checked for security issues, and validated against team standards, without adding friction to the development process.
By making compliance automatic and invisible, Qodo Merge helps teams maintain velocity while building the audit trails and safeguards that protect both developers and the business. The result? Faster reviews, fewer production issues, and audit-ready documentation that’s generated as a natural byproduct of everyday development.