8 Best AI Code Review Tools Compared (2026 Guide)
By the end of 2025, AI expedited code generation for software delivery. But it also created a bottleneck: code review.
Based on GitHub’s Octoverse report, monthly code pushes crossed 82 million, merged pull requests hit 43 million, and about 41% of new code was AI-assisted. The number of pull requests climbed dramatically, a large share of new code became AI‑assisted, and pull requests grew broader, touching services, shared libraries, infrastructure, and tests in a single change.
The question became: “Can we safely review what AI produces before it hits production?” and whether automated code review could realistically scale to meet this new level of complexity.
In 2026, the next era of AI code review will be defined by system‑aware agentic reviewers that understand contracts, dependencies, and production impact.
This guide is for engineering leaders, staff+ engineers, and platform teams asking the following:
- What changed in AI code review between 2025 and 2026?
- Which tools are worth my team’s time for our architecture?
- Can these tools really detect breaking changes, or just style issues?
- How do you measure whether an AI reviewer is worth keeping?
I’ve spent a decade writing code as a professional software developer, and I’m now fully immersed in the AI-augmented engineering world. So I decided to evaluate AI code review tools against production‑style systems. This article is the result of that work.
What Changed in AI Code Review in 2026: Three Major Shifts
Two big things changed since late 2025: how tools approach breaking change detection, and what engineering leaders expect in return for adopting AI review.
1. Breaking change detection grew up in AI Code Review
In 2023-2024, most tools behaved like smart linters over diffs. They analyzed the changed lines in isolation, applied pattern-based checks, and had no understanding of how the code was used elsewhere in the system. A change like “add a required field to a shared request schema” looked “small” in the PR, but silently broke dozens of downstream services and jobs.
By the end of 2025, better tools had moved from simple text diffs to more semantic analysis of code structure, dependencies, and contracts. They:
- Know where a shared type or function is consumed
- Recognize when a change is a contract change, not just a refactor
- Flag likely breaks before the merge, not after the incident review
Breaking changes are not “solved,” but the gap between tools that maintain persistent system context and those that only see a diff widened significantly.
2. Context‑aware reviewers became a distinct category
- Diff‑aware tools: Built to understand a PR or a file within a repo. Great at local correctness, duplication, and refactoring.
- System‑aware tools: Built to understand relationships between services, shared libraries, and long‑lived contracts across repositories.
Context‑aware code review is now a real category, not just some buzzword for “AI‑powered.” System‑aware reviewers with the context window carry context across repos and runs; diff‑aware reviewers reset their understanding on every PR.
3. Leaders started demanding measurable ROI
By the end of 2025, many organizations had already rolled out AI code review tools across their teams. After a few months of use, the outcome was clear: tools that only added comments without minimizing review effort were ignored or turned off, while a small number became part of the standard review workflow. Engineering leaders are now skeptical of any tool that can’t demonstrate impact on:
- Time‑to‑first‑review and time‑to‑merge
- Number of review iterations per PR
- Developer review hours per week
- Escaped defects or incidents tied to recent changes
In 2026, “the AI bot left comments” is not a meaningful outcome. But “we cut review load by 20-30% while keeping incident rates flat or lower” is. Now, let’s go through how tools behave in day-to-day workflows.
AI Code Review Tools Landscape in 2026
The AI code review ecosystem now roughly falls into three groups:
| Category | Scope & Focus | Capabilities | Examples |
| System-aware / Context-engine tools | Multi-repo context with deep architectural understanding | • Multi-repo indexing & dependency graphs
• Cross-service impact analysis • Breaking change detection • Organizational knowledge integration |
Qodo |
| Repo-scoped helpers | PR-centric, diff-aware analysis focused on local correctness | • Line-by-line suggestions
• Duplication detection • Style & readability checks • Single-repo context |
GitHub Copilot Review
Codex-style reviewers |
| Security-first engines | Static and AI-driven vulnerability detection | • Vulnerability scanning
• Data-flow analysis • Compliance checks • Security-focused only |
Snyk
Semgrep CodeQL OX Security |
The strongest enterprise stacks pair one system‑aware reviewer with one security‑first engine, and then sprinkle diff‑level helpers where appropriate.
Best AI Code Review Tools in 2026: Features, Use Cases, Hands-on Examples
I evaluated AI code review tools based on how they are used in enterprise environments, not by feature count or popularity. Learn more about the criteria I used to test and evaluate each tool.
The goal is to make it clear where each tool fits operationally in the complete SDLC, especially in enterprise setups where review challenges differ across teams.
Now that the criteria are defined, let’s walk through each tool.
The sections below evaluate every tool using the same framework, ensuring consistency. Each assessment focuses on how the tool performs in real enterprise environments, not on isolated features or idealized demos.
Each evaluation follows the same structure:
- What I tested: PRs that touched shared logic, crossed module or repo boundaries, and had the potential to affect multiple teams or services.
- What it did well: Where the tool reduced review cycles, surfaced risks early, or helped teams align on impact without back-and-forth.
- Where it struggled: The gaps were especially around system behavior, downstream impact, or cases where I still had to do the hard thinking manually.
- Who it actually fits: The kinds of teams and systems where I’d recommend the tool, based on day-to-day engineering constraints.
This makes it easier to compare tools based on operational impact, not marketing claims.
1. Qodo: AI code review for enterprise-scale codebases
Qodo is an AI code review platform that automates review workflows, enforces quality, and helps organizations ship code faster with confidence. It operates across your entire SDLC through Git interface (automated PR review), IDE plugin (validate code as you write), CLI tool (workflow automation and CI integration), and Context Engine (deep codebase research for complex technical tasks).
Quick Stats:
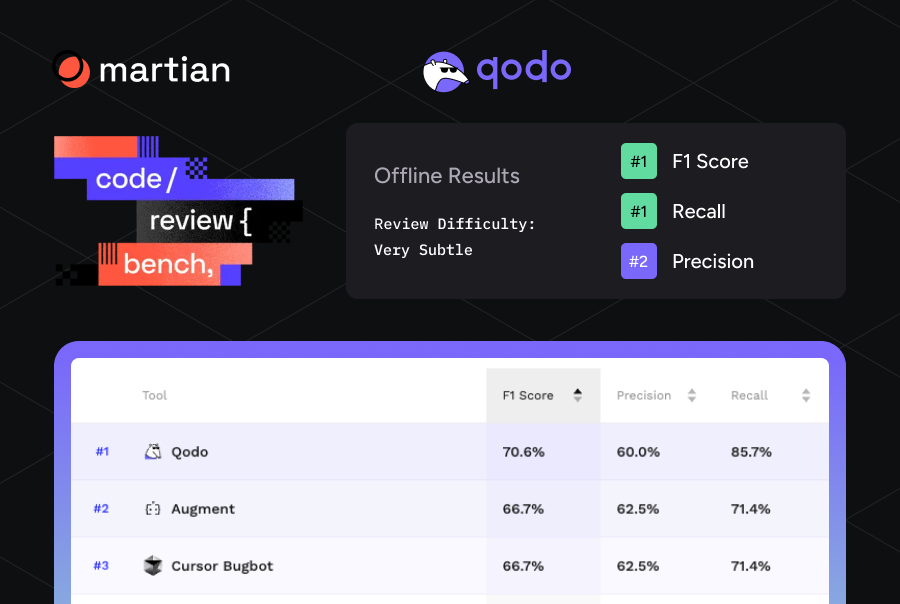
| Tool tested | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| Qodo | Data-flow analysis | Cross-repo aware | System-level | 95% actionable | Cross-service aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Strong. Issues are tied to real execution paths, not just patterns.
- Context alignment: Qodo’s main strength. It reasons across shared utilities and subsystems.
- Code quality & maintainability: Code quality focuses on structural and lifecycle risks, avoiding cosmetic feedback.
- Signal vs noise ratios: Produces a focused, prioritized review rather than scattered comments.
- Breaking change detection: Consistently flags changes that affect downstream consumers.
Hands-On Evaluation: Reviewing Cross-Module Telemetry Logic
To test Qodo in a realistic setting, I ran it against a pull request in the GrapesJS monorepo. GrapesJS contains dozens of packages, heavy reuse of shared utilities, and multiple subsystems wired together through Backbone models, views, and a deep utility layer:
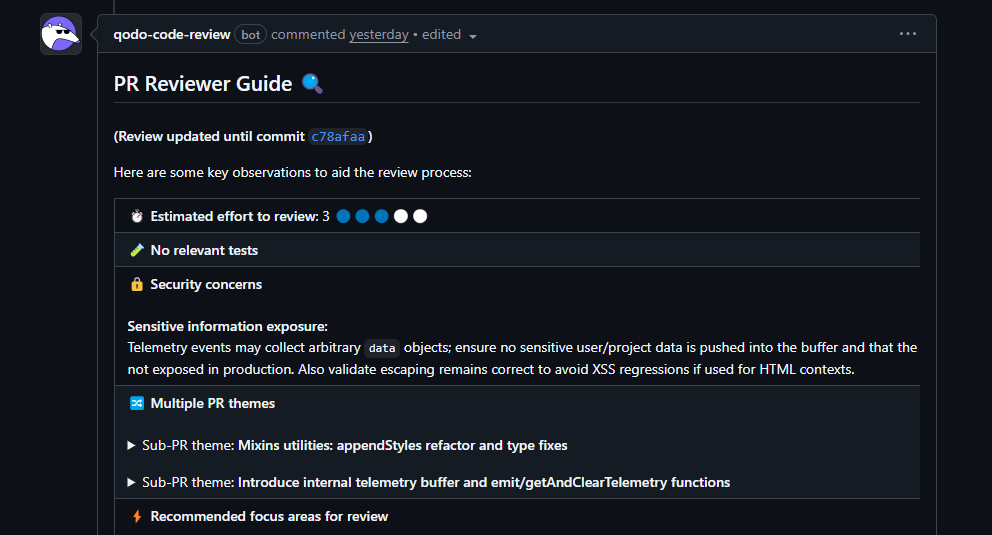
The PR intentionally mixed two different types of changes:
- a cleanup refactor in mixins.ts
- a new internal telemetry buffer for collecting lightweight editor events
This is the kind of PR that often slips through review with only partial scrutiny.
What stood out in the review, Qodo:
- Flagged a mixed‑concern PR that combined a cleanup refactor with new telemetry logic
- Highlighted a regex change in a shared stringToPath utility because it affected multiple downstream features, not just the file edited
- Called out an unbounded telemetry buffer that could lead to memory growth in long‑running sessions
- Caught an incomplete update to a shared escape() helper that risked rendering and security issues
- Identified DOM selector edge cases where interpolated href values could throw at runtime
- Pointed out missing tests exactly where shared behavior changed
Qodo behaved like a principal engineer who understands shared utilities, global state, and cross‑module behavior, not like a pattern matcher.
Best fit:
- Multi‑repo, large codebases with shared libraries and internal SDKs
- Organizations where contract drift and cross‑service breaking changes are main risks
- Enterprises needing SaaS, VPC, or on‑prem deployment with zero‑retention options
Pros
- System-aware review across repositories, not just diffs
- Reliable breaking-change detection for shared utilities and services
- Strong signal-to-noise ratio; avoids cosmetic feedback
- Review workflows align well with Jira/ADO-driven enterprise processes
Cons
- Best not to use for small teams or single-repo projects
- Requires initial setup to ingest repositories and context
- Best value appears only once system complexity is non-trivial
Pricing
- Developer (Free): $0/month, includes 75 credits/month, access to AI code review features, IDE plugin, Git integration, and CLI workflows.
- Teams: $30 per user/month (or $38 when billed monthly), includes 2,500 credits/month, collaboration features, private support, and enhanced privacy controls.
- Enterprise: Custom pricing, contact sales for options that include multi-repo context engine, advanced dashboards, analytics, SSO, governance controls, and enterprise deployment (SaaS, private cloud, or on-prem).
2. GitHub Copilot Review: repo-scoped AI review
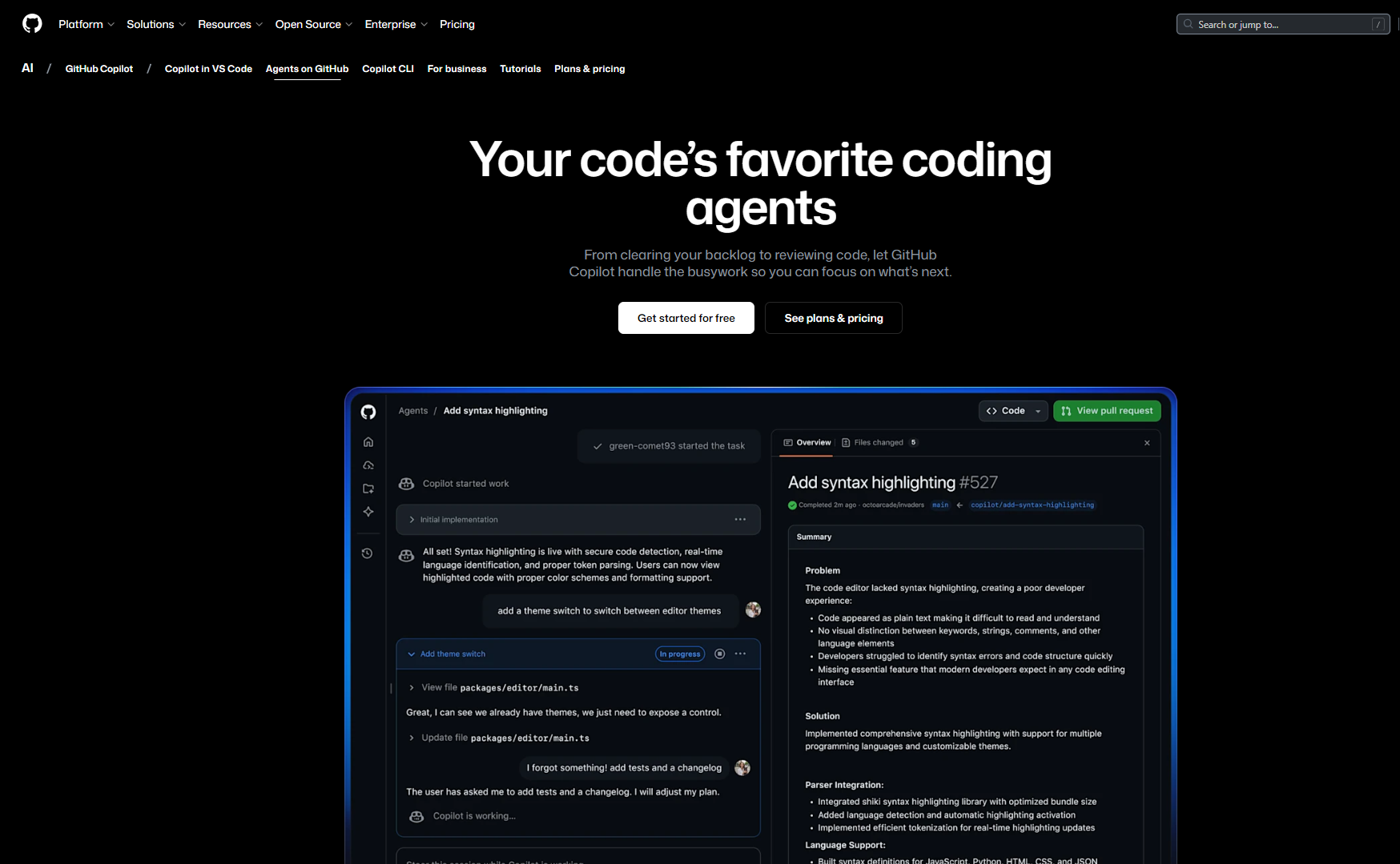
GitHub Copilot Review operates directly inside GitHub pull requests and focuses on improving review quality within a single repository. It analyzes diffs, generates inline comments, and suggests localized refactors. It behaves like a repo-scoped reviewer rather than a system-aware one.
Quick Stats:
| Tool tested | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| GitHub Copilot Review | Pattern matching | Diff-only | System-level | 70% actionable | Diff-aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Basic. Flags obvious unsafe patterns, but does not perform deep data-flow or runtime reasoning.
- Context alignment: Limited to the current repository. No awareness of shared libraries or downstream consumers.
- Code quality & maintainability: Strong for duplication, readability, and small refactors.
- Signal vs noise ratio: Clear inline comments, but feedback is distributed across the diff.
- Breaking change detection: Weak. External API or contract impact is out of scope.
Hands-On Evaluation: Swift File-Naming Logic in a FinderSync Extension
Copilot Review was tested on a Swift pull request inside a FinderSync extension. The method under review, createFileDirectly(in directory: URL), constructs a filename using a base name and extension, then iterates with FileManager.default.fileExists(atPath:) to find the first available filename before writing content. As shown in the snapshot below:
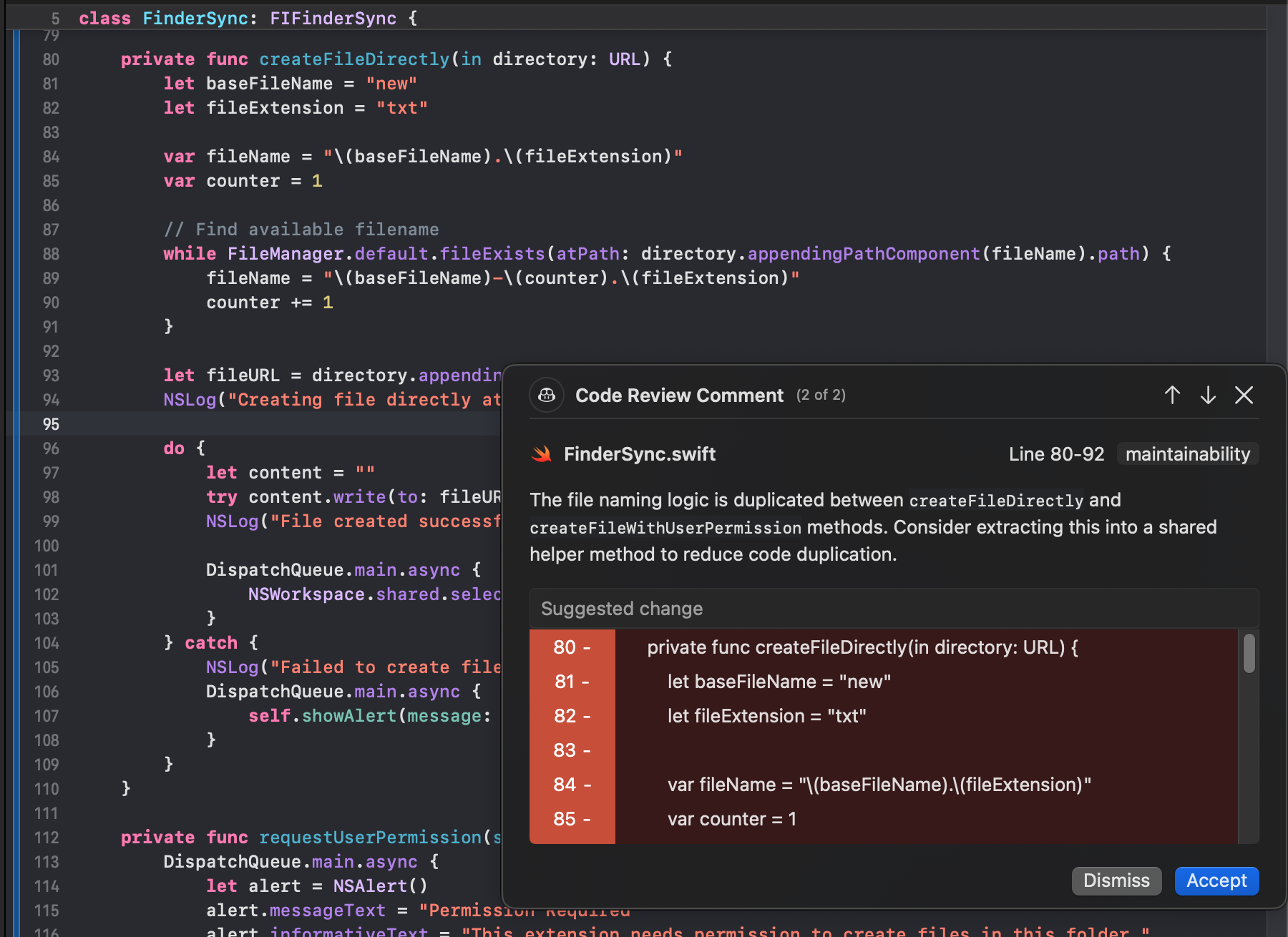
Copilot generated a review comment on FinderSync.swift (lines 80–92), tagged as maintainability, pointing out that the filename-generation logic was duplicated between createFileDirectly and createFileWithUserPermission.
What Copilot did well
- Detected intra-file duplication: It correctly identified that both methods shared identical filename construction logic, including the base name, extension, and existence-check loop.
- Classified the issue accurately: The maintainability tag matched the actual concern.
- Scoped the finding precisely: The comment pointed to the exact line range and highlighted the duplicated block.
- Stayed focused: Feedback was limited to a single concern without unrelated suggestions.
What it did not attempt
- It did not reason about extension lifecycle, permissions, or calling context.
- It did not evaluate whether the logic had implications outside this repository.
What this test shows
Copilot Review behaves like a local static reviewer. It improves maintainability and reduces small review units, but does not help reviewers reason about system behavior or downstream impact. It fits GitHub-native teams with largely isolated repositories, not multi-repo or microservice environments.
Pros
- Native GitHub integration with seamless PR experience
- Good for duplication detection and small refactors
- Low barrier to adoption for GitHub-centric teams
Cons
- Limited to repo-scoped context
- Cannot reason about downstream effects or shared libraries
- Weak at catching breaking changes across services
Pricing
GitHub Copilot Review is bundled with GitHub’s Copilot plans. Current published pricing (as of 2026) is:
- Copilot Individual: ~$20 per user/month
- Copilot Business: ~$40 per user/month
- Copilot for Teams / Enterprise: custom/volume pricing via GitHub
Copilot Review access is included in these subscriptions once enabled in the organization.
3. Codex: on-demand review for critical issues
Codex Cloud provides an AI-driven code review workflow that runs directly inside GitHub pull requests. Reviews are triggered by tagging @codex review, after which Codex analyzes the diff, applies repository-specific rules defined in AGENTS.md, and posts findings as standard PR comments. It behaves as an additional human reviewer focused on high-severity issues, not like a CI job or a linter.
Quick Stats:
| Tool tested | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| Codex | Pattern matching | Repository-wide | Runtime-level | 90% actionable | Repository-aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Good for targeted checks when explicitly requested. Not comprehensive by default.
- Context alignment: Limited to the current repository and the rules defined in AGENTS.md. No cross-repo awareness.
- Code quality & maintainability: Focuses on correctness and behavioral gaps rather than style or formatting.
- Signal vs noise ratio: Produces a small number of high-signal comments directly in the PR.
- Breaking change detection: Limited to what is visible in the diff; downstream impact is not inferred.
Hands-On Evaluation: Approval Flow Logic in a Tool Invocation Method
Codex was tested on a pull request that modified an approval method responsible for handling tool calls. The method accepts an approvalItem, forwards it into the internal context, resolves the corresponding tool, and applies additional logic when the tool represents a callable function. As shown in the snapshot below:
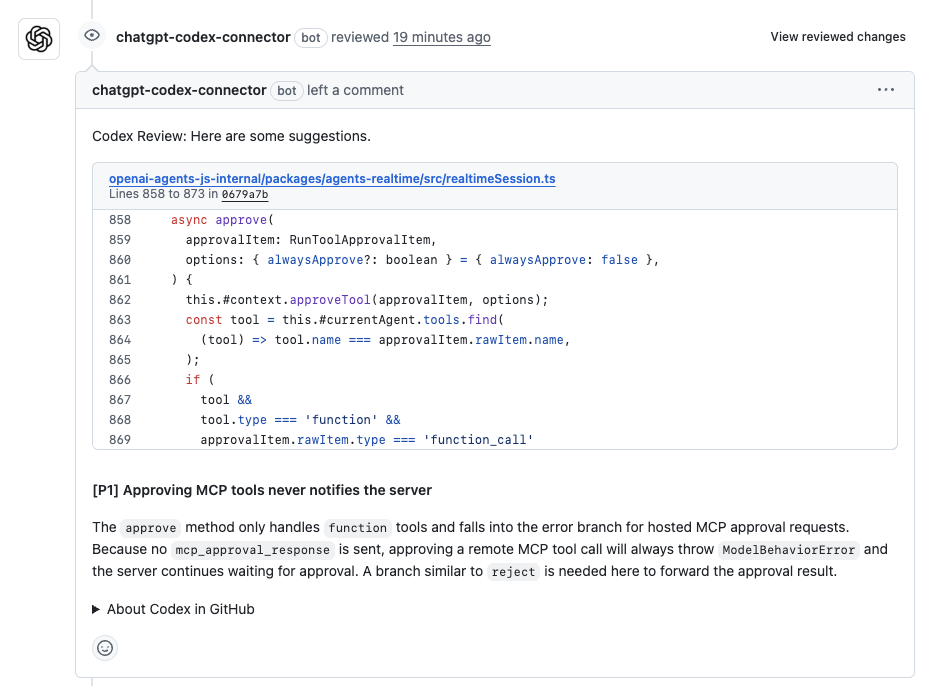
Codex flagged a single P1 issue in the modified logic.
What Codex flagged:
- Incomplete approval handling: The method correctly handled tools marked as “function” with a “function_call” payload, but for all other tool types, it updated local state without sending an approval response back to the caller.
- Clear runtime consequence: Remote or hosted tools expect an explicit approval response. Without it, the system waits indefinitely, and the approval flow fails.
- Actionable recommendation: Codex suggested adding an explicit branch to forward the approval result for non-function tools, similar to the existing reject path.
This issue would not get flagged through local testing alone. The code looked correct in isolation, but failed to complete the approval lifecycle end-to-end.
What this test shows
In this case, Codex behaved like a focused, PR-level reviewer. It ignored style and formatting concerns and zeroed in on a real behavioral gap introduced by the change. The feedback was specific, tied to exact lines, and highlighted a runtime failure mode that would be costly to debug post-merge.
Codex works well for teams that want high-signal, on-demand review inside GitHub, especially for correctness and security-sensitive paths. Its scope is intentionally narrow, which keeps noise low, but it does not replace system-level review or cross-repo reasoning in larger environments.
Pros
- Focused, high-signal review comments for behavioral gaps
- Triggered directly in PRs using @codex review
- Low comment noise due to severity defaults
Cons
- Limited to repo and AGENTS.md rules
- No persistent system context or cross-repo reasoning
- Requires explicit invocation for broader checks
Pricing
Codex Cloud pricing is tied to OpenAI / ChatGPT subscription tiers:
- ChatGPT Plus: ~$20 per month (gives access to Codex features)
- ChatGPT Pro: ~ $200 per month (higher throughput/priority)
- OpenAI business plans: custom pricing (usage quotas, enterprise controls)
Actual costs depend on model usage, tokens consumed, and subscription tier.
4. Snyk Code: security-first static and AI analysis
Snyk Code is a developer-focused SAST engine built to identify security vulnerabilities and risky data flows early in the development lifecycle. It integrates into IDEs, CI pipelines, and pull requests, and uses semantic analysis to detect issues such as injection risks, unsafe deserialization, weak input validation, insecure regex usage, and misconfigurations in application and infrastructure code.
Quick Stats:
| Tool tested | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| Snyk Code | Data-flow analysis | Repository-wide | N/A | 85% | Diff-aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Strong. Detects real data-flow–based vulnerabilities, not just pattern matches.
- Context alignment: Scoped to analyzed files and repositories. No system-level or cross-repo reasoning.
- Code quality & maintainability: Out of scope. Focuses strictly on security-relevant concerns.
- Signal vs noise ratio: Centralized dashboard with consistent categorization and traceability.
- Breaking change detection: Not a goal of the tool.
Hands-On Evaluation: Release Script Injection and HTML Parser Sanitization
Snyk Code was run against the GrapesJS monorepo, covering both release automation scripts and editor-side parsing logic.
Instead of focusing on a single PR, Snyk performed a full static analysis pass across the codebase. Based on the snapshot below:
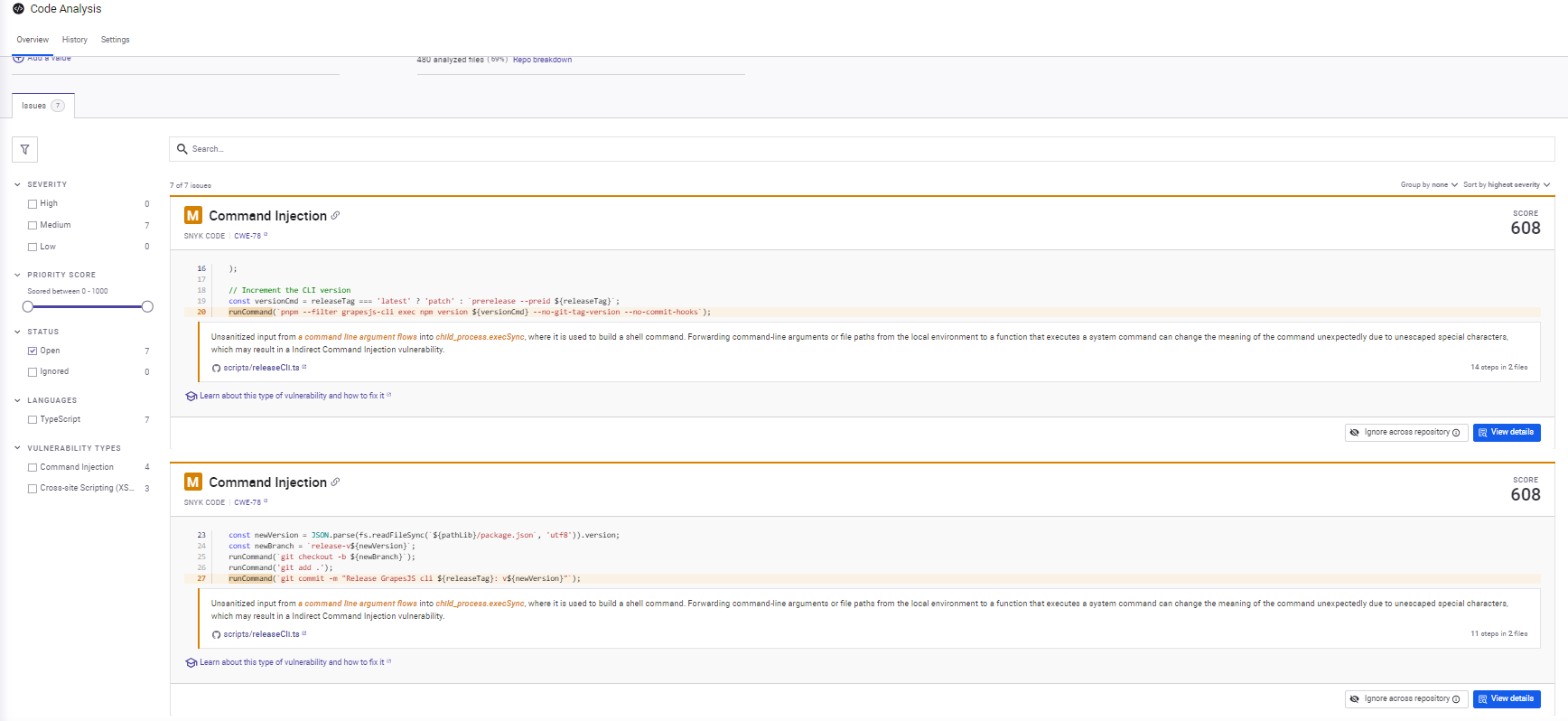
What Snyk flagged
- Command injection risks in release scripts: Snyk identified multiple cases where unescaped input flowed into shell commands constructed with execSync. It traced how values like releaseTag, newVersion, and newBranch propagated into command strings. While these scripts typically run in controlled CI environments, the pattern itself is unsafe and worth flagging, especially in shared tooling.
- Incomplete URI sanitization in the HTML parser: In the HTML parsing module, Snyk flagged missing checks for data: and vbscript: URI schemes. The existing logic handled common cases but left gaps that can be abused when importing raw HTML. The finding was precise and scoped to the sanitization logic, not a blanket XSS warning.
Why the findings were useful
- Issues were explained through data-flow paths, not vague warnings.
- Repeated patterns were flagged consistently across files.
- Findings focused strictly on security impact, ignoring style or structure.
What this test shows
Snyk Code behaves exactly as a security-focused static analyzer should. It ignores non-security concerns and concentrates on how untrusted input reaches sensitive sinks. Its value lies in consistency and traceability, not in PR-level reasoning or architectural awareness.
Snyk works best as a security baseline layered alongside other review tools. It does not replace functional or architectural review, but it reliably surfaces security issues that are easy to miss during manual PR review.
Pros
- Strong data–flow–based vulnerability detection
- Consistent patterns and traceability across the codebase
- Focused on real security risk rather than stylistic issues
Cons
- Security-only focus; does not cover architectural or functional behavior
- Adds another layer of output that must be triaged
- No system-level, cross-repo reasoning
Pricing
Snyk Code is part of the larger Snyk platform; published pricing is:
- Ignite: starts at $1260 per-dev / per year (often listed on plan page)
- Enterprise: custom quote, volume discounts, and additional security features
Exact pricing depends on chosen tiers, number of seats, and included modules beyond code scanning.
5. CodeRabbit: lightweight PR-level code review
CodeRabbit is an AI-assisted pull request reviewer that runs directly inside GitHub. It focuses on fast, readable PR feedback: summaries, inline comments, and suggested fixes. The tool stays close to the diff and is built to improve day-to-day review efficiency rather than reason about system-wide behavior.
Quick Stats:
| Tool tested | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| CodeRabbit | String flagging | Diff-only | Strong | 80% | Diff-aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Basic. Can flag obvious issues, but it is not a security analysis tool.
- Context alignment: Limited to the current repository and PR diff. No cross-repo or service awareness.
- Code quality & maintainability: Strong at catching concrete runtime issues introduced in the change.
- Signal vs noise ratio: Clear PR summary plus focused inline comments with low noise.
- Breaking change detection: Limited. Does not reason about downstream consumers or contracts.
Hands-On Evaluation: Trait Manager Refactor in GrapesJS
CodeRabbit was tested on a pull request in the GrapesJS monorepo that extracted trait-related logic from Component into a new ComponentTraitManager. The PR also included small utility changes touching shared helpers.
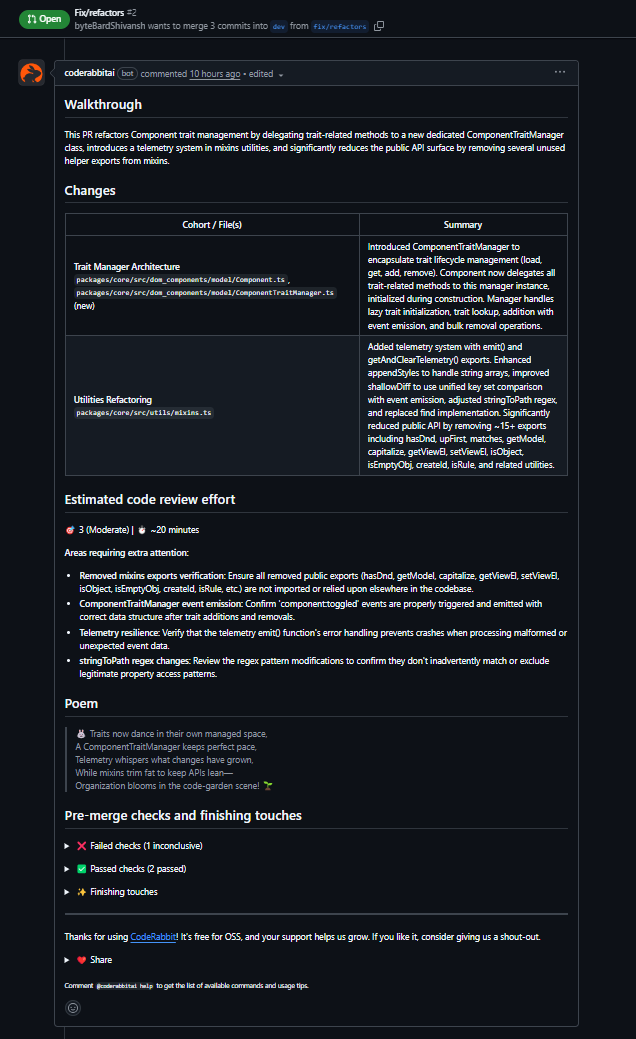
What CodeRabbit surfaced
- Initialization order issue: It flagged that ComponentTraitManager was instantiated before initTraits() completed. Since the manager loads traits in its constructor, this would lead to runtime failures due to an uninitialized state. The suggested fix, moving instantiation after initTraits(), was correct.
- Null safety in collection operations: It identified that getTrait() returns null and recommended filtering values before passing them into Backbone’s collection remove call.
- Broken utility implementation: It caught an incomplete escape() implementation that would fail at runtime and noted that the function shadowed the global escape, which is relevant for a shared utility.
What this test shows
CodeRabbit behaves like a diff-focused reviewer that catches real runtime and maintainability issues early. It stays within PR boundaries and does not attempt architectural or cross-module reasoning. For refactors where ordering, null handling, or correctness matter, the feedback aligns closely with what a careful human reviewer would flag.
CodeRabbit fits teams that want fast, low-friction PR feedback inside GitHub. It improves review quality for localized changes but does not reduce review effort in environments with cross-repo dependencies or system-level risk.
Pros
- Fast, readable PR summaries and inline feedback
- Good at catching runtime issues and ordering bugs
- Easy adoption through the GitHub app
Cons
- Diff-level context only
- No cross-repo or enterprise system awareness
- Limited use once architectural code complexity increases
Pricing
CodeRabbit pricing is typically structured as:
- Per-user subscription: common range ~$24–$30 per user/month when billed monthly (varies by billing term)
- Team pricing: Annual billing or larger seats
6. Cursor Bugbot: Repository-Scoped Review for Logic Bugs
Cursor Bugbot is an AI-powered code review agent built directly into the Cursor IDE and GitHub workflow. It automatically analyzes pull requests to detect logic bugs, edge cases, and security issues before code reaches production. Designed for teams practicing “vibe coding” (AI-assisted development), Bugbot optimizes for catching hard-to-find bugs while ensuring a low false positive rate.
Quick Stats:
| Tool | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| Cursor Bugbot | Pattern matching | Repository-wide | Strong | 90% actionable | Diff-aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Pattern matching. Detects security issues, edge cases, and vulnerability patterns. Especially strong at reviewing AI-generated code, but does not perform comprehensive data-flow tracing.
- Context alignment: Repository-wide. Gathers context from PR changes and understands code intent within the repository. Custom rules via BUGBOT.md allows project-specific context, but no cross-repo awareness.
- Code quality: Strong. Focuses specifically on logic bugs, edge cases, and runtime correctness. Avoids style and formatting noise entirely.
- Signal vs noise ratio: 90% actionable. Engineered for low false positives with a “less noise, more signal” approach. Only flags high-impact issues that matter.
- Breaking change detection: Diff-aware. Limited to changes visible in the PR. Does not track downstream consumers or cross-service contract violations.
Hands-On Evaluation: Global Blob Store Data Leakage
Bugbot was tested on a pull request in an agent client connection module (packages/agent/src/client/connect.ts). The change introduced a new line:
const blobStore = new InMemoryBlobStore();
At first glance, this looks like standard initialization code. It passed local testing and would likely pass human review without deep scrutiny. But Bugbot flagged it immediately as visible in the snapshot below:
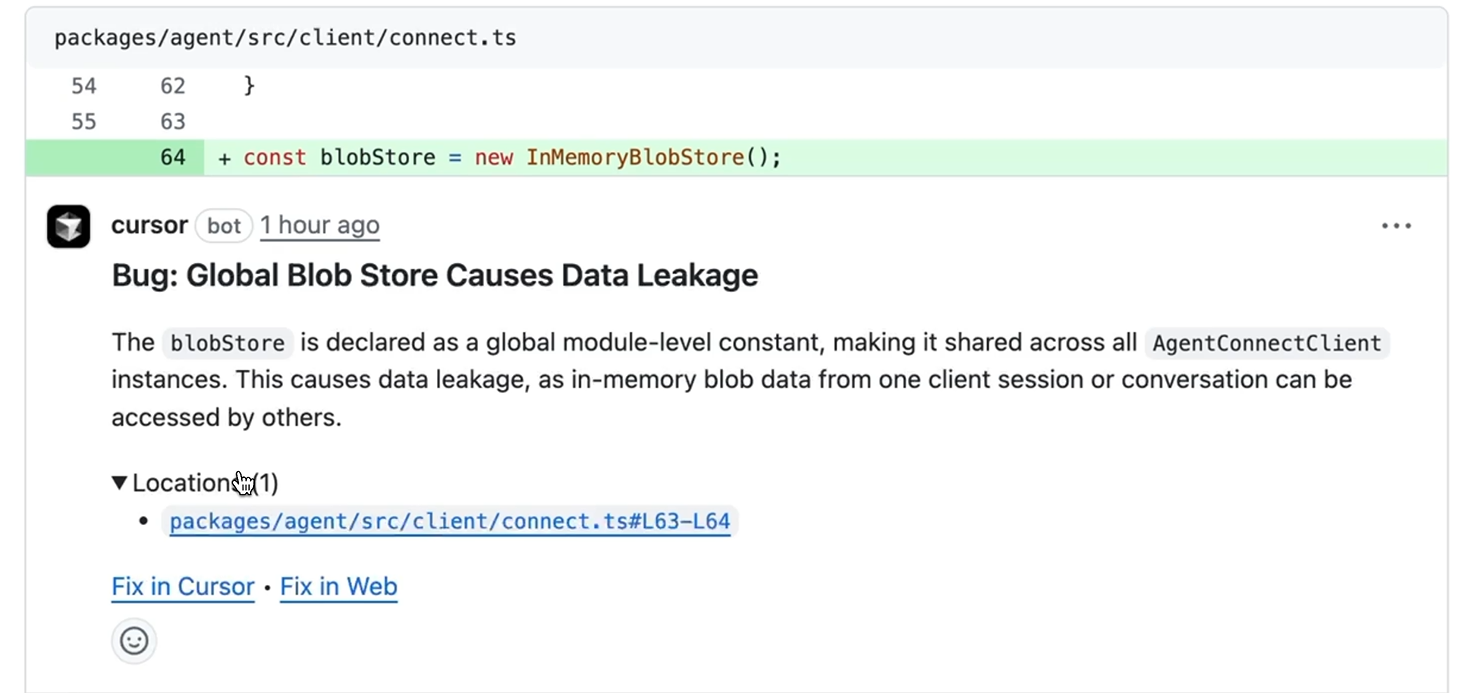
Bug: Global Blob Store Causes Data Leakage
The issue: blobStore is declared as a global module-level constant, making it shared across all AgentConnectClient instances. This causes data leakage, as in-memory blob data from one client session or conversation can be accessed by others.
The finding was:
- Specific: Pointed to the exact line (L63-L64) where the global constant was declared
- Clear on consequence: Explained how shared state leads to cross-session data leakage
- Actionable: Provided “Fix in Cursor” and “Fix in Web” buttons for immediate remediation
What this test shows
This is the type of bug that’s easy to introduce, especially with AI-assisted coding. The code looks correct locally. Tests pass if they only create one client instance. But in production with multiple concurrent sessions, data bleeds across boundaries.
Bugbot caught it by understanding:
- Module-level scope and shared state
- The lifecycle of client instances
- The security implications of shared memory stores
The tight integration meant the fix could be applied immediately without leaving the review workflow. This is where Bugbot adds value: catching simple logic and security issues that humans miss because the code “looks fine.”
Pros
- Catches simple logic bugs humans miss (shared state, lifecycle issues, edge cases)
- Extremely low false positive rate with focused, high-signal feedback
- Cursor IDE integration with one-click fixes
- Custom rules system (BUGBOT.md) for project-specific requirements
- Especially strong at reviewing AI-generated code
Cons
- GitHub-only integration (no GitLab or Azure DevOps)
- Repository-scoped (no cross-repo or multi-service context)
- Requires Cursor IDE for full workflow benefits
- Cloud-only (no self-hosting option for compliance-sensitive teams)
Pricing
- Free trial: 14 days
- Pro plan: $40 per user/month (includes Cursor Pro features + Bugbot)
Bugbot is bundled with a Cursor Pro subscription.
7. Graphite Agent: review for stacked PRs
Graphite Agent is an AI-powered code review assistant that provides immediate feedback on pull requests directly within the Graphite workflow. Built on Claude, it analyzes code changes to detect logic errors, edge cases, and potential bugs before they reach production. Designed for teams using stacked PRs and development workflows, Graphite Agent focuses on catching non-obvious bugs and keeping codebase-wide context across your repository and PR history.
Quick Stats:
| Tool | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| Graphite Agent | Pattern matching | Codebase-aware | Runtime-level | ~97% actionable | PR diff-aware |
How it performed against the criteria
- Security review: Detects logic bugs, edge cases, and common vulnerability patterns. Strong at catching array bounds issues, null pointer risks, and type mismatches. Does not perform deep data-flow analysis or cross-service security validation.
- Context alignment: Maintains context across the entire codebase and PR history. Understands code intent within the repository and can reference related files and past changes. Custom rules via GRAPHITE.md allows project-specific context, but is limited to a single repository scope.
- Code quality: Specifically engineered to catch logic errors, runtime bugs, and edge cases that humans miss. Focuses on correctness and behavior rather than style or formatting issues.
- Signal vs noise ratio: Achieves less than 3% false positive rate according to Graphite’s published metrics. Provides focused, high-impact feedback on issues that actually matter. Avoids noise from style preferences or minor refactoring suggestions.
- Breaking change detection: Reviews changes visible in the current PR. Does not track downstream dependencies, API contract violations across services, or impact on external consumers.
Hands-On Evaluation: Array Bounds Off-by-One Error
Graphite Agent was tested on a pull request in a feature page component (src/components/internal/feature-page/use-cases/index.tsx). The change added a useEffect hook with carousel scrolling logic:
useEffect(() => {
if (inView && api) {
api.scrollTo(8);
}
});
This code looks reasonable at first glance; it’s simple, follows common patterns, and would likely pass basic testing. The syntax is correct, and the logic appears sound. But Graphite Agent immediately flagged it as shown in the screenshot:
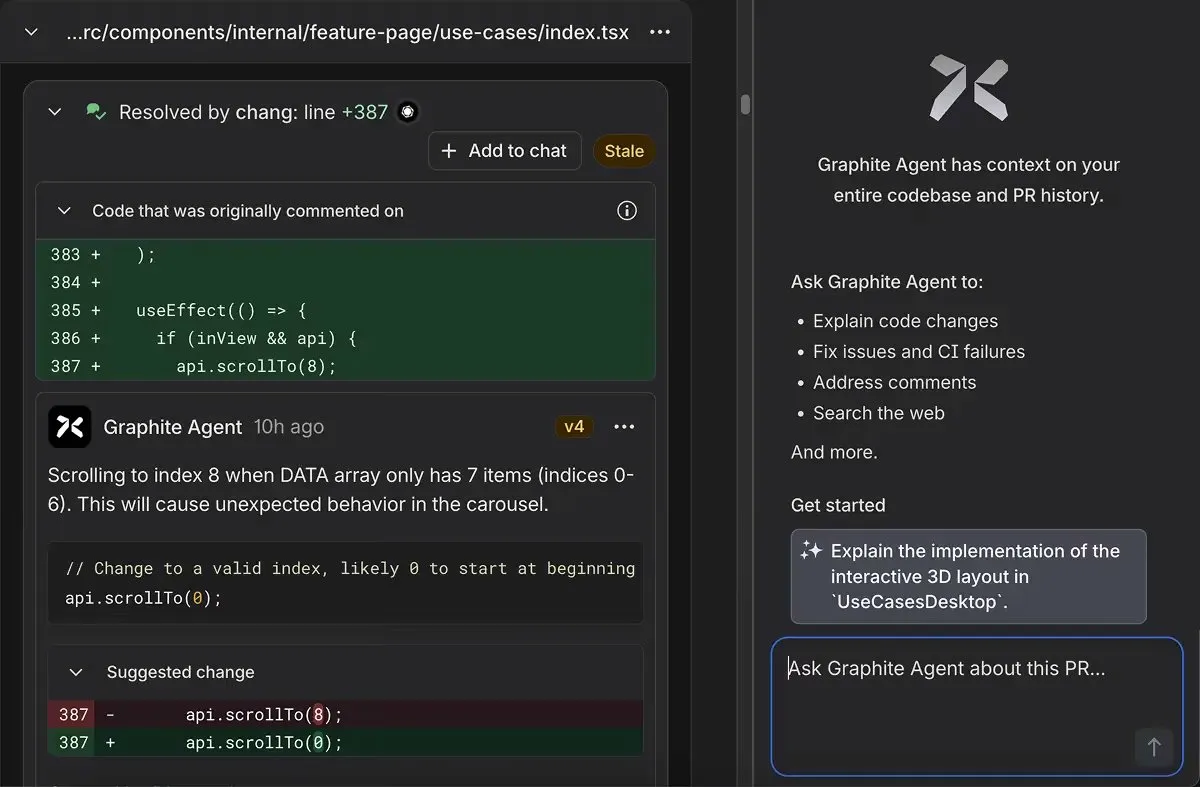
Bug: Off-by-One Array Index Error
The issue: The code attempts to scroll to index 8 when the DATA array only contains 7 items (indices 0-6). This causes unexpected carousel behavior as the scrollTo function tries to access a non-existent item.
The finding was:
- Specific: Pointed directly to line 387, where api.scrollTo(8) was called
- Clear on consequence: Explained that this would cause unexpected behavior in the carousel component
- Actionable: Provided a suggested fix to change the index from 8 to 0 (starting at the beginning)
- Context-aware: Understood that this was within a useEffect hook tied to component visibility and API availability
What this test shows
This is a classic off-by-one error that’s easy to introduce, especially when working quickly or with AI-assisted coding. The code functions without crashing, but it just behaves incorrectly. Manual testing misses it if you don’t specifically test the edge case of scrolling to the last (non-existent) position.
Graphite Agent caught it by understanding:
- Array bounds and zero-based indexing
- The relationship between the DATA array length and valid scroll positions
- The behavioral implications of scrolling beyond available indices
- The context of carousel/scrolling patterns in React components
The integration within the Graphite PR workflow meant the issue was surfaced immediately during code review, with a clear explanation and suggested fix. This demonstrates Graphite Agent’s value in catching logic errors that look syntactically correct but fail at runtime.
Pros
- Low false positive rate (~3%) with focused, actionable feedback
- Full codebase context awareness across the repository and PR history
- Integration with Graphite’s stacked PR workflow
- Provides suggested fixes with clear explanations
- Powered by Claude for strong reasoning about code behavior
Cons
- GitHub-only integration (no GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps support)
- Single repository scope (no cross-repo or multi-service context)
- Requires Graphite workflow adoption for full benefits
- No self-hosting option for compliance-sensitive organizations
- Limited to PR diff analysis (doesn’t track downstream breaking changes)
Pricing
- Hobby plan: Free (limited AI reviews)
- Starter plan: $20 per user/month (limited AI reviews, billed annually)
- Team plan: $40 per user/month (unlimited AI reviews, billed annually)
- Enterprise plan: Custom pricing (includes advanced features, SAML, audit logs, GHES support)
8. Greptile: deeper than diff-only, but single-repo focused code review
Greptile is an AI-powered code review agent that analyzes pull requests with a complete understanding of your entire codebase. While traditional tools review files in isolation, Greptile builds a language-agnostic graph of every function, class, and dependency to catch bugs that span multiple files and understand how changes ripple through the system.
Quick Stats:
| Tool | Security review | Context alignment | Code quality | Signal vs noise ratio | Breaking change detection |
| Greptile | Pattern matching + dependency tracing | Full codebase graph | Runtime-level | ~85% actionable (improves with learning) | Cross-file impact analysis |
How it performed against the criteria
Security review: Pattern matching + dependency tracing. Detects security vulnerabilities, logic bugs, and edge cases by tracing dependencies across the entire codebase. Does not perform deep symbolic execution or formal verification.
Context alignment: Full codebase graph. Builds a complete graph of functions, classes, variables, and dependencies across the entire repository. Primarily focused on single-repository analysis with limited cross-repo capabilities.
Code quality: Comprehensive. Catches logic errors, edge cases, inconsistencies with existing patterns, and architectural violations. Goes beyond syntax to understand behavioral correctness and system-wide implications.
Signal vs noise ratio: ~85% actionable (improves with learning). Initial reviews include more suggestions as Greptile learns codebase patterns. After 2-3 weeks of team feedback via 👍/👎 reactions, noise reduces significantly while ensuring high bug detection.
Breaking change detection: Cross-file impact analysis. Traces the full stack of changed functions to identify all callers and dependencies. Does not track external API consumers or cross-repository breaking changes.
Hands-On Evaluation: RBAC System Authorization Bypass
Greptile was tested on a pull request that included multiple refactoring changes: migrating tests from Jest to Vitest, adding test infrastructure, centralizing validation logic, and adding performance improvements. Among these seemingly routine changes, the PR removed a critical security check from server/middlewares/requireMinimumRole.ts.
The removed code was a 23-line SUPER_ADMIN authorization check (lines 41-64 in the previous version) from the validateViewingRoleHeader() function. This check prevented non-super-admin users from using the X-Viewing-Role header for role switching. The deletion appeared minor within a greater refactoring effort and could easily be missed as “cleanup” during code review.
Critical Security Issue: Authorization Bypass
Greptile immediately flagged this as a critical security vulnerability, demonstrating its graph-based cross-file analysis capabilities:

The issue: Removing the SUPER_ADMIN authorization check allows any authenticated user to send X-Viewing-Role: super_admin (or any other role) in request headers to completely bypass all role-based access controls. This undermines the entire RBAC system.
Greptile’s analysis revealed multiple cross-file inconsistencies:
- Test expectations broken: Security tests in tests/security/role-switching-validation.test.ts (lines 206-309) explicitly expect non-super-admins to be denied when attempting role switching. The enforcement code has been removed, but the tests and their expectations remain.
- Documentation drift: Project documentation files (CLAUDE.md, AGENTS.md) still claim “Only SUPER_ADMIN can use role switching”—but this statement is no longer enforced in the codebase.
- System-wide impact: The vulnerability affects all protected endpoints across the entire application that rely on the RBAC system. Any route using role-based permissions is now bypassable.
- Access control regression: The change transforms a privileged admin-only feature into a privilege escalation vector for any authenticated user.
The findings included:
- Specific location: Identified the exact file and line numbers where the security check was removed
- Impact analysis: Explained how this affects the entire RBAC architecture, not just the modified middleware
- Cross-reference validation: Connected the code change to test expectations and documentation claims in completely separate files
- Severity assessment: Correctly classified this as a critical security issue requiring immediate attention
What this test shows
This is precisely the type of vulnerability that’s nearly impossible to catch without a full codebase context. In isolation, removing 23 lines of code during a refactoring PR looks like reasonable cleanup. The change doesn’t introduce syntax errors. It doesn’t break the build. Tests even pass if they’re not running the specific security validation suite.
But Greptile caught it by understanding the system holistically:
- How the removed security check connects to test expectations in a different directory
- Where documentation makes claims about security guarantees
- What are the broader implications for the RBAC architecture
- How does this affect all protected routes across the application
The graph-based approach transforms code review from file-level syntax checking to system-level security analysis. This is valuable for large codebases where changes in one middleware file can silently break security assumptions throughout the entire application, while documentation and tests continue to claim protections that no longer exist.
Pros
- Conversational interface, developers can request fixes by replying @greptileai
- Provides a clear severity assessment with detailed impact analysis
- SOC2 Type II certified with enterprise security features
Cons
- Learning period of 2-3 weeks before noise reduction fully optimizes
- Single repository focus (pattern repos feature helps, but doesn’t provide true cross-repo analysis)
- No native IDE integration (works through GitHub/GitLab PR interface only)
- Graph building and maintenance add computational overhead
Pricing
- Free trial: 14 days with full access to all features
- Standard plan: $30 per developer/month (unlimited code reviews)
- Enterprise plan: Custom pricing (includes self-hosting, SSO/SAML, audit logs, custom SLAs, bring-your-own-LLM)
- API pricing: $0.15 per query unit ($0.45 for genius mode with advanced model)
Best AI Code Review Tools in 2026: Comparison
The table below provides a side-by-side view of the tools evaluated in this guide. The goal is not to compare feature lists, but to highlight how each tool fits operationally in the SDLC: how much context it provides, how well it scales in enterprise environments, and which review problems it actually solves.
This comparison is most useful for engineering leaders trying to answer a practical question: Which tool reduces review load in our environment, rather than adding another layer of feedback?
| Tool | Best For | Key Differentiator | Context Depth | Enterprise Readiness | Deployment Options | Pricing Model |
| Qodo | Multi-repo systems, microservices, shared libraries | Persistent system-level context and breaking-change detection | Cross-repo, system-aware | High (100–10,000+ dev orgs) | SaaS, VPC, on-prem, zero-retention | Free: $0 (75 credits/month)
Teams: $30/user/month ($38 monthly billing) Enterprise: Custom |
| GitHub Copilot Review | GitHub-native teams with isolated repos | Inline AI review for maintainability and refactoring | Repo-scoped | Medium | GitHub Cloud | Individual: ~$20/user/month
Business: ~$40/user/month Enterprise: Custom |
| Codex Cloud | High-signal PR review on demand | Focused P0/P1 behavioral issue detection | Repo-scoped (rules-based) | Low–Medium | GitHub Cloud | ChatGPT Plus: ~$20/month
ChatGPT Pro: ~$200/month Business: Custom |
| Snyk Code | Security-first organizations | Data-flow–based vulnerability detection | File / repo-level (security only) | High (as security baseline) | SaaS, CI, IDE | Ignite: ~$1,260 per dev/year
Enterprise: Custom |
| CodeRabbit | Fast PR feedback and summaries | Lightweight diff-focused runtime issue detection | Diff-level | Low–Medium | GitHub App | ~$24–$30/user/month (billing-term dependent) |
| Cursor Bugbot | Fast-moving AI-assisted development teams | Low false-positive rate for AI-generated code | Repository-wide | Low–Medium | Cursor IDE + GitHub | Free trial: 14 days
Pro: $40/user/month (includes Cursor Pro + Bugbot) |
| Graphite Agent | Teams using stacked PRs and workflows | PR history–aware review that learns from feedback | Repo + PR history | Medium–High | GitHub Cloud, GitLab | Free: Limited
Starter: $20/user/month Team: $40/user/month Enterprise: Custom |
| Greptile | Complex multi-module codebases | Graph-based full codebase understanding | Full codebase graph | High (SOC 2 Type II) | SaaS, Docker, and Kubernetes | Free trial: 14 days
Standard: $30/dev/month Enterprise: Custom API: $0.15/query |
How to Choose the Right Code Review Tool Based on Your Constraints – Decision Map
The right tool depends less on its feature list and more on your primary constraint.
| If the main constraint is | Look for | Best fit |
| Multi‑repo systems and cross‑service impact | Persistent system context, cross‑repo breaking changes | Qodo |
| GitHub‑native, repo‑scoped workflows | Inline PR feedback, maintainability focus | GitHub Copilot Review, CodeRabbit |
| AWS‑heavy codebases and cloud correctness | Deep AWS SDK/IAM/infra awareness | Amazon Q Code Review |
| High‑signal correctness checks in critical PRs | On‑demand, low‑noise, behavioral focus | Codex‑style reviewers |
| Security as a first‑class requirement | Strong data‑flow analysis, vulnerability traceability | Snyk Code (along with Semgrep/CodeQL) |
| Fast feedback on localized PRs | Diff‑focused runtime and ordering issue detection | CodeRabbit |
I’m seeing teams do well with a code review stack similar to this:
- 1 system‑aware reviewer (like Qodo)
- 1 security engine (Snyk, Semgrep, or CodeQL)
- 1 diff‑level helper used tactically in specific workflows (Copilot)
- 1 static analysis tool (SonarQube, Checkmarx)
They do not try to make a single diff‑aware bot carry system‑level responsibility. In other words, 1 limited, lightweight bot isn’t enough to carry software on its back into production.
Where AI Review Still Overpromises
There is a real “AI code review bubble” effect in the market. Many tools overpromise in predictable ways:
- “No more code review” – but they only detect style issues and minor refactors.
- “Understands your entire codebase” – but cannot identify a single cross‑repo breaking change.
- “Enterprise‑grade security” – but dump hundreds of “critical” findings that teams mute within a month.
Overconfidence in AI feedback, especially when context is incomplete, creates a false sense of safety. Tools that generate too many low‑impact comments quickly lose developer trust. Once trust is gone, even the good signals get ignored.
That’s why system-aware context, consolidated analysis, and measurable ROI matter more than any single AI feature.
Why System Context Matters
Consider a real‑world pattern I’ve seen more than once:
- A shared billing SDK changes a monetary type from string to a richer object
- The PR is “small,” passes all tests in the main repo, and looks reasonable in isolation
- Dozens of services, jobs, and reports that depend on that SDK silently break over the next few days
Every diff‑level tool had passed the change. No one had persistent knowledge of who depended on that SDK and how.
The incident report could be summarized as: “No one had system‑level context at review time.”
System‑aware review is not about being more “AI‑advanced” in the abstract. It is about making sure that when you change something central, there is at least one human or AI who knows who else is going to feel it.
Where Developer Judgment Matters
Even with 2026‑era AI tools, there are hard limits:
- Tools will be overconfident when the context is incomplete.
- System‑level reasoning is still difficult without rich, persistent context across repos and services.
- Security findings without an execution context will still generate noise.
- Excessive low‑impact comments will still erode trust.
AI code review is meant to be a force multiplier for human judgment, not a replacement for it. Tools handle repeatable patterns, flag non‑obvious risks, and carry context that humans cannot keep in their heads. Humans still own intent, tradeoffs, and system design.
If you’re assessing AI code review in 2026, the practical question is “Which tool makes my reviewers more effective at keeping our system safe, while letting us ship at the speed AI generation now demands?”
How I Tested the Top AI Code Review Tools
I evaluated each tool against production-style systems, not demo projects. This approach mirrors how large engineering organizations actually ship code at scale.
For example, enterprises like Netflix operate thousands of independently deployable microservices, maintained by hundreds of teams, with changes getting pushed into production. In environments like that, even a small update to a shared utility, schema, or SDK can ripple across dozens of downstream services. Review is no longer about spotting mistakes in a diff. It’s about understanding system behavior at scale.
Here’s the visual to explain how the context can impact code review at an enterprise scale:
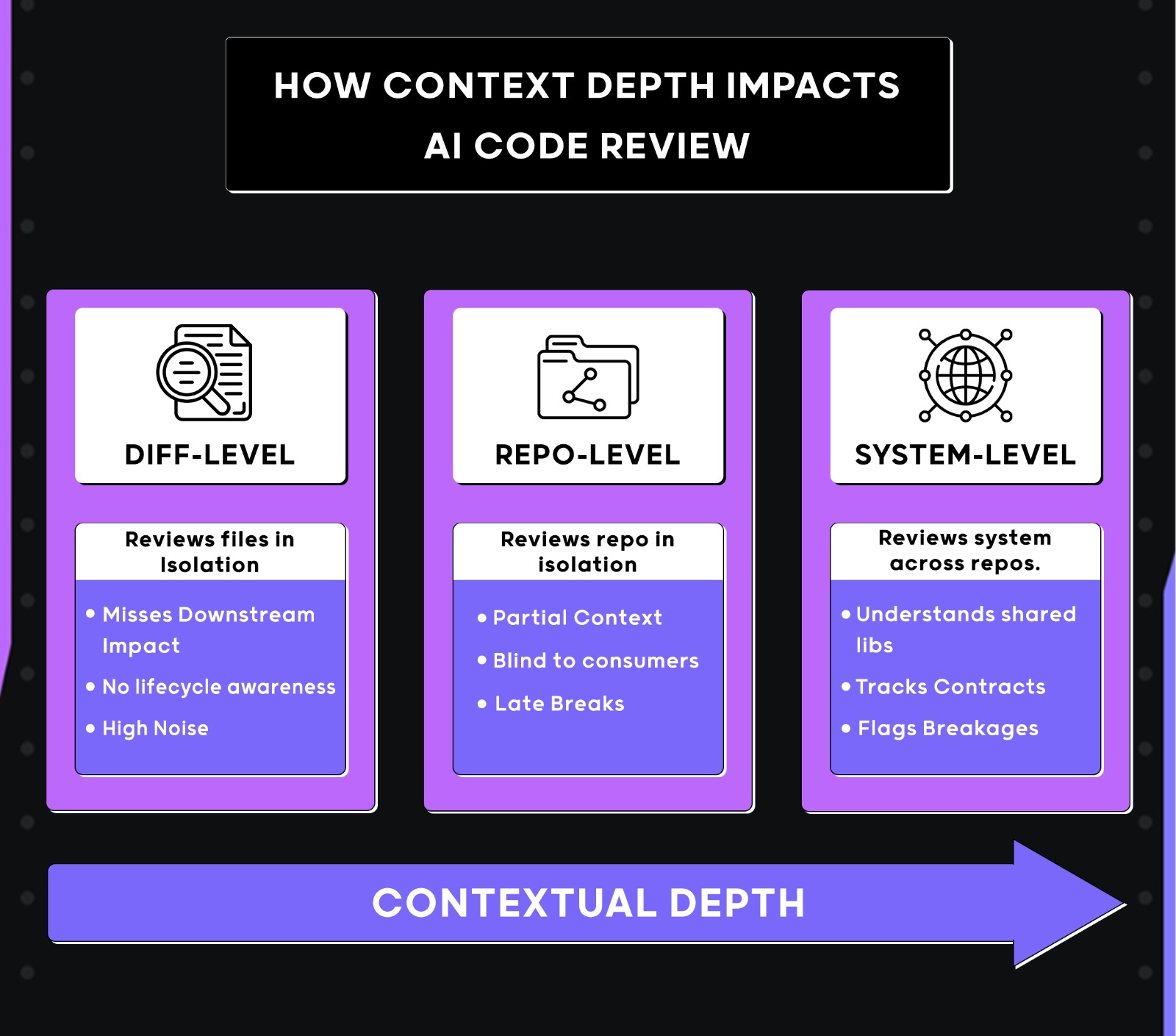
I evaluated each tool against production-style systems, not demo projects. The test suites reflected how real engineering teams ship changes day-to-day:
- Multi-repo complexity: Microservices, monoliths, and shared libraries used across teams
- Legacy + new codebases: Mixed patterns, frameworks, and tech debt
- Cross-boundary changes: API contracts, data flows, and service dependencies
- Infrastructure as code: Configuration and deployment manifests
- Dependency complexity: Version drift and transitive dependencies
- Runtime behavior: Environment-specific assumptions (staging ≠ prod)
- Hidden consumers: Non-obvious downstream services and async side effects.
During POC or MVP trials, teams evaluate AI review tools on isolated repositories with limited history, few consumers, and no active production dependencies. They hide shared dependencies, historical decisions, schema drift, and the knock-on effects of a tiny change. A tool that looks great on a clean repo usually struggles when it must reason about contracts, compatibility, and operational risk.
The end goal: Determine whether each tool genuinely helps reviewers reason about system-wide impact and risk, or whether it stays at simple checks that still force engineers to do manual review.
Now that we’ve covered how code review works in production systems, let’s focus on the criteria used to evaluate the tools.
Criteria for Comparing Code Review Tools
Most AI code review tools score well in feature comparisons, benchmark examples, and isolated PR demos. The differences only show up when they’re used against real systems with real risk. For enterprise teams, the value of a reviewer is simple: does it help engineers reason about impact and failure modes without slowing delivery?
To keep the evaluation grounded, every tool was tested against the same 5 criteria. Each criterion is backed by hands-on failure scenarios that frequently occur in large codebases.
1. Security Review
Focusing on whether a tool can reason about real execution risk through data flow and context analysis, rather than relying on pattern matching alone.
Scoring:
- Data-flow analysis: Traces untrusted input through execution paths to identify exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Pattern matching: Detects common vulnerability patterns but misses context-dependent risks
- String flagging: Flags suspicious strings or keywords without understanding actual exploitability
What breaks without it: Pattern-only tools miss context-dependent vulnerabilities like injection attacks that only trigger under specific conditions. Data breaches happen when execution paths aren’t traced.
2. Context Alignment
Checking whether a tool can understand changes within the broader system context, identifying drift, scope creep, and downstream impact beyond the immediate diff.
Scoring:
- Cross-repo aware – Tracks dependencies across repositories and services, detects system-wide impact.
- Repository-wide – Understands cross-file dependencies within a single repo
- Diff-only – Reviews only the changed files without broader context
What breaks without it: Breaking changes ship undetected. Shared utility modifications affect downstream consumers without warning. Scope creep sneaks into PRs and creates maintenance issues.
“In code review, context is everything… making sure you’re not introducing breaking changes from another repo. Solving context is the hard part, and if we truly solved context, we’d pretty much solve software development.”
Itamar Friedman
3. Code Quality
Analysing whether a tool can detect runtime correctness and long-term maintainability issues, rather than just stylistic issues.
Scoring:
- System-level – Catches issues that only get flagged when a change connects to shared utilities, long-running state, or other parts of the codebase.
- Runtime-level – Understands how individual functions and modules behave. Catches logic bugs, edge cases, and correctness issues that will fail at runtime, but within the scope of the change.
- Surface-level – Looks at what code contains, not how it behaves. Flags duplication, style, and readability.
What breaks without it: Enterprise maintainability is about correctness over time, not formatting.
4. Signal vs noise ratio
Measuring how much of a tool’s feedback is actionable versus low-priority noise.
Scoring:
- ≥85% actionable – Most comments map to actual bugs, risks, or correctness issues in the changed code. No style suggestions or generic warnings
- 60-84% actionable – Useful feedback mixed with cosmetic or low-priority suggestions
- <60% actionable – High volume of low-signal comments, unclear prioritization
What breaks without it: Review fatigue. Engineers ignore all feedback when most of it is noise. Critical issues get buried in cosmetic suggestions.
5. Breaking Change Detection
Analysing whether a tool can identify breaking changes that won’t be caught by local tests, especially in shared contracts consumed by downstream services.
Scoring:
- Cross-service aware – Tracks dependency chains across repos, identifies affected consumers, flags contract violations
- Repository-aware – Detects breaking changes in shared utilities within the codebase
- Diff-aware – Only catches compile-time errors or changes visible within the PR scope.
What breaks without it: Production incidents when API contracts change. Downstream services fail at runtime. Rollbacks and emergency patches after breaking changes reach production.
These five criteria separate tools into two groups:
- Pattern-based tools look at the diff and match against known patterns. They catch obvious issues but miss anything requiring system knowledge.
- System-aware tools understand how the change affects the rest of the codebase. They track dependencies, reason about contracts, and catch issues that only show up in production.
With the criteria defined, the next section evaluates all the tools against them using changes with downstream impact.
FAQs
What are the best AI code review tools to improve code quality?
The answer depends on how code quality is defined in your organization. Tools like Qodo improve quality by catching system-level issues such as breaking changes, lifecycle errors, and missing tests across repositories. GitHub Copilot Review focuses on local improvements like duplication, readability, and small refactors within a single repo. Amazon Q Code Review improves structural quality in AWS-heavy codebases by surfacing error-handling gaps and boundary issues. Snyk Code improves quality from a security standpoint by identifying unsafe data flows and injection risks. In enterprise environments, quality improvements usually come from minimizing system-level failures, not from stylistic feedback alone.
What are the best AI code review tools for platform engineering teams?
Qodo is the best fit for platform engineering teams since they own shared libraries, internal SDKs, and services with a large blast radius. It reasons across repositories, detects downstream impact, and flags breaking changes before they reach consumers. Amazon Q Code Review can complement this for AWS-centric platforms by identifying cloud misconfigurations and SDK misuse. Snyk Code is often added as a security baseline. Tools limited to diff-level or repo-scoped review usually fall short for platform ownership.
What are the best AI code review tools for GitHub?
For teams working mainly in GitHub, Qodo is the better choice when repositories are part of a larger system. It reviews pull requests with awareness of shared libraries, APIs, and service dependencies, helping catch breaking changes and downstream impact that GitHub-native tools miss. For more localized workflows, GitHub Copilot Review provides low-friction, inline feedback directly in pull requests. Codex Cloud is useful for on-demand reviews focused on correctness and behavior, and CodeRabbit works well for quick summaries and catching obvious runtime issues.
What are the best AI code review tools for architecture owners?
Architecture owners care about contracts, service boundaries, lifecycle assumptions, and long-term system integrity. Qodo is the strongest fit because it detects architectural drift, breaking changes, and cross-service impact early in the review process. Amazon Q Code Review can help maintain architectural hygiene in AWS-centric systems, but does not enforce review outcomes. Snyk Code supports architecture owners from a security perspective rather than a behavioral or structural one. Diff-only tools rarely flag architectural risk early enough to be useful at this level.
What are the best code review tools that run in your CLI?
Qodo also gives CLI capabilities for workflow automation, custom agent configuration, and CI/CD integration. Snyk Code provides CLI scanning for security analysis. However, comprehensive AI code review typically requires PR-level context and system-wide awareness. Most enterprise teams use CLI tools for automation and triggering workflows, while the actual review reasoning happens in Git platforms and IDEs, where tools can access the full codebase context, historical patterns, and cross-repo dependencies.
What are the best code review tools that run in your terminal?
Terminal-based tools are best suited for static checks such as linting or security scanning. Snyk’s CLI is useful for identifying vulnerabilities, but it does not replace review reasoning. AI-driven code review today lives primarily in pull requests and IDEs, where tools can access context, history, and collaboration signals. Terminal workflows remain complementary, not central, to enterprise code review.
Which AI code review tool is best for enterprises?
There is no single best tool for every enterprise. The right choice depends on system complexity. Teams operating multi-repo systems, shared libraries, and microservices benefit most from system-aware review, which is where Qodo fits best because it reasons about downstream impact beyond the diff. Cloud-centric organizations often need a review that understands infrastructure and SDK usage. Security tools work best as a baseline layer rather than a complete review solution. Repo-scoped PR reviewers are effective only when architectural complexity is low.
Can AI code review tools detect breaking changes?
Most tools cannot reliably detect breaking changes. Diff-level reviewers like GitHub Copilot Review, Codex, and CodeRabbit are limited to what’s visible in the PR. Tools designed with persisted system context code review platforms, such as Qodo, are better suited for detecting downstream impact in multi-repo environments.
Do AI code review tools replace human reviewers?
No. AI tools reduce reviewer load by catching repeatable issues, but they do not replace human judgment. Humans are still required to validate intent, system behavior, and tradeoffs, especially in complex systems.
Are AI code review tools safe for proprietary code?
It depends on the deployment model.
- Some tools run only as cloud services and require data to leave your environment.
- Enterprise teams should look for options that support VPC-hosted, on-prem, or zero-retention modes, especially in regulated industries. Security and data handling should be evaluated before rollout.
Should teams use multiple AI code review tools together?
Yes, but only with clear boundaries. Use one primary review platform like Qodo to manage a complete system context code review and ensure code quality.