Top 10 Code Analysis Tools For Enterprises Based on Use Cases
TL; DR
- Code quality has become a strategic investment in 2025, with organisations spending significant budgets to reduce long-term technical debt, and this guide explores how tools help catch issues early so they never spread across large systems.
- Large engineering organizations are shipping code faster than their security and quality processes can validate it. AI boosts output volume, but AppSec teams still face thousands of unprioritized vulnerabilities, uneven enforcement across pipelines, and no clear view of how code, images, APIs, and runtime systems connect.
- Code analysis in 2025 is no longer a single function. It is an SDLC-wide practice that spans AI review, SAST, linting, cloud pipeline checks, and policy enforcement. Enterprises need tools that maintain governance and clarity across large codebases with many teams contributing in parallel. Documentation must align with implementation, and AI-generated changes require stronger verification at creation time.
- Qodo is the AI Code Review Platform and the missing quality layer in your AI stack. It effectively bridges the critical gap that exists between “AI code” and “production-ready,” helping enterprises to enforce consistent quality and security standards at scale.
- This guide outlines ten tools that mark different parts of the quality and security problem. Each tool fits into a broader stack that helps enterprises keep delivery speed aligned with long-term stability, architectural intent, and SDLC governance.
As engineering organizations expand and AI increases delivery speed, security and quality processes struggle to keep pace. AppSec and Platform leaders manage polyglot codebases, multiple CI/CD systems, hybrid cloud deployments, and pipelines that trigger thousands of builds each day.
Under this level of scale, the key challenge is not chasing unusual edge cases. It is keeping up with governance, auditability, and consistent engineering standards across environments where change occurs constantly.
Recent industry research shows that more than 40% of enterprises now invest over $1 million annually in software quality initiatives. Gaps in documentation, ambiguity in reviews, and inconsistent engineering intent create systemic risk. Security teams deal with large vulnerability queues, fragmented ownership across services, and policies that do not translate cleanly into developer or AI workflows.
AI has shifted expectations further. The Stack Overflow 2025 Developer Survey reports that 84% of respondents are using or plan to use AI tools in their development process this year, yet many of them still do not fully trust the output and need stronger review layers.
Independent research on automated code review in industry found that about 73.8% of automated code review comments were resolved, and developers reported a measurable improvement in code quality, although pull requests sometimes took longer to close.
This challenge marks the gap that enterprise leaders must convey. While AI dramatically increases output volume, organizations risk shipping work faster than they can validate without a governance-driven quality layer tied to established intent.Research shows that high-quality reviews correlate with roughly 50% stronger delivery performance. Quality is the multiplier, not the blocker.
Qodo functions as this important component: The missing quality layer in your AI stack. By integrating agentic code review with deep codebase context, Qodo maintains consistent review quality, documentation alignment, and SDLC governance across large teams and complex systems, ensuring velocity is achieved responsibly.
Qodo understands the entire codebase (including those with 1000+ repositories) and reasons about impact and dependencies across services, going far beyond the single-file or single-diff view offered by competing tools.
This guide outlines 10 leading code analysis and code quality tools for 2025. Each section explains what the tool focuses on, the scenarios where it fits best, and the trade-offs enterprise teams should expect when analyzing solutions at scale.
Top 10 Code Analysis Tools For Enterprises Based on Use Cases
Use case 1: Enterprise-wide AI code review and SDLC governance
Use case 2: Security-first SAST and DevSecOps pipelines
Use case 3: Cloud-based automated code review for Git workflows
Use case 4: Deep static analysis for complex and large-scale codebases
Use case 5: Language-specific linting and style consistency
Top 10 Code Analysis Tools Based on Use Cases
Enterprise-wide AI code review and SDLC governance
1. Qodo
Qodo is the missing quality layer in your AI stack. It is the AI Code Review Platform purpose-built to bridge the critical gap between “AI wrote it” and “production-ready” software.
For VPs of Engineering and Head of Product Security leaders managing 100 to 10,000+ developers and complex, multi-repo environments, the challenge is scale. Qodo is the review layer across your SDLC that sustains code quality, security, and enterprise governance across potentially 1,000+ repositories where manual review is operationally impossible.
With its agentic code review, Qodo embeds deep code context and automated governance into the SDLC to give the highest quality, high-signal review on the market:
1. SOTA Context Engineering
Qodo’s intelligence is its SOTA context engine. It gives agents full codebase awareness, allowing reasoning that goes far beyond the current file or Pull Request (PR) diff. It has agents that analyze impact across your entire architecture, understanding 10 repos or 1000 to catch cross-repo dependency conflicts, breaking changes, and architectural risks.
2. Agentic Quality Enforcement
Qodo uses specialized review agents to automate complex quality tasks and enforce standards effortlessly that can help enterprises to avoid 800+ potential issues monthly.
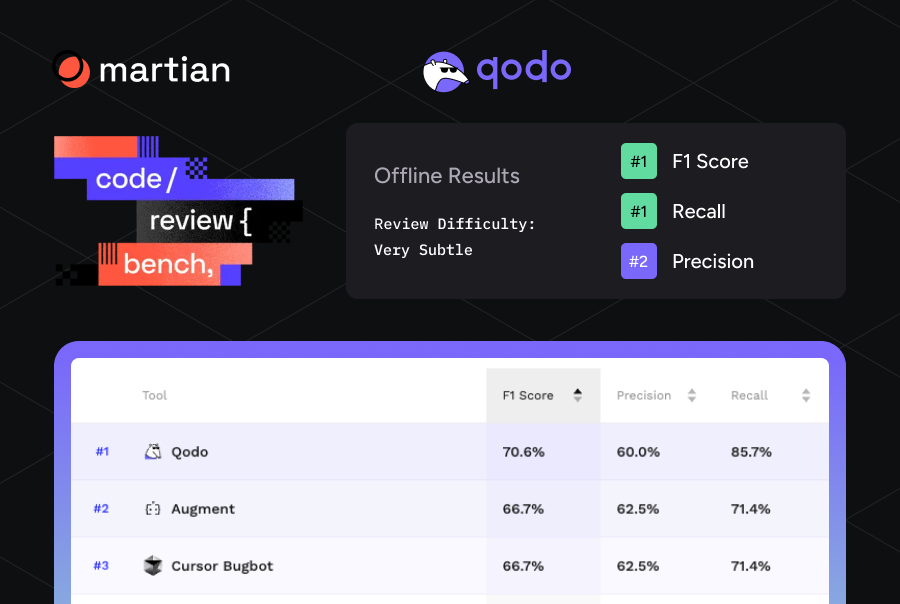
- Proven Accuracy: Agentic code suggestions boast a 73.8% acceptance rate, validating their relevance and precision.
- Shift-Left Quality: Agents run across the full SDLC: inside the IDE (for local self-review), in Pull Requests (for automated checks), and in CI pipelines (for compliance).
- Automated Workflows: Features include 15+ automated workflows in PRs covering rules enforcement, compliance checks, code duplication detection, and more. Critical issues found often include 1-click resolution.
Qodo deploys agentic code review to enforce engineering intent and compliance standards, ensuring every change is production-ready before it merges. It is purpose-built for enterprises scaling code quality.
Key features
- SOTA Context Engine & Multi-Repo Awareness: Utilizes SOTA context engineering for full codebase context, detecting breaking changes and code duplication across multi-repository environments.
- Proven Agentic Review: Deploys specialized review agents with a 73.8% acceptance rate on code suggestions for immediate bug, boundary, and security risk fixes.
- SDLC-Wide Governance: Enforces shift-left quality by running agents in the IDE, Pull Requests, and CI pipelines to control architectural drift.
- Automated PR Workflows: Runs 15+ automated workflows in pull requests covering rules enforcement, compliance checks, and automated documentation updates.
- Constant Learning: The platform reduces review noise and improves accuracy by learning directly from PR comments and accepted suggestions over time.
First Hand Example
When I applied Qodo to a complex enterprise pull request, the impact on quality governance was immediate. The platform generated a reviewer guide that went deep, fetching hidden architectural debt and systemic risk, not just reporting simple syntax errors. The calculated effort score immediately allowed me to gauge the true complexity of the review and manage resource allocation for the team.
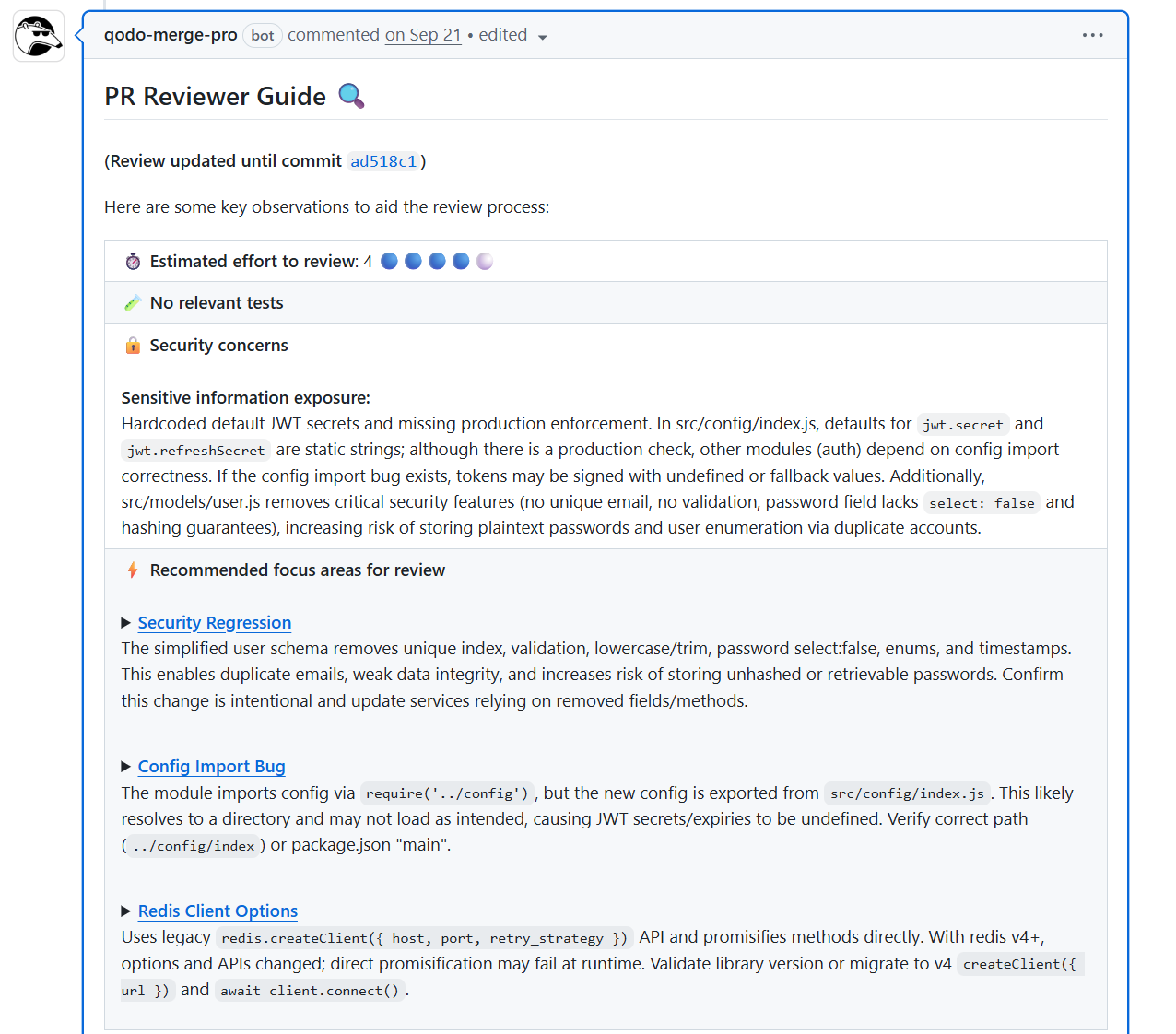
The security analysis proved invaluable for our organizational risk posture. I saw it proactively identify high-risk vulnerabilities like hardcoded secrets and validation removals, the specific issues that typically slip through standard manual review in our large, distributed environment and accumulate as silent risk.
Critically, Qodo also caught systemic schema changes that would have impacted data integrity across multiple microservices. This capability is key: it allows my teams to resolve these critical issues in the review environment, ensuring we avoid major financial and reputation risks associated with production data incidents.
Furthermore, Qodo operates as a strategic quality gate by executing 15+ automated workflows during the build process, helping me to enforce compliance and security rules before a merge can occur.
I rely on it to flag configuration load path errors and legacy client usage, the type of cross-service problems that appear in isolated PRs and slowly erode stability across the organization.
This early, contextual analysis helps my teams resolve problems where they have the code and documentation context, maximizing engineering efficiency and avoiding costly, cascading production incidents at scale.
Pros
- Context Engine Capability: Provides full codebase context via SOTA Context Engineering, delivering true architectural analysis and breaking change detection across distributed, multi-repo services.
- Unified Agentic Quality Layer: Provides a single, consistent quality layer from local development (IDE) to CI/CD, powered by sophisticated agentic code review capabilities.
- High-Signal Risk Mitigation: Specifically engineered for enterprise-scale to mitigate risks from AI-generated code by enforcing strict standards and quality gates.
- Instant Resolution: Boosts developer efficiency with high-signal suggestions and available 1-click issue resolution.
Cons
- Requires initial configuration to align with specific enterprise workflows.
- Likely overkill for single-repo projects or small teams.
- Requires tuning of rules to minimize noise in highly specific contexts.
2. SonarQube
SonarQube is a static code analysis and constant inspection platform that organizations use to measure code quality and maintain long-term consistency across large engineering environments. It scans source files to identify bugs, vulnerabilities, and code smells, and it helps enterprises track maintainability, technical debt, and coverage across multiple languages and repositories. It is often deployed in environments with multiple repos where leadership needs a common reporting standard for security and code quality.
Key features
- Large library of rules for bugs, vulnerabilities, and code smells across 30+ languages.
- Quality gates that define pass or fail conditions based on metrics such as bugs, security issues, and coverage.
- Deep integration with CI/CD tools and pull requests so issues appear directly in the development workflow.
- Dashboards that track technical debt, maintainability ratings, and quality trends over time.
First Hand Example
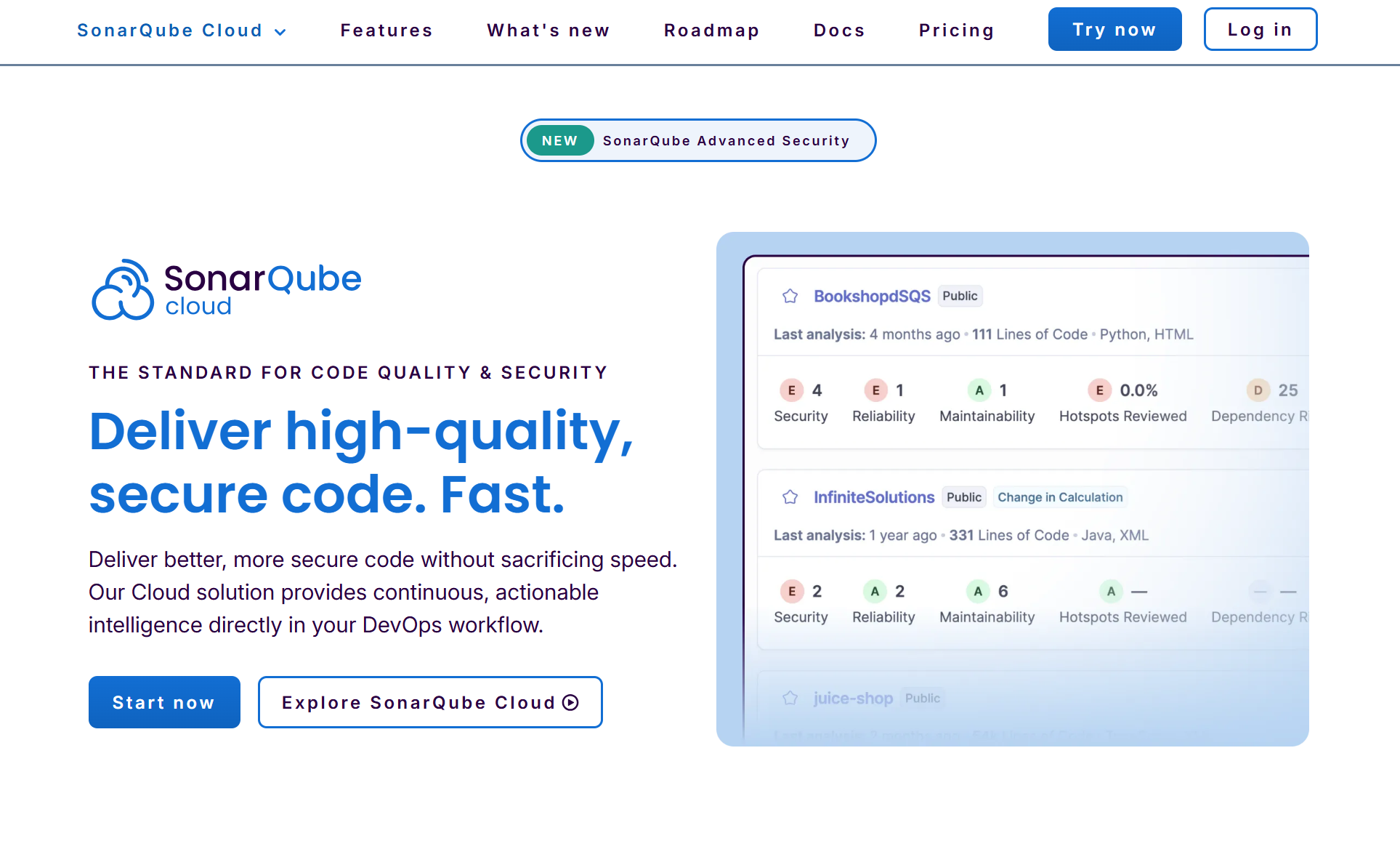
When I opened SonarQube for my Petclinic project, the dashboard gave me an immediate sense of where the code stood. The quality gate showed a passing status, but the detailed metrics painted a more realistic picture: zero bugs, nine vulnerabilities, and seventeen code smells across a codebase of around 2.7k lines.
That combination represents that the project is functionally stable, yet carrying several issues that could turn into long-term maintenance problems if I ignored them. Having these readings in one place helped me see that even a familiar demo application like Petclinic can accumulate structural issues quietly over time.
The surrounding indicators helped me narrow down what to work on next. Coverage at more than eighty percent reassured me that the main logic was well tested, while the duplication score sitting at zero showed that no repeated logic had crept in during recent changes.
At the same time, the vulnerability rating pushed me to open the rule list and inspect the specific files responsible. This kind of snapshot made it easier to prioritise fixes instead of relying on intuition, allowing me to mark potential risks before they spread deeper into the project.
Pros
- Mature, widely adopted platform with strong community and enterprise usage.
- Provides a centralized view of code quality across teams and repositories.
- Supports many languages, making it suitable for polyglot environments.
- Quality gates make it easy to turn code standards into enforceable policies.
Cons
- Can generate a high number of findings in legacy codebases if not properly tuned.
- Initial setup and configuration can be time-consuming for large or complex environments.
- Less focused on AI-driven insights or automatic remediation compared to newer platforms.
Security first SAST and DevSecOps pipelines
3. Snyk Code
Snyk Code is a static application security testing tool that focuses on identifying security vulnerabilities directly in source code. It scans application code during development and helps organizations integrate security checks into IDEs, pull requests, and CI pipelines. Enterprises that manage many services and security workflows use Snyk Code to establish a baseline level of application security across polyglot codebases and distributed teams.
Key features
- Fast, developer-centric static analysis focused on security vulnerabilities in source code
- IDE and Git integrations that bring up issues early in the development lifecycle
- Suggestions and examples for secure code alternatives
- Part of the broader Snyk platform, alongside dependency, container, and IaC scanning
First Hand Example
Working inside my IDE, Snyk Code immediately surfaced the risks buried in my deployment manifests and container images. The left panel showed a breakdown of configuration issues in the Kubernetes YAML files. Lines that looked harmless during development were flagged as running without user control, missing privilege restrictions, and relying on outdated images.
Having Snyk annotate them directly in the editor helped me understand the impact while still in context.

Snyk’s image analysis was even more revealing. The Redis base image I was using carried more than one hundred vulnerabilities, with a clear split across critical, high, medium, and low severity. Instead of just listing them, the tool compared my current image version to safer upgrade paths and showed how many issues each option would eliminate.
This saved me the usual back-and-forth of checking CVE databases and trying to guess which upgrade path offered the least friction. A Cloud Native Computing Foundation report mentioned that outdated container images remain a major cause of security regressions, and seeing this broken down visually inside my editor made that statistic feel very real.
Pros
- Very accessible for developers and easy to integrate into existing workflows
- Fast scans allow it to be used frequently without significantly slowing down pipelines
- Clear, actionable recommendations help non-security experts fix issues correctly
- Can be combined with other Snyk products for broader application security coverage
Cons
- Focused on security, not on general code quality, maintainability, or style
- Advanced policy configuration often requires security team involvement
- Commercial pricing may be high for very small teams or individual projects
4. GitHub Advanced Security with CodeQL
GitHub Advanced Security with CodeQL is GitHub’s built-in application security solution that allow automated code scanning, secret scanning, and dependency security checks. It uses the CodeQL analysis engine to find security vulnerabilities and coding errors directly in GitHub repositories, surfacing results in pull requests and the GitHub interface so developers can fix issues early and in context.
Key features
- Code scanning powered by CodeQL to detect security vulnerabilities and common coding flaws
- Support for custom CodeQL queries, allowing teams to create organization-specific security rules
- Native integration with GitHub repositories and GitHub Actions for automated scanning
- Centralised security dashboard for tracking risks across multiple repositories
First Hand Example
I was going through the security alerts for the DotNetCoreCryptography project when CodeQL flagged a critical issue that I would have easily dismissed as harmless test code. The alert showed a hard-coded password value sitting directly inside a unit test, and although the string looked like a placeholder, the system treated it as a real credential flowing into a cryptographic API.
Seeing the alert framed with CWE references helped me recognise that even test inputs can create patterns that slip into production codebases later.
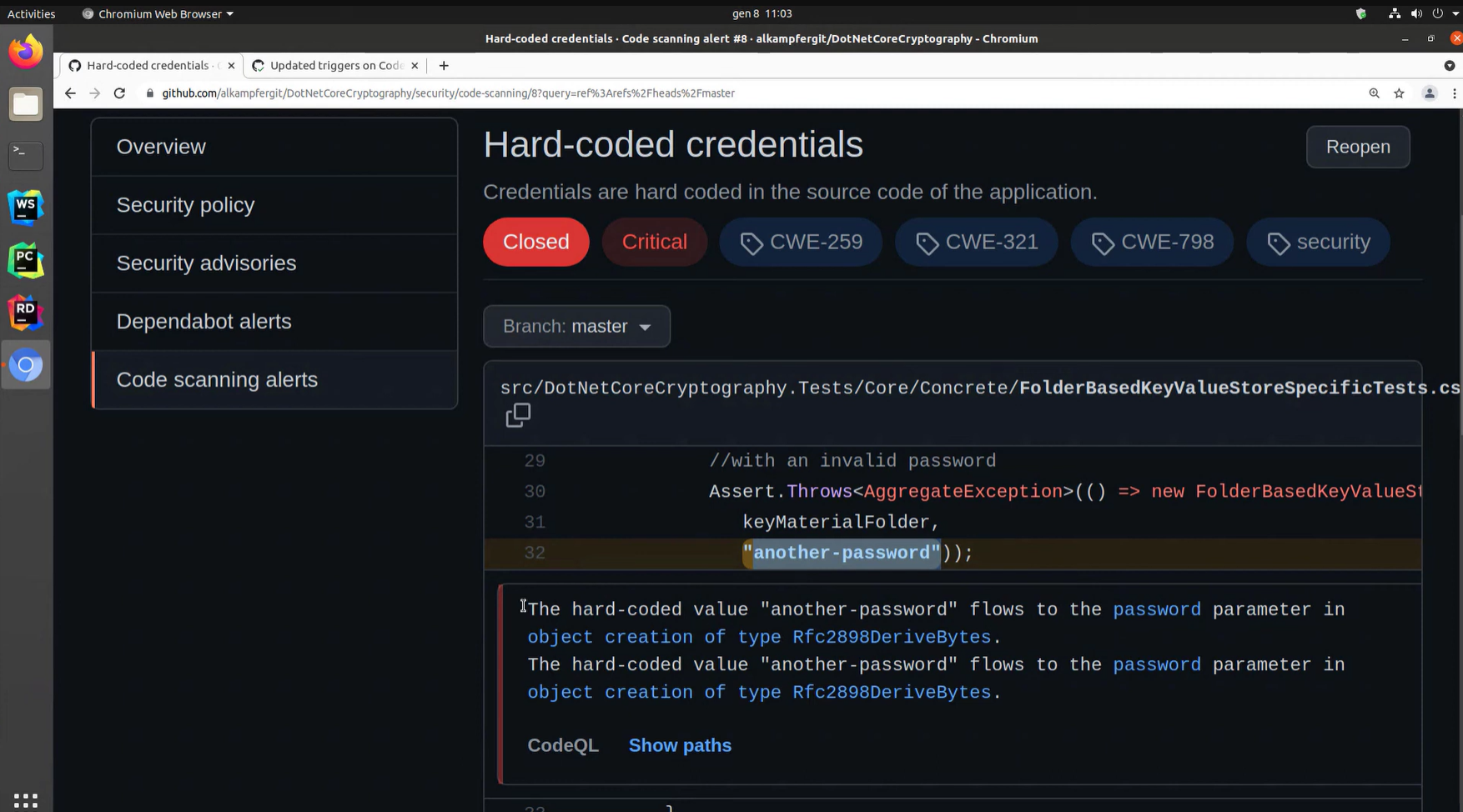
The diagnostic panel below the snippet made the situation clearer. CodeQL mapped the exact path the value followed and pointed out that it reached the password parameter of a sensitive class. Without that explanation, I would have assumed the value stayed inside the test method.
Instead, I could see precisely how it propagated, which made the fix straightforward. It was a useful reminder that small shortcuts in test files can still create security debt if the behaviour goes unnoticed.
Pros
- Deep, native integration with GitHub simplifies setup and adoption
- Highly useful for teams that invest in building and custom CodeQL rules
- Combines code scanning with secret and dependency scanning in one platform
- Scales well across large GitHub organizations and enterprise environments
Cons
- Requires GitHub Advanced Security licensing, which increases cost
- CodeQL has a learning curve for developers unfamiliar with query-based analysis
- Less suitable for teams that primarily use non-GitHub source control systems
Cloud based automated code review for Git workflows
5. Codacy

Codacy is a cloud-based automated code review and static analysis platform that scans code to detect quality issues, security problems, duplication, and complexity. It integrates directly with Git providers to run checks on every commit and pull request, helping teams enforce consistent coding standards across multiple repositories.
Key features
- Multi-language static analysis for code quality, security, and style issues
- Centralized rule management to enforce consistent standards across teams and repos
- Native integrations with GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket for automated PR feedback
- Dashboards to track code quality trends, technical debt, and hotspots over time
First Hand Example
Codacy gave me a clearer sense of how my codebase was behaving over time rather than forcing me to look at issues in isolation. The quality evolution chart immediately highlighted a spike where forty-seven issues appeared across only two hundred and fifty-one lines of code.
That was a strong signal that the project was drifting faster than I expected. I have seen similar patterns discussed in community forums where developers admit that small games or demo apps gather messy code because no one tracks quality trends early on. Codacy made that drift visible in a way that was hard to ignore.
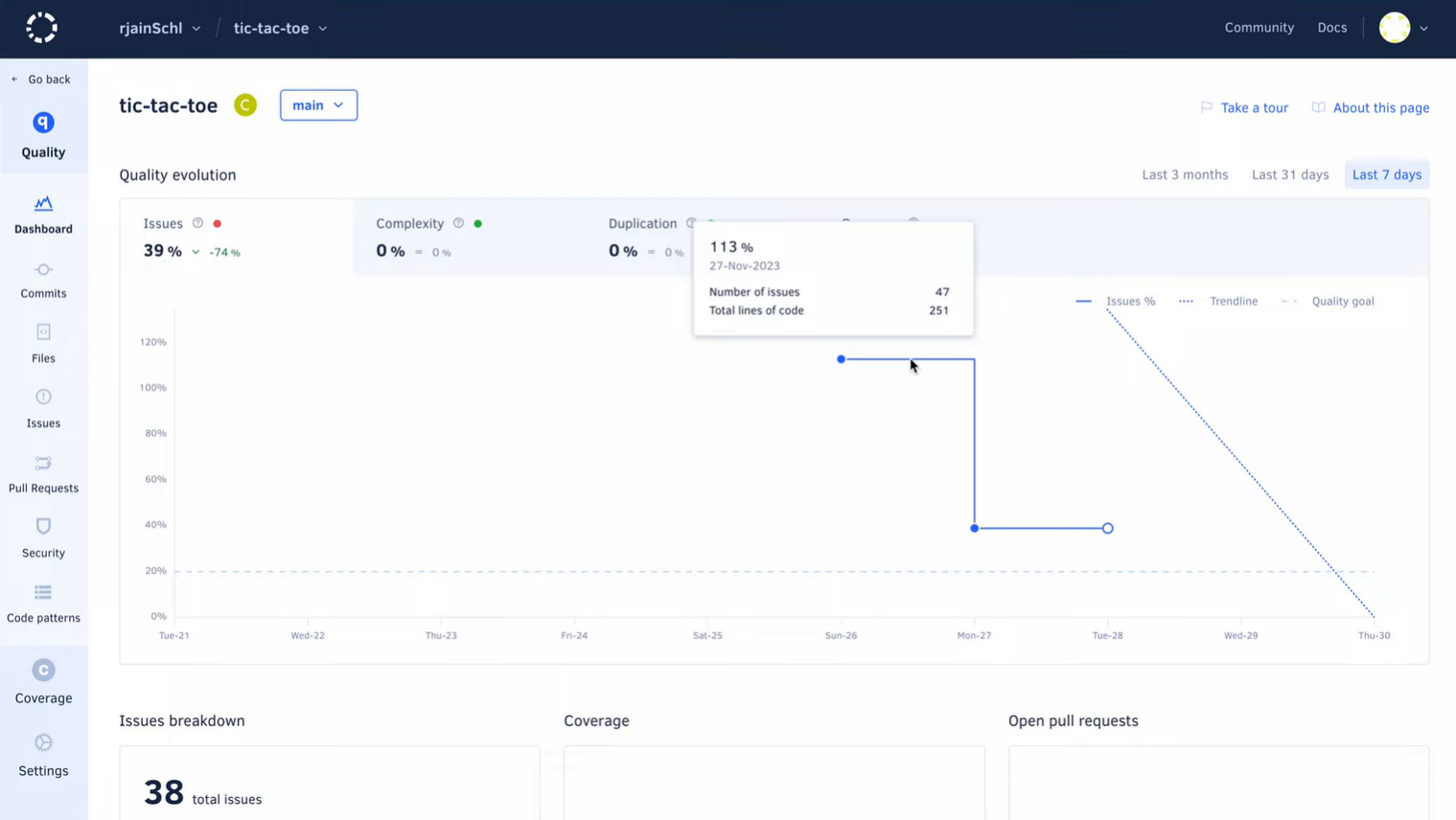
As I explored the dashboard, the stability of complexity and duplication told me that the structural layout of the project was fine, but the rising issue percentage showed something else: inconsistent coding habits across recent commits.
Codacy linked each change to the exact day it affected the trendline, which helped me revisit the right pull requests instead of scanning the entire commit history. A JetBrains developer survey mentioned that regression tracing is one of the most time-consuming parts of maintenance, and this view lowers that overhead significantly.
Pros
- Easy to roll out across many repositories for consistent enforcement
- lower downs repetitive manual review comments by automating common checks
- Cloud-based, so there is no infrastructure to maintain
- Supports a wide range of programming languages used in stacks
Cons
- Primarily focused on detection, not on automatically fixing issues
- Security depth is more limited compared to dedicated SAST tools
- Requires rule tuning to avoid excessive low-priority alerts
6. Code Climate

Code Climate is a cloud-based code quality and maintainability platform that integrates directly with Git workflows. It analyzes code for complexity, duplication, and maintainability issues, then surfaces insights and trends directly in pull requests and dashboards, helping teams understand how changes impact long-term code health.
Key features
- Automated analysis for maintainability, complexity, and duplication
- Pull request integration that shows how a change affects quality and coverage
- Configuration through a .codeclimate.yml file stored in the repository
- Historical reporting to track quality trends over time
First Hand Example
I logged into Code Climate to get a snapshot of how the test-codeclimate-ci repository was holding up, and the summary immediately put things into perspective. The maintainability grade showed a C with an estimated three days of technical debt, which was higher than I expected for a relatively small project.
That quick comparison between actual code and the debt ratio helped me see that a few shortcuts had slowly accumulated into something more noticeable, even though the code still felt manageable while I was writing it.
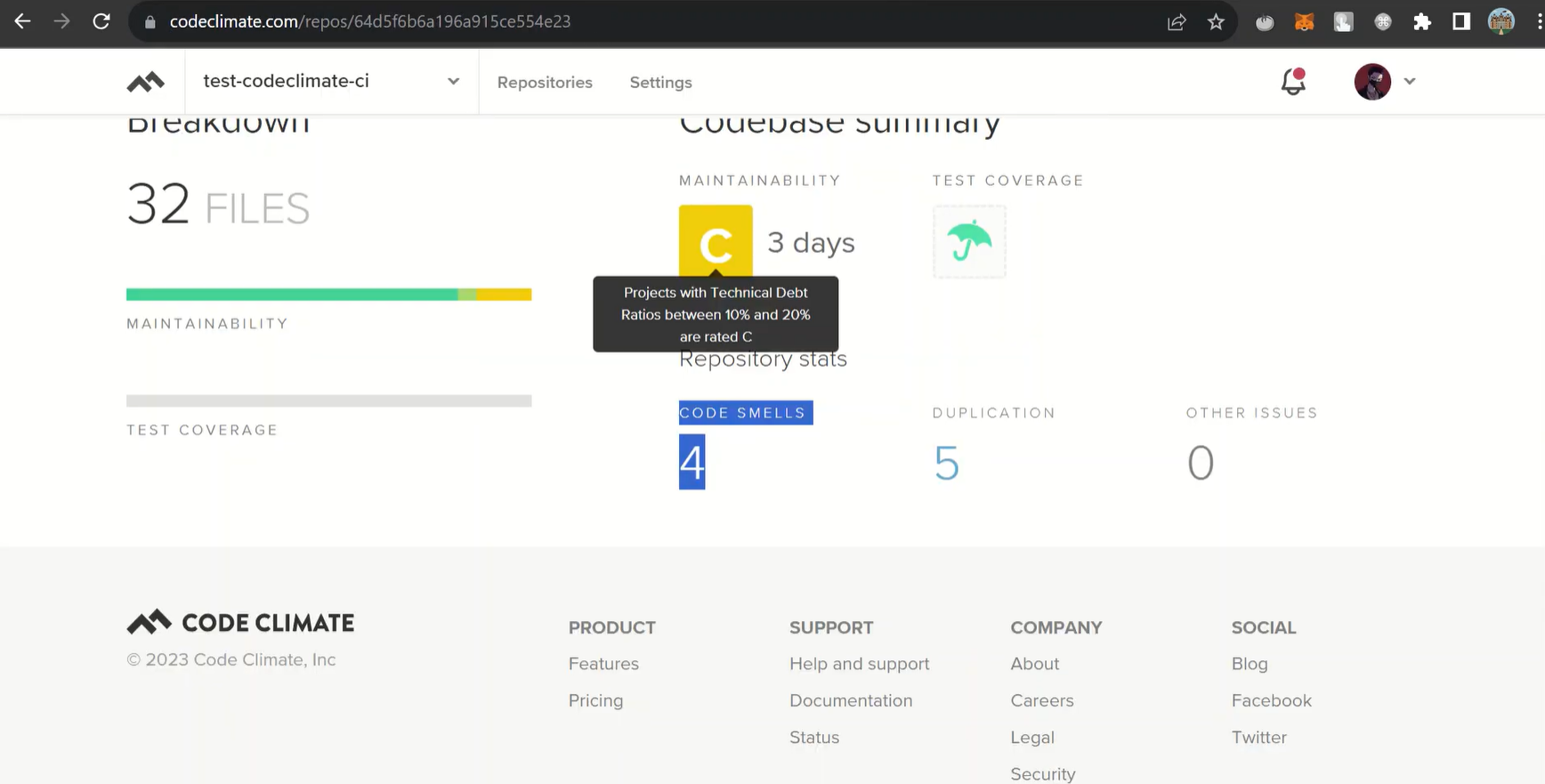
Looking deeper into the breakdown, the platform pointed out four code smells and five duplication cases across the thirty-two files. None of these issues were severe on their own, but together they highlighted sections where I had repeated logic or left patterns less consistent than they should be. Having this grouped into a clean dashboard made it easier to prioritise where to start refactoring rather than relying on intuition. It reinforced how small inconsistencies, when left unchecked, can gradually shape the long-term maintainability of a codebase.
Pros
- Easy to connect to GitHub-based workflows and start using quickly
- Clear visibility into code quality hotspots and growing technical debt
- Lightweight setup compared to heavier enterprise platforms
- Encourages ongoing conversations around test coverage and maintainability
Cons
- Focuses more on maintainability and complexity than on deep security analysis
- Limited flexibility for creating highly custom or domain-specific rules
- May need to be paired with other tools in larger enterprise environments
Deep static analysis for complex and large scale codebases
7. Coverity

Coverity, by Synopsys, is a deep static analysis tool that finds complex reliability and security defects in large codebases. It is commonly used in industries like automotive, aerospace, telecom, and enterprise systems where accuracy and defect traceability are critical.
Key features
- Deep semantic analysis for languages such as C, C++, Java, and C#
- Highly detailed defect tracking with root cause and data flow visualization
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines, ALM tools, and issue trackers
- Enterprise dashboards for compliance and large-scale reporting
First Hand Example
When I looked at the Coverity results, the first thing that struck me was how many of the flagged issues were related to SQL injection. Instead of giving me a long list, it grouped them by type and impact, which helped me see that several problems were coming from the same pattern.
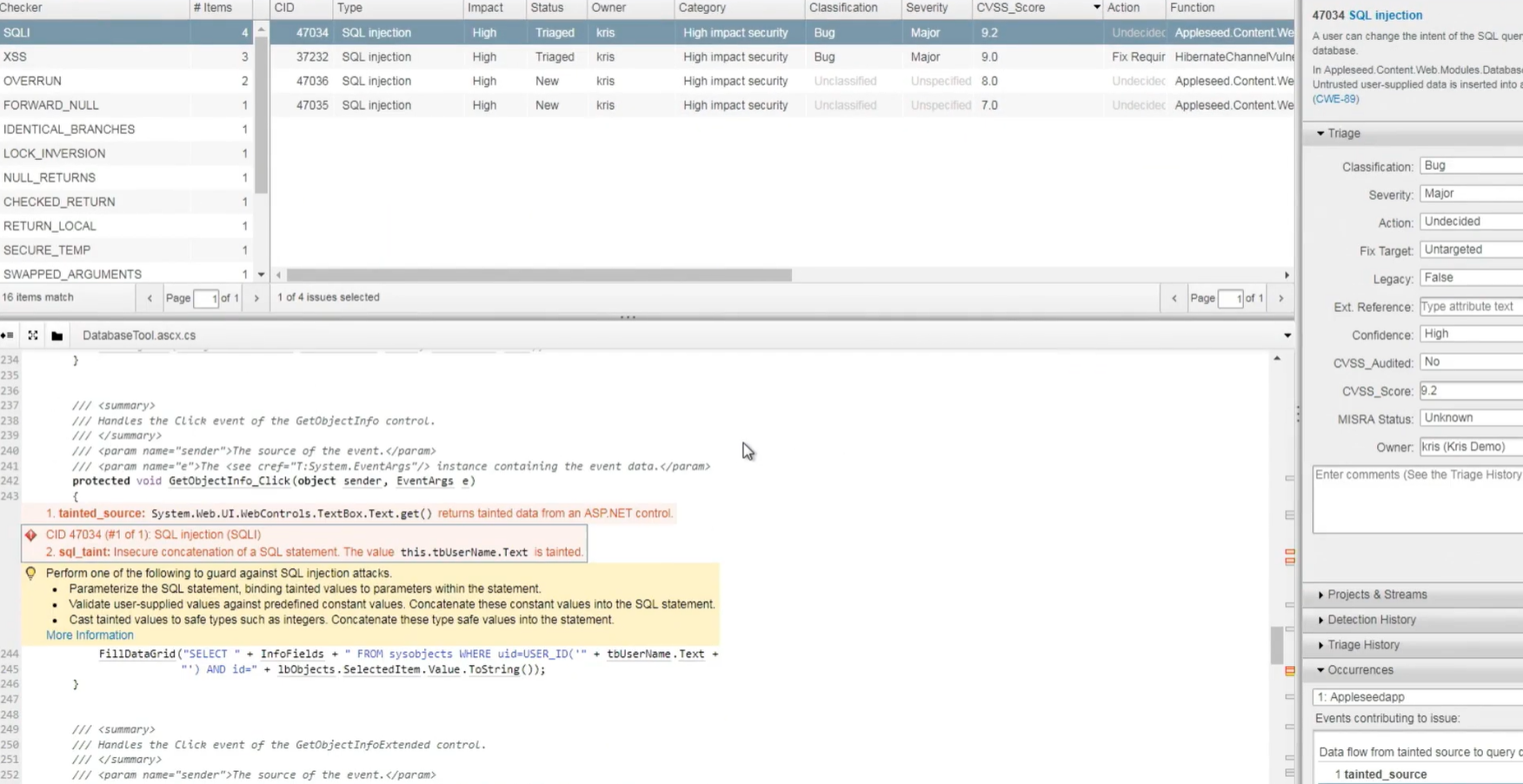
In the highlighted file, it traced data flowing from a textbox directly into a SQL query. Seeing the full path laid out made it easier to understand where the risk started. This matched something I had read on Reddit where developers often mention that injection flaws hide in code paths that feel harmless during implementation.
The triage panel on the right added context I normally do not get during manual review. It showed the severity, CVSS score, and confidence level, which helped me assess whether this was a minor sanitation issue or something that could lead to unsafe behaviour in production. With a score above nine, it became clear why the tool flagged it so strongly. I also noticed that it showed how many places this input flowed into, which saved me the usual back-and-forth of searching through the file to find related calls.
Pros
- Very accurate at identifying complex defects like memory leaks and race conditions
- Well suited for safety-critical and regulated environments
- Effective at analyzing large, legacy, and highly complex codebases
- Strong reporting and audit capabilities
Cons
- Setup and tuning often require expert knowledge
- Slower and heavier than lightweight tools
- Interface feels more traditional compared to newer SaaS platforms
8. Semgrep

Semgrep is a fast, pattern-based static analysis tool that scans code for bugs, security vulnerabilities, and policy violations. It matches code at the syntax tree level, not just text, making it more striking than simple pattern matching while remaining very fast and flexible.
Key features
- Pattern-based rules that analyze code structure, not just strings
- Works with many languages and frameworks
- Large open-source rule registry for security and best practices
- Commercial platform with noise reduction and rule management
First Hand Example
I checked the Semgrep findings for the r2c-testing/holden test project to understand what had changed over the past month, and the first thing that stood out was a cluster of medium-severity alerts tied to regular expression usage. Several functions were using non-literal RegExp patterns, which Semgrep warned could block the main thread or create denial-of-service behaviour if unexpected input reached them.
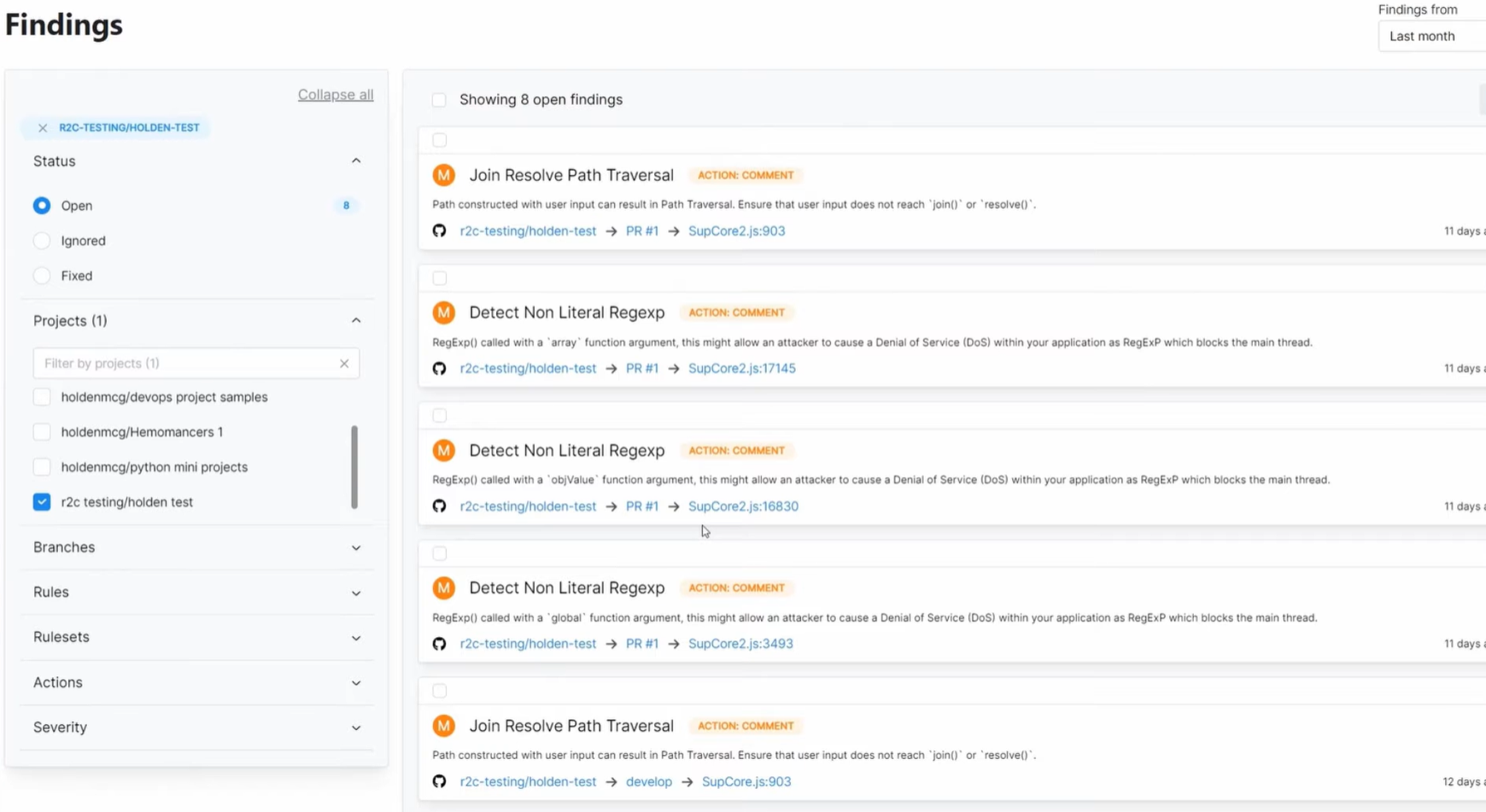
These were small helpers I wrote quickly, and I had not focused how flexible patterns might behave under load. Seeing the explanations attached to each alert helped me revisit the logic with a clearer sense of what the risk actually was.
The list also included a pair of path traversal findings, each pointing to simple join operations that looked harmless in isolation. Semgrep highlighted how user input could influence those joins, which is something I might have missed without a structured scan.
The ability to jump directly from the alert to the exact file and pull request made it easier to track when the issue was introduced and how widespread the pattern was. Instead of treating these as isolated warnings, the dashboard gave me a focused view of habits that needed tightening before they turned into bigger security or performance problem
Pros
- Extremely fast, suitable for frequent CI runs and local scanning
- Easy to write and customize rules for internal policies
- Open-source option makes it accessible to most teams
- Useful for enforcing organization-specific patterns and rules
Cons
- Detection quality depends heavily on the rule used
- Advanced use often requires writing and creating custom rules
- Without tuning, it can create false positives
Language specific linting and style consistency
9. ESLint
ESLint is a highly configurable, pluggable linter for JavaScript and TypeScript. It is used to detect code style issues, common bugs, and problematic patterns in frontend and backend JavaScript projects, and is the de facto standard in JS/TS ecosystems.
Key features
- Plugin-based architecture with a large ecosystem of community rules
- Support for JavaScript, TypeScript, JSX, and popular frameworks
- Integration with IDEs, pre-commit hooks, and CI/CD pipelines
- Auto-fix capability for many formatting and minor logic issues
First Hand Example
While editing this small JavaScript file, ESLint immediately pointed out a pattern I tend to overlook when moving quickly: a variable that was assigned but never used. In this case, didShowMessage was defined at the top but never referenced again. It is the kind of minor oversight that does not break anything today, yet it slowly adds clutter as the codebase expands.
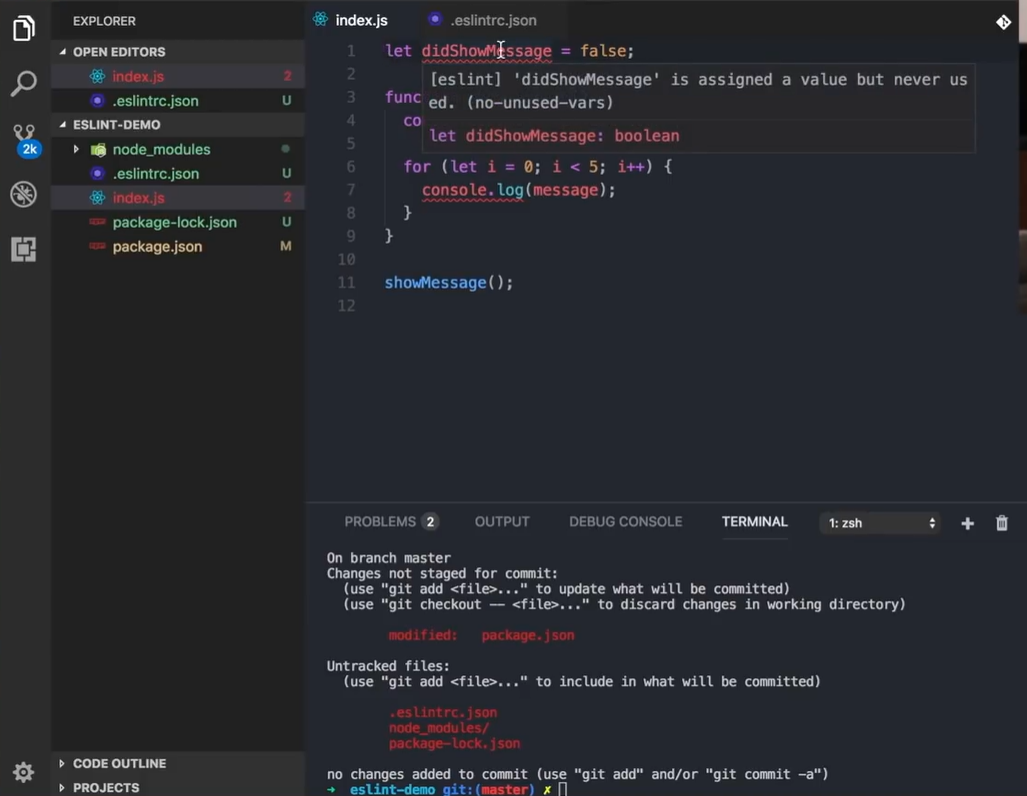
I have come across similar comments in Reddit threads where developers admit that unused variables pile up because they feel too small to fix during early development. Seeing it highlighted inline made the cleanup straightforward instead of something I would postpone.
The linter also flagged a type annotation that did not belong in plain JavaScript. I had added it out of habit, and while it did not cause an immediate error, ESLint exposed it as misleading code. These mismatches often complicate onboarding for new contributors because they try to infer rules that are not actually enforced. By surfacing this inconsistency directly in the editor, ESLint helped me keep the file predictable and easier to read, which pays off later when functions multiply and responsibilities shift.
Pros
- Widely adopted standard for JavaScript and TypeScript projects
- Extremely flexible and customizable to match team style guides
- Works effortlessly with React, Vue, Node.js, and other JS frameworks
- lower downs style-related feedback in manual code reviews
Cons
- Configuration can become complex as plugins and rules increase
- Overly strict settings can negatively impact developer experience
- Not intended for deep security analysis
10. RuboCop

RuboCop is a static code analyzer and formatter for Ruby that enforces the Ruby style guide and identifies common mistakes, complexity issues, and code smells in Ruby and Rails projects.
Key features
- Enforces Ruby community style standards through a large groups of “cops”
- Includes lint, security, and metrics checks such as complexity and method length
- Auto-correction for many violations
- Integration with editors, Git hooks, and CI/CD pipelines
First Hand Example
I was running the test suite for one of my Ruby projects when RuboCop surfaced a failure inside the node_pattern_spec.rb file. The output showed that a pattern match expectation returned false where it should have returned true, which immediately pointed me toward an issue in how I had defined the matcher.
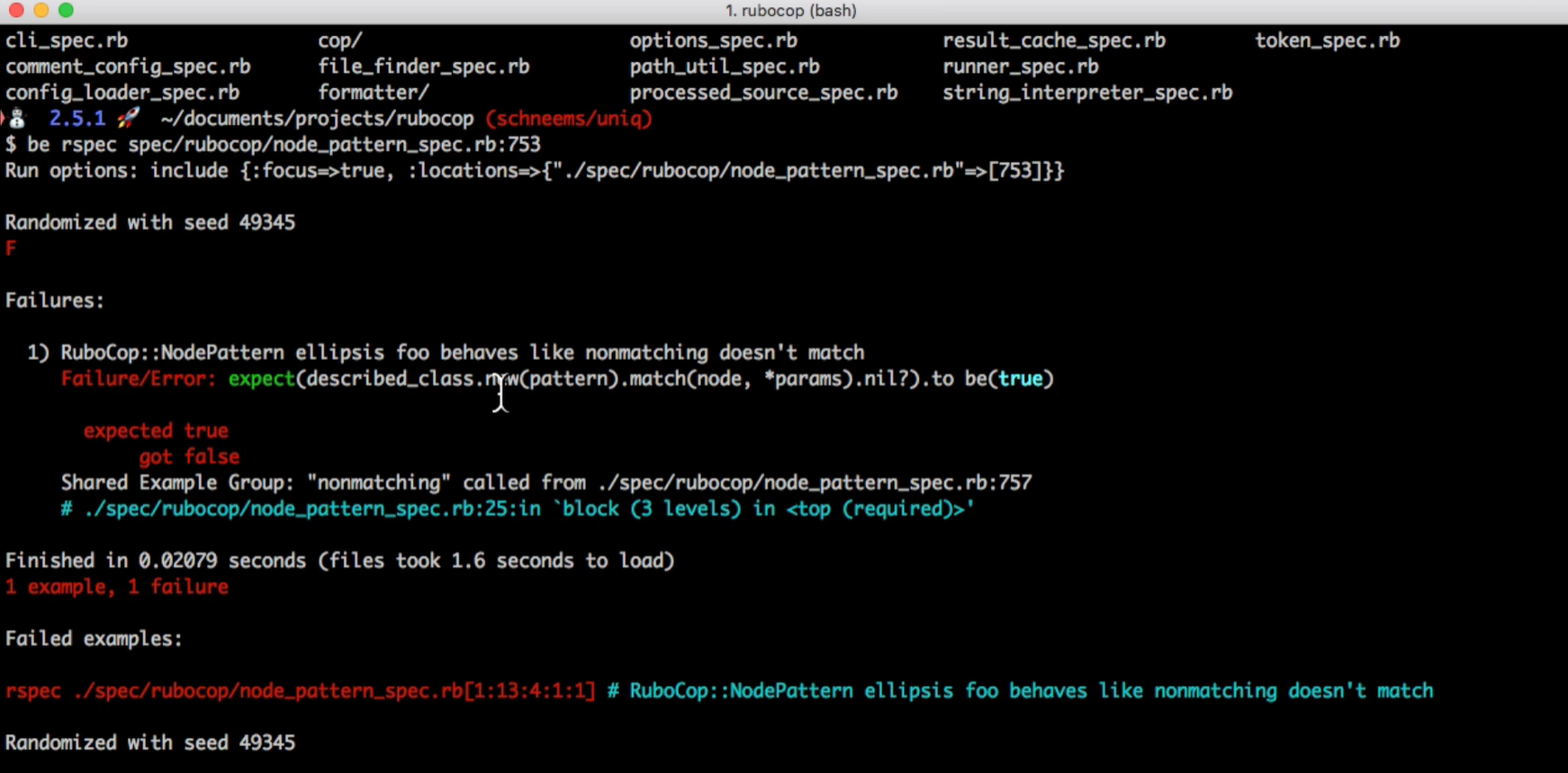
This was one of those internal rules I had assumed was behaving correctly, and without the failure message calling out the exact line and shared example, I probably would have missed the mismatch between the pattern and the supplied parameters.
Scrolling through the trace made it clear where the problem originated. RuboCop highlighted the nested block in the spec and showed how the pattern behaved differently than expected under certain inputs.
The detailed error output, including the seed used for test randomisation, gave me enough context to reproduce the behaviour consistently and adjust the matcher logic. Instead of guessing where the inconsistency was coming from, the test failure gave me a focused entry point to refine the rule, which helped keep the linter’s checks predictable across the rest of the codebase.
Pros
- Standard tool in many Ruby and Rails codebases
- Keeps Ruby style and formatting consistent across teams
- Auto-correction significantly lower downs manual cleanup work
- Highlights overly complex methods and risky patterns
Cons
- Strict configurations may feel heavy for small or early-stage projects
- Auto-corrected changes still need review in critical areas
- Security analysis is limited compared to dedicated SAST tools
Conclusion
As engineering organizations expand, leaders are responsible for more than feature delivery. They must ensure that systems remain stable, secure, and manageable as AI increases the amount of code entering pipelines.
By 2025, AI coding tools and automated generation tools shape a significant share of daily development activity, which places new pressure on the review and governance layers that sit before production.
Each tool in this ecosystem marks a different part of the quality and security challenge. Qodo is the best code review platform that helps enterprises hold consistent standards across the SDLC and align code with architectural intent.
Security platforms such as Snyk Code, CodeQL, and Veracode focus on application-level risks. Cloud-oriented services including DeepSource and Codacy streamline repetitive review tasks. Language-specific linters such as ESLint, Pylint, and RuboCop keep common issues from reaching pull requests.
Large organizations do not rely on a single platform. Effective strategies combine multiple tools that match the architecture, and the maturity of the engineering teams involved.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between code analysis and code quality tools?
Code analysis tools inspect source code for defects, risky patterns, and security issues, while code quality tools focus on maintainability, duplication, complexity, and consistency. Both categories work together to keep codebases reliable as they grow.
2. Are AI-powered code review tools replacing manual reviews?
AI tools assist reviewers by highlighting risks, inconsistencies, and edge cases earlier, but they do not replace human judgment. Most teams use AI analysis to lower down noise so reviewers can focus on logic, architecture, and correctness.
3. Why do teams combine multiple tools instead of relying on one platform?
Systems today span many languages, frameworks, and deployment models, and no single tool covers every layer. Teams typically mix enterprise governance, SAST, cloud PR checks, and language-specific linters to cover the full SDLC.
4. How do these tools help lower down technical debt over time?
They bring up risky patterns, enforce coding standards, detect regressions, and avoid unsafe shortcuts from accumulating. Since many defects originate from repeated small mistakes, early detection keeps long-term maintenance costs lower.
5. Are these tools suitable for small teams or only for enterprises?
Most tools scale across both small and large teams, but the required setup varies. Lightweight linters and cloud PR scanners work well for smaller codebases, while enterprises often use governance platforms and deep static analysis for complex systems.