The missing quality layer: Qodo’s AI code review platform


By 2025, many companies using AI coding tools started running into the same problem: productivity and code volume climbs, but so do code review bottlenecks. All while gaps in code quality lead to issues that slip through and show up later as failures in production. In the last quarter of this year alone, we’ve seen at least three major outages, impacting teams and services across industries.
When Qodo began working with larger engineering orgs, the story repeated. Teams aren’t struggling to write code. They are struggling to review it. AI tools produce changes that look fine in isolation but introduce edge case failures, broken contracts, and inconsistencies that spread across services. More than half of developers said they often can’t tell whether an AI-generated change matched their team’s patterns or past decisions. A rising number of incidents traced back to missing context: a dependency no one noticed, a pattern that differed across repos, or a test path the AI never saw.
Instead of accelerating code generation, Qodo strengthens the step where quality is decided: review. Qodo is the AI Code Review Platform that brings system-level context, structured analysis, and reliable review automation into every stage of development. It helps teams understand how a change fits into the system, surfaces risks early, and gives developers the review processes they need to ship fast without losing quality.
Qodo: the AI Code Review Platform
Review across the SDLC
Qodo’s AI Code Review Platform brings context-aware review into every stage of the software development lifecycle. The platform reviews code from the moment it is written to the moment it is ready to merge, applying the same system-level understanding at each step.
In the IDE, Qodo reviews local changes as they are written. Developers see how a change affects related files, dependencies, and patterns across the broader system. Qodo flags issues that are easy to miss when working in a single repo, surfaces the downstream effects of an update, and proposes concrete fixes that can be applied before a commit is even made. This shifts review left and reduces the amount of rework that usually shows up later in pull requests.
In Git providers, Qodo performs automated review workflows to enhance PR and code quality. Pull requests are analyzed with awareness beyond the PR code or single repo. The platform identifies breaking changes, logic gaps, and policy violations based on user rules and knowledge of the larger codebase, and provides structured suggestions that guide reviewers through the most critical issues. These automated pre-checks, along with generated summaries and commands for generating tests and docs, give users their most effective review tool.
Through the CLI, Qodo supports custom workflows that help teams scale quality across large codebases. Organizations can build their own quality agents, enforce rules, codify internal standards, automate ticket-driven steps and more using the same context engine and agents available in the IDE and Git. These workflows make it possible to turn quality practices into reliable automation rather than manual effort.
Power AI reviews with context
At the center of the platform is Qodo’s context engine, the system that gives every agent and workflow a shared, multi-repo codebase-wide understanding of how the software actually behaves. The engine encodes repositories structurally, semantically, and with embeddings, turning raw code into a searchable knowledge layer that captures meaning, relationships, and intent. Instead of scanning files in isolation, it builds a connected map of modules, interfaces, dependencies, data flows, and test paths, allowing agents to reason about how changes affect the broader system.
To support deeper exploration, the context engine includes purpose-built research tools that go beyond typical retrieval techniques. These tools track how data and logic move across services, expose subtle cross-repo breakages, and help agents evaluate a change not just by its diff but by its real impact on system behavior.
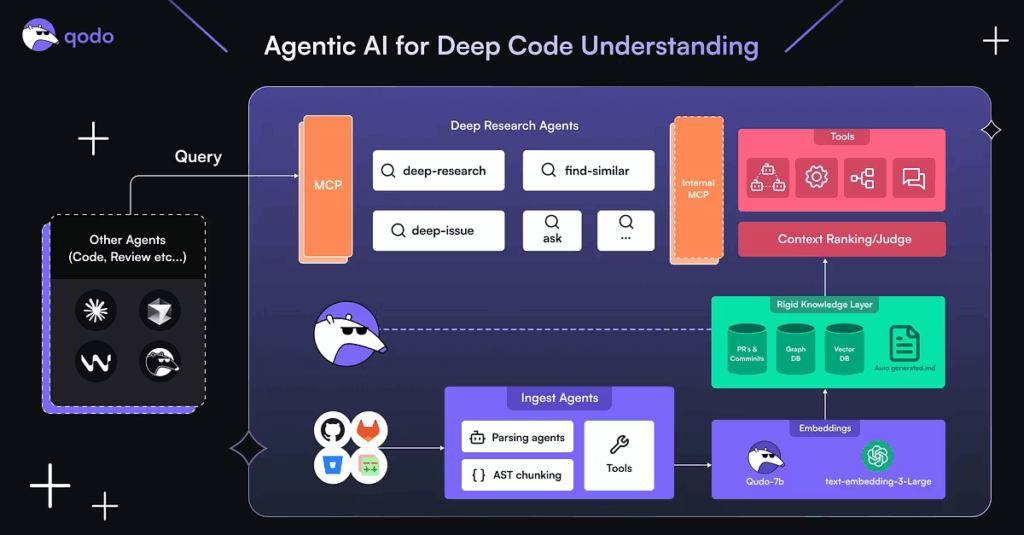
The context engine extends beyond Qodo’s own tools. Through a flexible MCP and API, teams can connect the engine to other AI tools, IDEs, or terminals, embedding their codebase knowledge directly into their existing workflows.
Execute reviews with a multi-agent system
Qodo’s platform leverages a multi-agent system, where each agent focuses on a different dimension of code quality and review. Using the same underlying context engine, agents shares the same view of dependencies, patterns, tests, and history.
Distinct reasoning guides each agent through multi-step analysis, whether identifying issues, answering complex questions, or uncovering hidden insights that span repos. This makes the platform consistent: all agents work from the same source of truth and interpret changes with the depth of an engineer who knows the entire system.
Examples of Qodo agents:
Critical Issue Agent
Detects bugs, logic errors, bad branches, and edge-case failures. For example, it can flag an API update that introduces unreachable states, missing null handling, or mismatched return shapes.
Breaking Changes Agent
Evaluates whether a change breaks upstream or downstream consumers. If a refactor alters a return type or removes a field used by another service, this agent surfaces it early.
Ticket Compliance Agent
Checks whether the code matches the intent of the ticket or requirement. It identifies missing acceptance criteria, unimplemented steps, or incomplete updates across repos.
Duplicated Logic Agent
Finds repeated logic across repositories and flags places where code diverges from established abstractions. This reduces drift and helps large teams avoid silently re-implementing the same functionality in multiple places.
Rules Agent
Enforces internal best practices, architecture rules, security constraints, or naming conventions. Because teams can define their own rules, this agent becomes a guardrail that scales with the organization
Test Coverage Agent
Suggests missing tests, identifies under-tested branches, and proposes test cases based on how similar code paths are exercised elsewhere. This increases confidence when shipping high-impact changes.
Continuous Learning
Qodo doesn’t stay static. As developers accept or reject suggested fixes, Qodo records those decisions and learns from real usage. Over time, this feedback trains the system to match your team’s style, priorities, and patterns.
For example, if across multiple pull requests developers consistently accept suggestions that align code formatting or rename functions, Qodo will treat that pattern as an accepted convention. The next time similar code appears, the agents will prioritize suggestions aligned with that convention rather than default generic rules.
What you can do with Qodo’s AI Code Review Platform
Local code review in the IDE
Qodo can turn your IDE into an intelligent review environment where agents review code, surface issues and validate quality, giving developers immediate feedback. As you make changes, Qodo analyzes committed and uncommitted changes, understands how it relates to the rest of the system, and highlights issues before a single commit is created. This shifts review earlier in the process, where fixes are cheapest and easiest. The agents run alongside AI coding assistants like Copilot and Cursor, reviewing the code those tools generate before it leaves your machine.
Qodo can also identify untested logic and generate relevant test cases from code changes and dependencies, so every update ships with validated coverage. One-click apply lets developers adopt fixes directly in the editor without breaking flow. The result: fewer noisy PRs entering the review queue and shorter cycles downstream.
Pull request review in the Git
When code reaches a pull or merge request in GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, Qodo performs a full AI-driven review. Qodo analyzes each PR for bugs, logic gaps, missing tests, risky changes, compliance violations, security issues, and inconsistencies across repos. With more than 15 automated workflows, the platform performs a complete set of checks to help reviewers identify problems, ensure standards are followed, validate requirements, and generate the artifacts needed to keep code quality high. Users can run commands for missing test coverage and test generation, documentation, CI failures and more.
Qodo also brings ticket-aware validation into the review flow. When a PR is linked to a Jira ticket, Qodo retrieves the ticket, reads its acceptance criteria, and checks whether the code actually fulfills each requirement. If a ticket requires input validation, logging, a certain auth method, or a security check, Qodo verifies the implementation and flags any gaps directly in the PR with specific references. If a PR is missing a ticket, Qodo can automatically generate one. This creates an automatic audit trail between tickets and code, giving teams confidence that requirements are met.
A new foundation for code quality
Qodo gives engineering teams the quality layer they’ve been missing as AI accelerates development. It brings context, structure, and confidence back into the process, turning review into a repeatable practice rather than a bottleneck. As teams adopt more AI coding tools and code volume continues to rise, review becomes the place where safety and consistency must hold. Qodo makes that possible. It helps developers move faster without sacrificing stability, gives reviewers the depth they need to make informed decisions, and helps organizations keep quality steady across every repo and every change.