Top 3 OpenAI Codex Alternatives for Developer Teams in 2025


TL;DR
- OpenAI Codex is an adaptable AI coding model that powers tools like GitHub Copilot, enabling developers to translate natural language into code across multiple languages.
- High subscription costs, limited advanced features, and cloud-only data processing lead many teams to explore alternatives like Qodo, Cursor, and Google Jules.
- Qodo uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), static analysis, and commands like /review and /improve to generate context-aware code, PRs, tests, and documentation aligned with enterprise standards.
- Cursor provides IDE-native refactoring, multi-line edits, and agent-based coding tasks, while Google’s Jules handles asynchronous tasks in a secure VM with PR-ready updates and audio changelogs.
- Qodo fits enterprise-scale teams, Cursor is best for smaller IDE-centric workflows, and Jules excels for background task automation, offering flexibility based on team needs.
Of the many AI coding tools in the market, OpenAI Codex was initially released in 2021 as a research preview grounded in GPT‑3. It gained prominence by powering GitHub Copilot, offering developers real-time code suggestions within IDEs like Visual Studio Code and Neovim. In May 2025, OpenAI relaunched Codex as Codex‑1, now built on the more advanced o3 architecture.
The o3 architecture represents a major leap forward in reasoning and task orchestration. Rather than merely generating code, o3 functions as an autonomous reasoning agent capable of chaining together multiple tools, such as web queries, code execution, visual analysis, and iterative debugging, without direct user intervention.
However, it comes with certain limitations. As a Senior Developer, I have researched the issues with Codex and found that, in an interview with The Verge, OpenAI’s CTO Greg Brockman noted that Codex does not always interpret user intent accurately, often requiring developers to experiment with prompts to achieve the desired outcome.
Community feedback reflects similar experiences. As one Reddit user noted:
OpenAI is still testing Codex for upcoming developments and enhancements as it continues to provide better features. In my experience, other tools can help you generate higher code quality, especially under budget constraints.
In this post, I’ll summarize the best OpenAI Codex alternatives for 2025. All of them are recommended by my personal experiences working across different projects and software development lifecycles.
When to Consider an OpenAI Codex Alternative
I find OpenAI Codex to be a foundational model for coding, but there are a few considerations that often lead my team and others to explore alternative tools. These usually come down to real-world workflows, compliance needs, and the demands of enterprise-scale development.
High Subscription Costs
One of the main reasons teams explore Codex alternatives is its $200 monthly Pro subscription, which is often more expensive than other AI coding tools. For teams like mine working with tighter budgets, I’ve found platforms like Qodo to be a more cost-effective choice while still offering similar functionality, including code generation, testing, and pull request reviews. This helps us stay productive without taking on high recurring costs.
Limited Features in Its Current Stage
Codex is still in its research preview stage and does not include certain advanced features yet. Capabilities like image inputs for frontend development or the ability to adjust an agent’s actions during execution are unavailable.
Data Privacy and Security Considerations
Codex processes code in cloud environments, which can raise concerns for teams with strict data privacy or intellectual property requirements. Organizations operating in regulated industries often need solutions that keep all code and data on-premises. Alternative tools can help us address this by offering deployment options that ensure sensitive code remains fully under the company’s control.
Alternatives Detailed Tool Reviews
I’ve shared detailed reviews of the OpenAI Codex alternatives I’ve tested in this section. I’ve focused on their core features, best use cases, real-world examples, and pricing to help teams find the right fit for their workflows.
Feature-by-Feature Comparison of OpenAI Codex Alternatives
Below, getting started, I have made a table of comparison for a better overview for you to understand the comparison better:
| Feature | Qodo | Cursor | Jules | OpenAI Codex |
| Repository-wide context | Yes (RAG and full indexing) | Yes (indexed in IDE) | Yes (repo cloned in VM) | No (single-file only) |
| Static analysis | Yes | No | No | No |
| Pull request review | Yes (via /review) | No | Yes (auto PRs) | No |
| CI/CD integration | Yes (via CLI and Qodo Command) | No | No | No |
| Code improvements | Yes (via /improve) | Yes (smart rewrites) | No | No |
| Test generation | Yes (unit and integration tests) | No | Limited | No |
| Full-feature generation from prompt | Yes (step-by-step with patch) | Yes (Agent Mode) | Yes (task planning and edits) | Limited (short completions) |
| IDE support | Yes (VS Code, JetBrains) | Yes (custom VS Code fork) | No | Yes (VS Code, JetBrains) |
| Compliance and rule enforcement | Yes (bestpractises.yaml support) | Partial (manual only) | No | No |
| Async background execution | No | No | Yes | No |
| Enterprise controls (SSO, on-prem) | Yes | Yes (on higher plans) | Yes | Limited |
Qodo (Top Pick)
Qodo is an AI-powered development platform built for enterprise-scale projects, combining Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with static analysis to deliver contextually accurate and review-ready code suggestions.
Unlike single-file assistants, Qodo indexes the entire repository, retrieves relevant references, and generates solutions that align with project-wide standards. It’s RAG-driven approach ensures that actual patterns, best practices, and architecture rules within the codebase inform the AI suggestions.
Best For
- Distributed teams building and maintaining multi-repo, large-scale codebases
- Development organizations need robust integration with CI/CD workflows, detailed code reviews, and cross-repository awareness
Key Features
- Graph-Aware Review: Qodo understands the semantic structure of your codebase, detecting changes that break architectural boundaries, drift from behavioral contracts, or circumvent critical cross-cutting concerns.
- RAG Context Enrichment: Leverages repository-wide retrieval to generate context-aware code and tests.
- Dual Publishing Mode: Qodo can surface AI-generated fixes as inline review comments or proposed code edits in a branch/PR. Suggestions are tracked until resolved, and developers retain full control over what gets merged.
- CLI & IDE Support: Available through extensions in VS Code, JetBrains, and CLI tools to embed AI agents into CI/CD pipelines, automating tests, coverage checks, and PR reviews.
- Compliance and Code Standards: Enforces organization-specific rules using configurations like bestpractises.yaml (a configuration file used to define and enforce organization-specific coding standards, architectural rules, and review guidelines)
First Hand Example
I used Qodo to build a REST API to generate PDF invoices that had to follow our existing service patterns. After indexing the repository, Qodo proposed a complete module with a FastAPI route, data models using Pydantic, and integrated error handling.
Prompt I used:
“Create a FastAPI endpoint POST /invoices that generates PDF invoices using the utils/pdf.py library, applies request schema validation, and follows the logging structure from billing/api.py. Add pytest unit tests with valid and invalid input cases.”
Here’s what Qodo created:
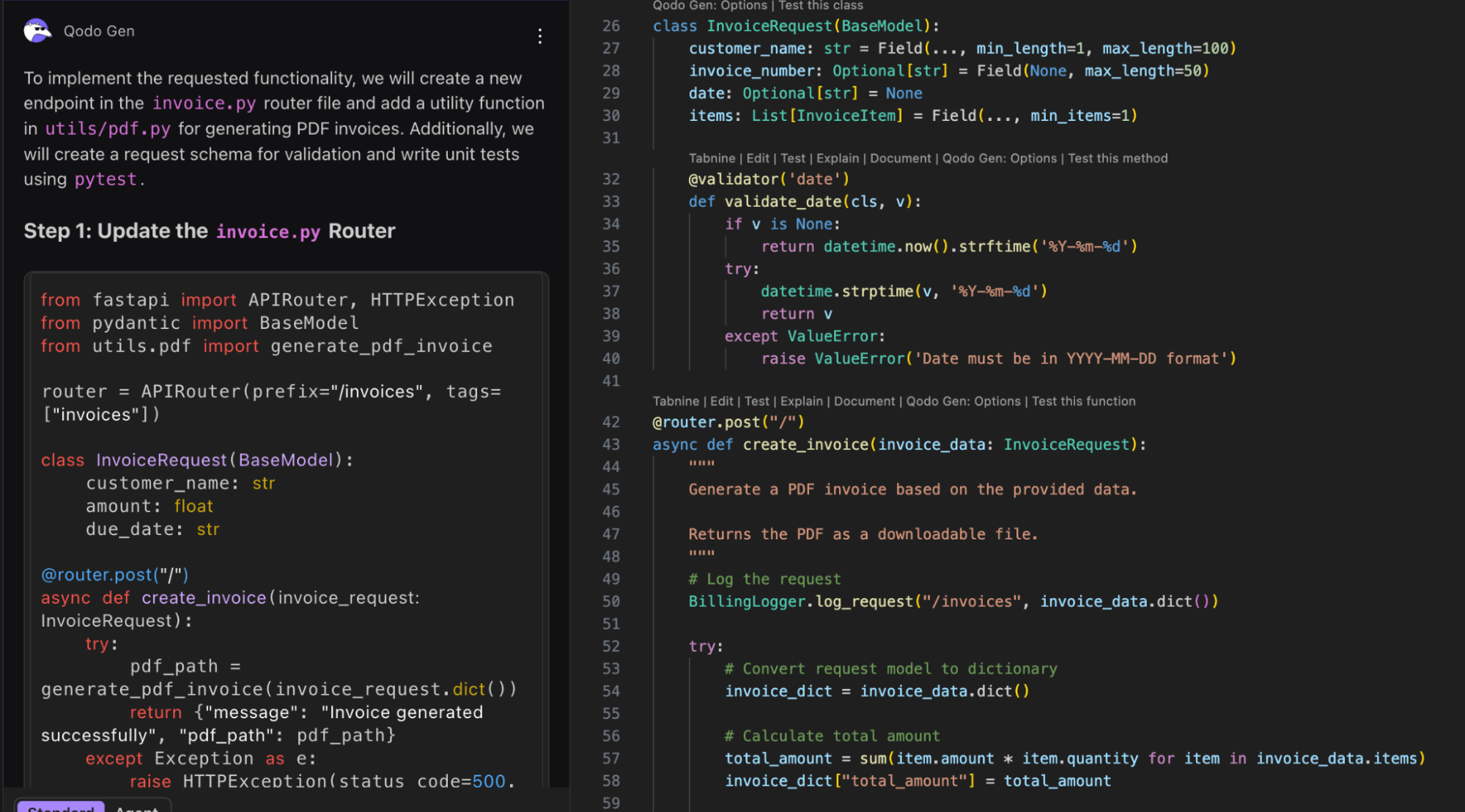
In the screenshot above, Qodo responds to my prompt with a step-by-step plan and the generated patch. On the left, it explains what it will do: add an /invoices route in invoice.py, call a generate_pdf_invoice helper from utils/pdf.py, define a typed request schema, and create pytest tests.
On the right, you can see the actual FastAPI code it produced, including the InvoiceRequest Pydantic model, a date validator, the POST/ handler that logs the request, converts the payload, calls the PDF generator, and returns a structured response with error handling stubs. The imports, router tag, and validation hooks align with the rules we defined in bestpractices.yaml, helping us stay on track with the team compliance standards.
Pros
- Accurate, context-aware suggestions thanks to its RAG pipeline and code embedding model
- Automated PR and CI/CD workflows reduce repetitive human review effort
- Secure deployment models, including on-premise or private-cloud options, designed for enterprise compliance.
Cons
- Initial setup, including indexing and configuration of team guidelines, takes some effort to unlock full benefits.
- Advanced features are more valuable for teams than solo developers, as they focus on PR workflows and CI/CD automation.
Pricing
Qodo’s free plan covers core features for individuals. The Teams plan costs $30/user per month with 2,500 credits, offering automated PR reviews, custom best practices, and private support. For enterprise plans, Speak to Qodo. Includes the full platform with an enterprise dashboard, multi-repo awareness, SSO, priority support, and flexible deployment options like SaaS or on-premise.
Cursor
I find Cursor particularly useful when I need an AI-powered editor that feels like an extension of my workflow rather than a separate tool. Built on a custom fork of Visual Studio Code, it helps me to make my tasks easier by turning natural language prompts into multi-line edits, refactoring, and code generation.
Unlike standard autocompletion tools, Cursor indexes my entire project so that I can search, edit, and update codebase-wide logic through conversational queries. This makes it easier to manage larger projects without switching contexts.
Best For
- Individual developers or small teams who prefer working within an IDE environment.
- Projects where inline AI suggestions, quick refactoring, and IDE-native workflows matter most.
Key Features
- AI Tab Autocomplete & Multi-Line Edits: Suggests edits across multiple lines based on recent context
- Smart Rewrites: Enables bug fixes and refactoring across opened files via natural language prompts
- Agent Mode (Ctrl + I): Executes full tasks like generating classes or updating references with developer confirmation
- Codebase Queries: Search the entire indexed codebase using natural language queries
- Shell Command Generation: Generates and runs terminal commands from prompts, with built-in safety checks
- Privacy Mode & SOC 2 Compliance: Ensures no remote storage of your code when enabled
First-Hand Example
I used Cursor’s agent mode (Ctrl + I) to create a fully functional React login page for an internal admin dashboard to test Cursor’s capabilities. My prompt was:
“Build a responsive login page in React with email and password inputs, real-time validation for empty or invalid fields, a submit button that calls authService.login(), and a loading state.”
Here’s a snapshot of Cursor’s output:
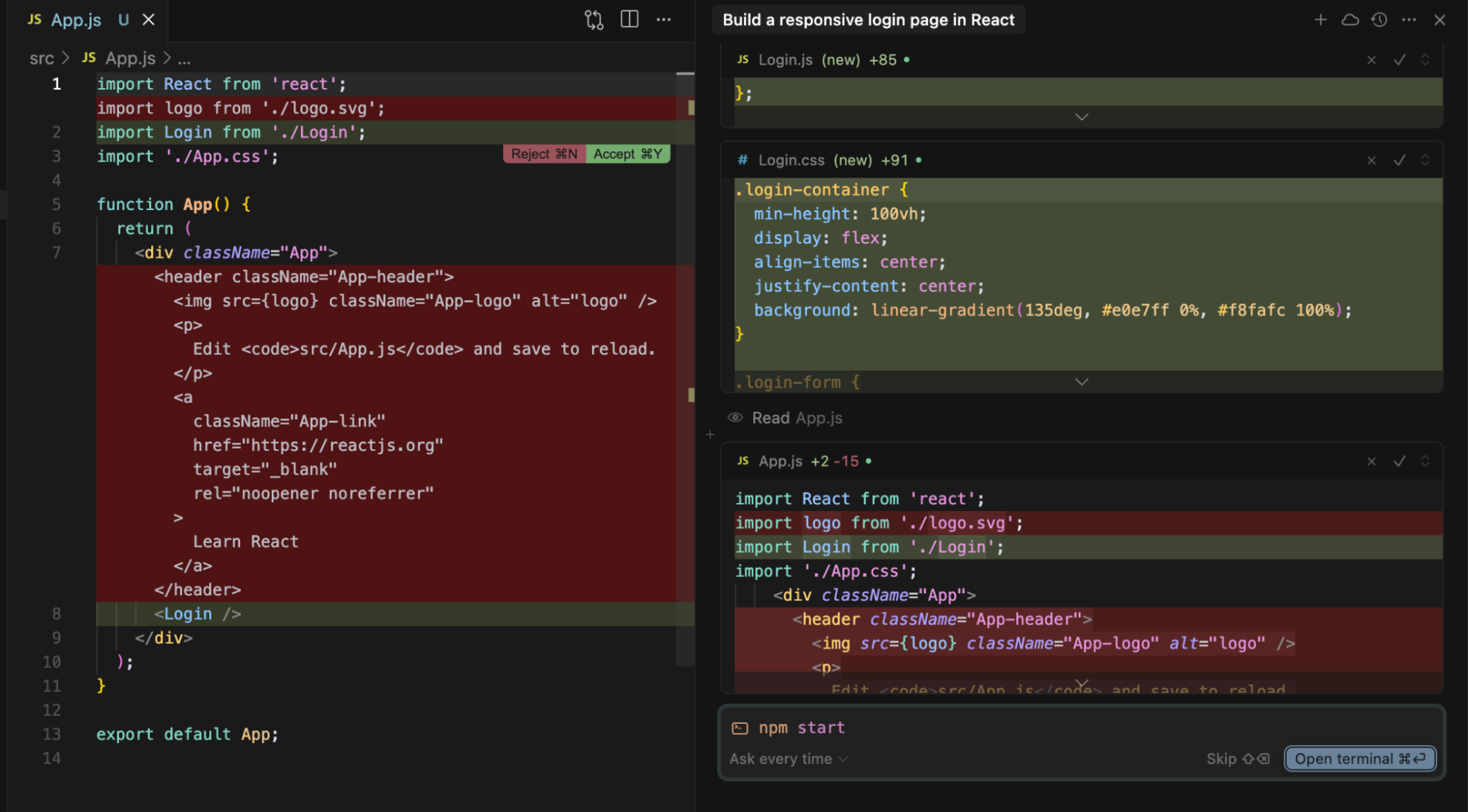
Cursor generated a Login.jsx component with a clean layout, pre-configured useState hooks for managing form data, and inline validation logic that displayed error messages dynamically. It also added a handleSubmit function to trigger authService.login() and integrated a loading spinner while processing the request. Cursor updated App.js with a protected route structure to ensure smooth navigation, redirecting authenticated users to the dashboard.
The UI looks like this:
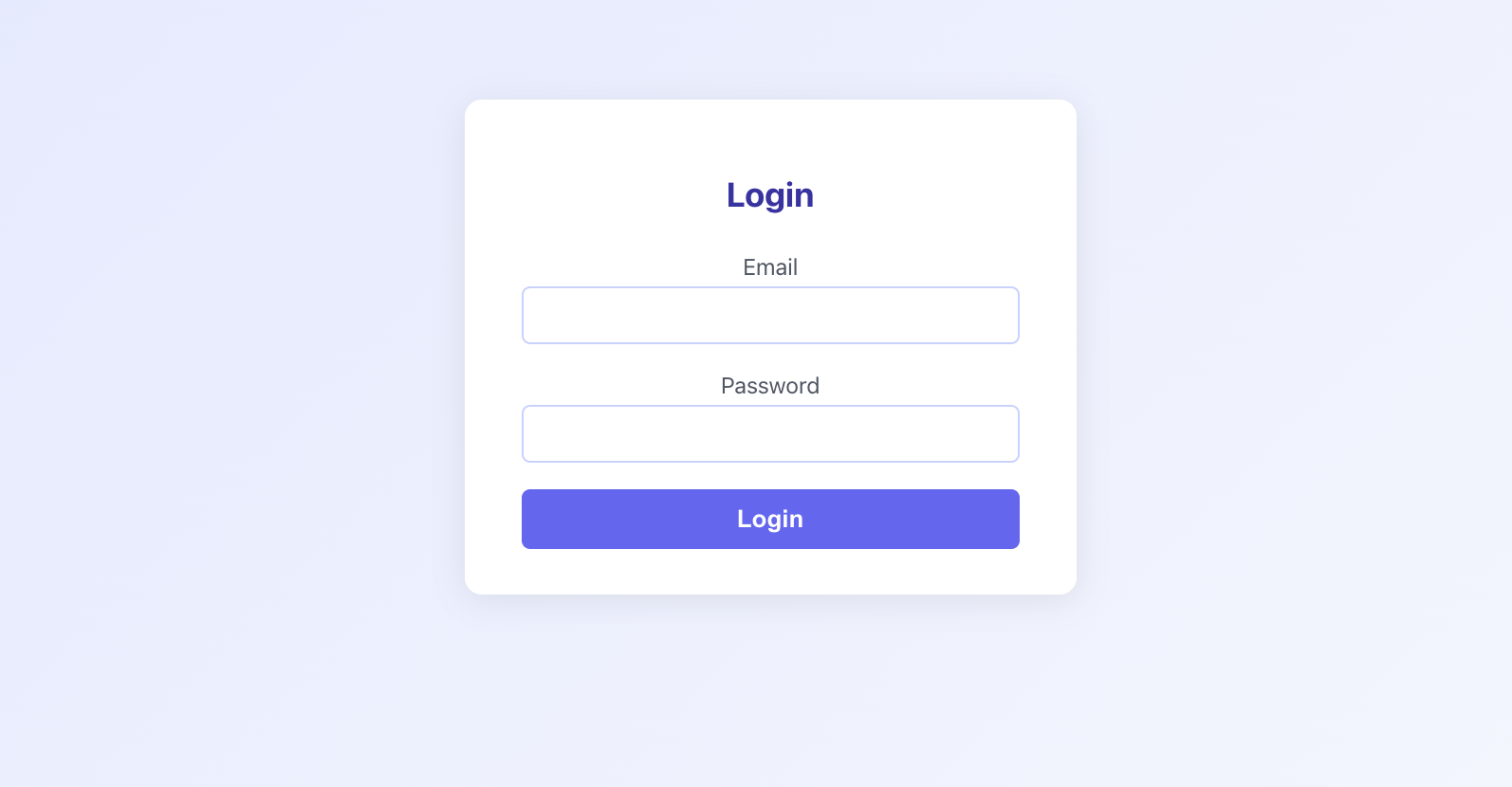
Handling both the UI and integration points delivered a ready-to-use component that required minimal tweaks, significantly cutting down the time I would have spent manually setting up the page.
Pros
- Deep IDE integration with a familiar VS Code experience.
- Fast, contextual multi-line edits and natural-language refactoring.
- Robust privacy features like SOC 2 certification and optional Privacy Mode.
Cons
- Primarily optimized for IDE-centric workflows and does not include built-in PR or CI/CD pipeline automation.
- Agent and multi-line editing capabilities depend on well-structured prompts and may require iteration for complex tasks.
Pricing
Cursor’s Free plan includes limited completions, 50 monthly slow requests, and an agent trial. The Pro plan costs $20/month with 500 fast requests, unlimited completions, and smart rewrites. The Ultra plan at $200/month offers 20× Pro’s usage. The Teams plan is $40/user/month with centralized billing, Privacy Mode, and SSO. Enterprise plans are custom, including extended usage, SCIM, advanced controls, and priority support.
Google Jules
Google’s Jules is an asynchronous, agentic coding assistant inside a secure cloud VM. When you assign a task, Jules clones your GitHub repository that you are working on, analyzes code with Gemini 2.5 Pro, plans each step, and executes changes across multiple files.
It integrates directly with GitHub, submitting changes as pull requests when you approve the plan. Jules is privacy-first; it does not train on your private code and provides audio summaries of changes made.
Best For
Engineering teams looking to automate routine development work, such as software dependency updates (libraries, frameworks, packages), test generation, bug fixing, or feature implementation, via background agents that let developers focus on higher-level design and strategy.
Key Features
- Asynchronous Task Execution: Submit tasks like “bump Next.js to v15” and Jules handles planning, execution, and PR creation in the background.
- Visible Planning & Steering: Jules outlines its approach before making changes, letting you review or modify the plan
- Secure Cloud VM Environment: Each task runs in an isolated VM where Jules clones your code and runs tooling, but cannot train on your private code
- Multi-File Updates & GitHub PR Support: Jules makes coordinated edits across multiple files and sends a pull request with a diff and audio changelog
- Audio Changelogs: After making changes, Jules generates an audio summary outlining what was done
First-Hand Example
I tested Google’s Jules by assigning it a task to set up a React-based admin dashboard with Tailwind CSS. My prompt was:
“Create a React admin dashboard with a sidebar, top navigation bar, and a responsive table using Tailwind CSS. Add mock data for the table and implement sorting by column headers.”
Here’s a snapshot of Jules’ output:
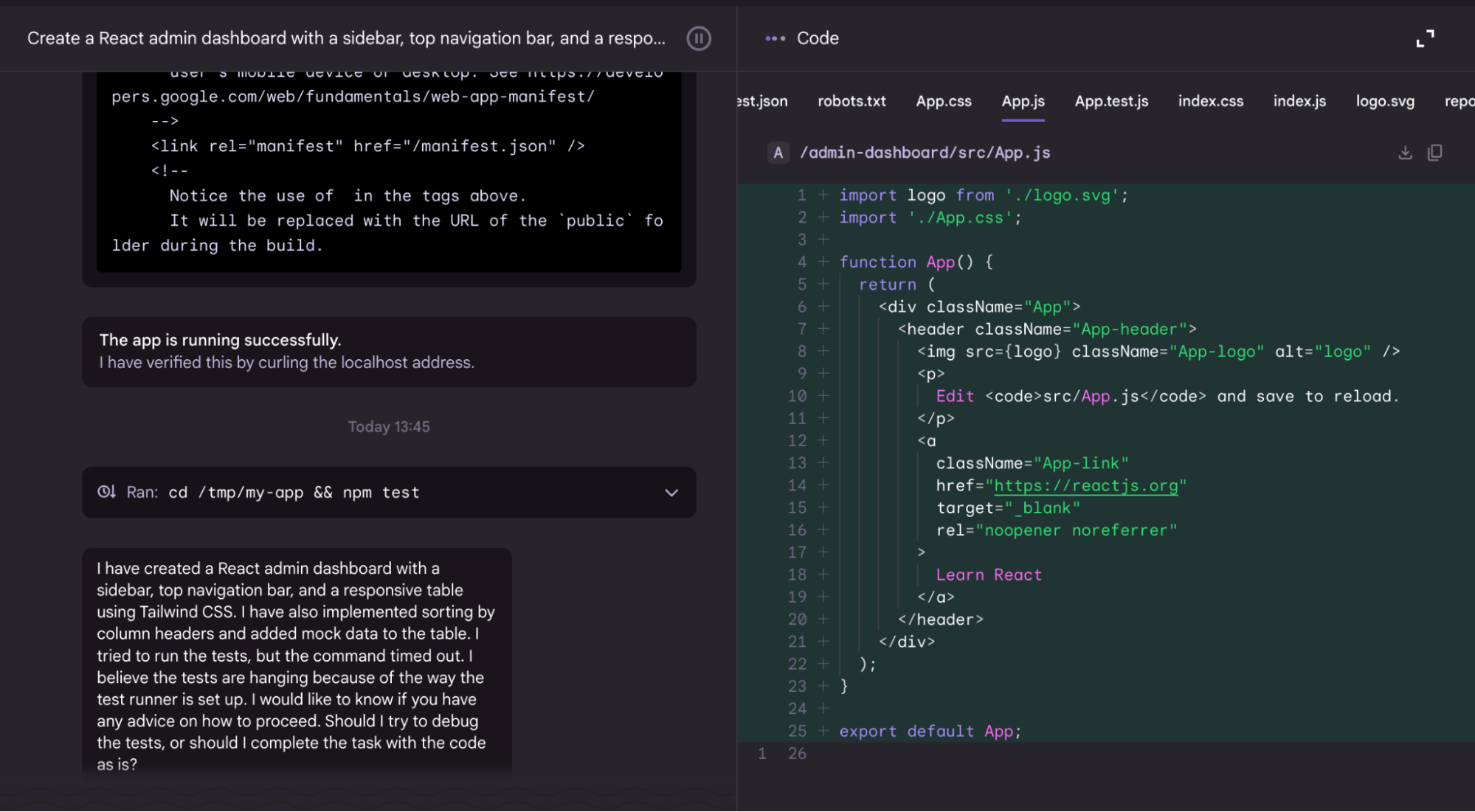
Jules planned the structure, built the components, and added mock data for the table, including sorting functionality on column headers. It ran the application in a secure VM, verified that it was running by curling the localhost address, and then attempted to run the tests.
Pros
- No waiting around: tasks proceed independently in the background.
- High transparency: Jules lays out its plan and reasoning before editing.
- Private-by-design: code stays within Google Cloud VM and is not used for model training.
Cons
- Still in public beta, so usage is limited (about five tasks per day by default)
- Learning to write effective prompts and review plans takes some adaptation.
- Response quality may vary based on task complexity and VM environment setup.
Pricing
Jules is free during public beta, with daily and concurrent task limits (5 concurrent tasks and 60 total daily tasks). Future pricing is expected once the platform matures.
Expert Advice
- Asynchronous vs. Real-Time Workflow: Jules is ideal for background, batch-style coding tasks, while Qodo works in real time within IDEs like VS Code and JetBrains, enabling faster iteration and immediate validation.
- Repository-Wide Context: Qodo uses RAG with static analysis to generate review-ready code, tests, and PR descriptions, ensuring changes align with project-wide standards.
- Seamless Integration: Unlike Jules’ isolated VM workflow, Qodo integrates directly into existing CI/CD pipelines and local dev environments, reducing context-switching for developers.
- Enterprise-Grade Controls: With best practices.yaml, Qodo enforces coding guidelines, architectural rules, and test requirements, which are crucial for large multi-repo systems.
Why Qodo is Better for Enterprises?
Qodo is designed to address the needs of enterprise-scale development teams by combining repository-wide awareness with strict compliance and collaboration workflows. It brings repository-wide awareness, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), and static analysis into developer workflows, making it especially relevant for Directors and Managers of Engineering who are responsible for delivery, team performance, and maintaining development velocity without compromising quality.
With Qodo, I rely on powerful commands like /ask, /review, and /improve to simplify my workflow. The /ask command lets me query the entire codebase for explanations, dependencies, or architectural details, which is invaluable for understanding complex systems.
Qodo directly supports this by automating high-effort tasks such as routine code reviews and test generation. Instead of senior engineers spending cycles reviewing pull requests manually, the /review command surfaces critical issues, like missing tests, security flaws, or architectural violations, using static analysis and RAG-powered understanding.
For example, directors who work with multiple cross-functional teams can use Qodo to reduce review overhead. They can easily integrate/review and /improve into their CI workflow so that every pull request is automatically checked for coverage, internal conventions, and architectural consistency. This can help them standardize expectations across teams and give reviewers a cleaner, more focused diff to look at, without needing to expand the QA team.
Beyond commands, Qodo can automatically generate unit tests, integration tests, and documentation that follow the existing patterns in the repository. It simplifies PR creation by drafting structured PR descriptions, checking for compliance using bestpractises.yaml, and validating code against defined organizational rules. This ensures that every AI-generated suggestion aligns with enterprise standards and security policies.
Conclusion
OpenAI Codex is a powerful coding assistant, but enterprises often need tools that provide deeper repository context, customizable workflows, and stronger compliance controls. In this blog, we explored top alternatives such as Qodo, Cursor, and Google’s Jules.
Qodo stands out for its RAG-powered context enrichment, static analysis, and enterprise-grade features like compliance enforcement, automated PR workflows, and test generation.
Each tool serves distinct developer needs, but for enterprise-scale workflows that demand security, context, and integration with CI/CD, Qodo remains the most comprehensive option.
FAQs
What is the best OpenAI Codex alternative for enterprise?
Qodo is one of the best alternatives for enterprise teams due to its repository-wide context awareness, RAG-driven AI generation, compliance checks using bestpractises.yaml, and seamless integration with Git and CI/CD pipelines.
What is OpenAI Codex best for, and what is not?
OpenAI Codex is best for single-file code completions, quick prototyping, and learning exercises. However, it is not as effective for repository-wide tasks, PR-ready reviews, or enterprise-level compliance requirements, where tools like Qodo or Google’s Jules excel.
Can I use OpenAI Codex for enterprise code?
Yes, you can use Codex for enterprise code, but you need to consider its cloud-based environment and lack of native compliance features. Many enterprises prefer alternatives like Qodo that support on-premise deployment and strict data governance.
Is OpenAI Codex secure and SOC2 compliant?
Yes. OpenAI’s business products and API, which includes Codex, have been evaluated for compliance with SOC 2 Type 2 Security and Confidentiality principles. This ensures enterprise users can rely on its infrastructure for secure data handling.





