Top 7 GitHub Copilot Alternatives
TL;DR
- AI coding assistants now offer strong competition to GitHub Copilot, enabling developers to write, debug, and understand code more efficiently with enhanced privacy and integration options.
- Qodo Gen, Zencoder, and Sourcegraph Cody provide advanced code understanding, automatic documentation, and unit test generation, great for developers working on large or complex projects, maintaining code quality.
- Tabnine focuses on privacy and speed, running locally or on-premises, and supports over 20 programming languages and major IDEs.
- Replit Ghostwriter is built into the Replit online IDE, making it easy for beginners and teams to code, debug, and collaborate in real-time.
- OpenAI Codex and Amazon Q Developer target power users. Codex works from the terminal for local automation, while Amazon Q integrates deeply with AWS to generate secure, cloud-ready code.
In a world of fast-paced software development, AI-powered coding assistants have emerged as game-changers, helping developers streamline workflows, reduce errors, and accelerate project timelines. These modern AI coding assistants help developers automate repetitive tasks, enhance accuracy, and collaborate more effectively within integrated environments. Among these tools, GitHub Copilot stands out as a pioneering solution, leveraging advanced machine learning models to provide intelligent code suggestions and automate repetitive tasks.
As the demand for AI-driven development tools grows, however, many developers are exploring GitHub Copilot alternatives to address specific needs, such as enhanced features, better integration with preferred development environments, or more budget-friendly options.
This article looks at the top competitors and some free alternatives to GitHub Copilot, offering insight into their capabilities and helping you identify the best fit for your development requirements.
What Is GitHub Copilot, and Why Might You Look for Alternatives?
GitHub Copilot is an AI-powered coding assistant developed by GitHub in collaboration with OpenAI. It uses machine learning models trained on vast amounts of publicly available code to provide real-time code suggestions, complete functions, and generate larger code blocks depending on the context. Integrated seamlessly into popular IDEs like Visual Studio Code, it has become a valuable tool for developers looking to enhance productivity and reduce coding errors.
Developers may seek GitHub Copilot alternatives for the following reasons:
- Cost: GitHub Copilot is a subscription-based service, and not all developers or teams can justify the expense, especially when free or more cost-effective solutions exist.
- Features: Some developers seek tools tailored to specific workflows, languages, or development environments that GitHub Copilot might not fully support.
- Privacy: Given its reliance on AI trained on public repositories, some developers worry about potential intellectual property risks or data privacy issues.
- Compatibility: GitHub Copilot may not integrate optimally with less common IDEs or niche tools used in specific industries.
The demand for alternatives arises as developers search for solutions that better align with their unique requirements.
Top 7 GitHub Copilot Alternatives

As the market for AI-powered coding assistants grows, several tools have emerged as strong GitHub Copilot alternatives. Below are the top GitHub Copilot competitors evaluated for their capabilities and suitability for modern software development.
Let’s explore each alternative in detail, starting with Qodo Gen, a powerful AI assistant that blends intelligent code generation with deep project understanding.
1. Qodo Gen
Qodo Gen is a cutting-edge AI coding assistant designed to enhance productivity and code quality. Built on Agentic AI Tools architecture, Qodo Gen functions as an advanced AI code generator that learns from your existing codebase to deliver contextual and accurate suggestions. It uses the latest generative AI technologies and fine-tuned models to generate code for your specific requirements.
Key Features:
- Provides a user-friendly chatbot for advanced code generation and completion for seamless coding.
- Supports seamless integration with popular IDEs such as Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, and other JetBrains IDEs.
- Explains generated code snippets part by part, helping you easily understand how they work.
- Supports a variety of programming languages, including Python, TypeScript, JavaScript, Java, Golang, and more.
- You can quickly test existing or newly generated codes and even build complete test suites to increase the code coverage.
Hands-on section: Creating a Google Compute Engine Instance
For this hands-on, I started with an existing Terraform configuration and needed to provision a Google Compute Engine VM that would run a containerized workload. Instead of manually writing out the resource, I prompted Qodo Gen with:
"Add a Google Compute Engine VM instance named nginx-instance that runs a container image from GCR. - type e2-medium - zone us-central1-a - base it on Container-Optimized OS - configure the container image gcr.io/PROJECT_ID/IMAGE:latest - ensure restartPolicy is Always"
Qodo Gen first inspected my Terraform files (main.tf, variables.tf, and resources.tf) to understand the current provider setup and structure. This was useful; it avoided breaking existing configurations and ensured consistency with the way my infrastructure was already organized.
It then updated resources.tf to add a new google_compute_instance resource with the required parameters:
- Machine type: e2-medium
- Zone: us-central1-a
- Boot image: Container-Optimized OS (cos-stable family)
- Container config: pulled from gcr.io/PROJECT_ID/IMAGE:latest
- Restart policy: Always
- Networking: default VPC with external IP (with a note that I could swap in a custom network if needed)
What stood out was the workflow:
- Analyze existing codebase: Qodo automatically checked the provider configuration and file structure.
- Generate resource: It created the new VM definition without disturbing my existing Terraform setup.
- Explain changes: The agent clearly documented what it added, why, and how to customize it.
- Next steps: It provided init/plan/apply commands so I could deploy right away.
This made the process far smoother than writing the block from scratch. Instead of toggling between documentation and trial-and-error, I had a ready-to-apply configuration tailored to my project. The only manual step was swapping in the correct container image reference.
In practice, this reduced my provisioning workflow from 20–30 minutes to a few minutes, while still providing me with visibility into every line of code Qodo Gen added.
Pricing
Offers a free version; Paid plans start at $19/User per month.
Review: “Very robust. Intuitive interface. Ability to pick right direction in unit test creation.” – G2 Review
2. Tabnine
Tabnine is an AI-powered coding assistant designed to provide intelligent code completions and snippets tailored to your development style.
Key Features:
- AI-powered contextual code completions.
- Supports over 20 programming languages.
- Privacy-focused with an on-premises option for enterprises.
- Integrates with VS Code, IntelliJ, PyCharm, and other major IDEs.
Hands-on section: Accelerating TypeScript Development
In this hands-on evaluation, Tabnine was tested while building a CLI Profile command in a TypeScript project. The task involved capturing user details such as name, email, address, state, and zip, and storing them in a structured format.
To simplify setup, Tabnine was prompted to generate an array of all 50 U.S. states with their 2-letter postal codes as visible in the IDE below:
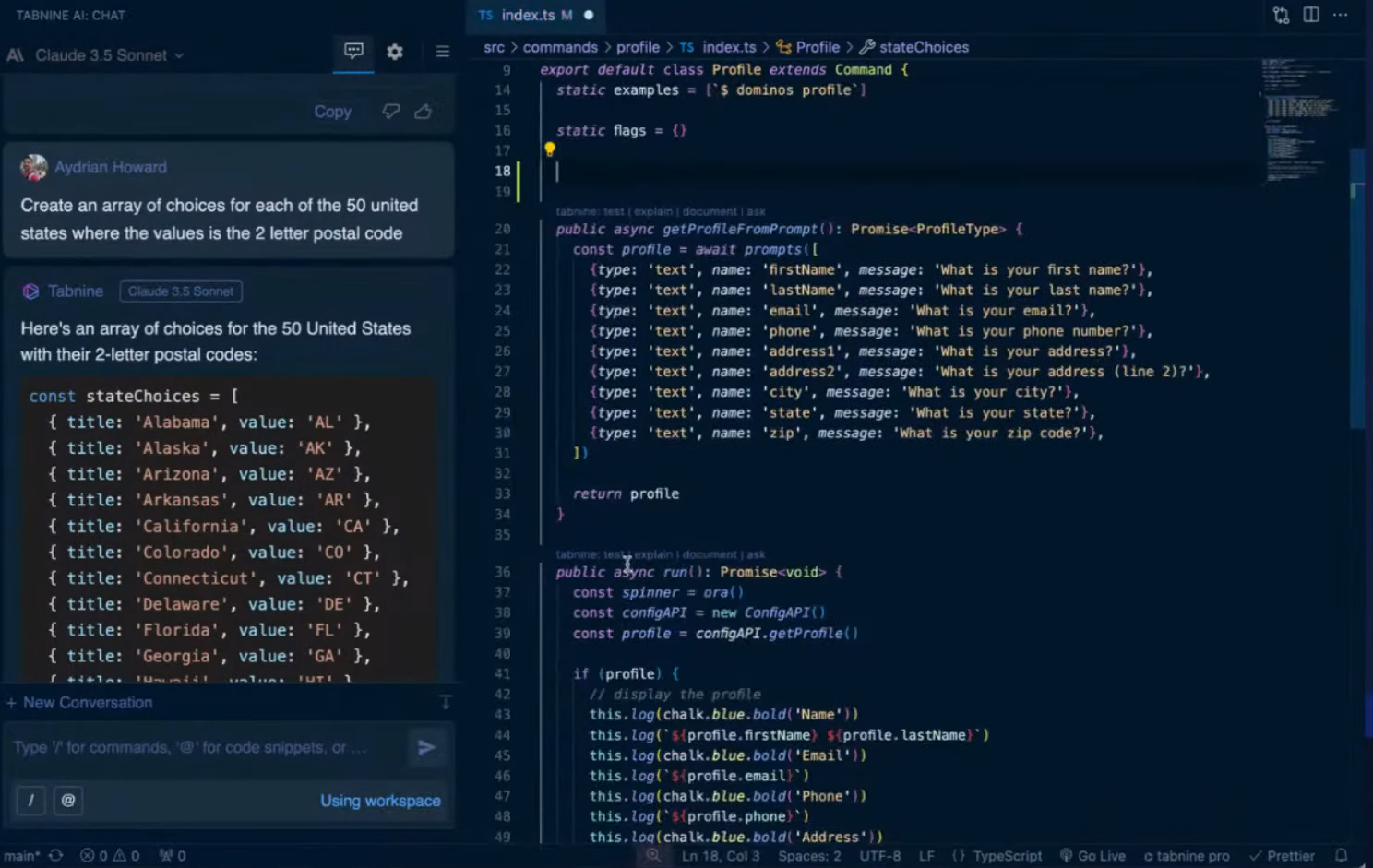
Within seconds, it produced a complete and accurate stateChoices array, eliminating the need for copy-pasting static data or searching external files.
Beyond scaffolding, Tabnine also suggested inline completions inside the getProfileFromPrompt method. As prompts were created for fields like firstName, lastName, email, and phone, it consistently provided the correct type, name, and message structures, aligning with the surrounding code style.
What stood out was Tabnine’s contextual awareness, detecting the broader intent of building a profile form and offering consistent field definitions. It accelerated repetitive setup tasks, like generating the state array, and ensured flow continuity by matching variable naming conventions such as profile.firstName and profile.email. The result was a streamlined workflow: start coding, receive intent-driven suggestions, validate, and commit, turning a 15–20 minute repetitive task into a 2–3 minute process without sacrificing accuracy.
Pricing
Offers a free version; paid plans start at $9/month.
Review: “Best AI Coding assistant where security & privacy is a must” – G2 Review
3. Replit Ghostwriter
Replit Ghostwriter is an AI-powered coding assistant embedded within Replit’s online development environment. Ghostwriter assists with code suggestions and identifies and fixes errors, making it a valuable tool for collaborative and rapid development.
Key Features:
- Real-time code completion and debugging.
- Built into the Replit development platform.
- Multi-language support, including Python, JavaScript, and more.
- Excellent for pair programming and educational use.
Hands-on section
For this hands-on evaluation, I tested Replit’s AI coding assistant by prompting it to create a simple Feature Flag API using Node.js and Express. The requirement was straightforward: the service should expose two endpoints, /flags to list active feature flags from a JSON file, and /toggle/:flag to switch flags on or off.
As shown in the interface below:
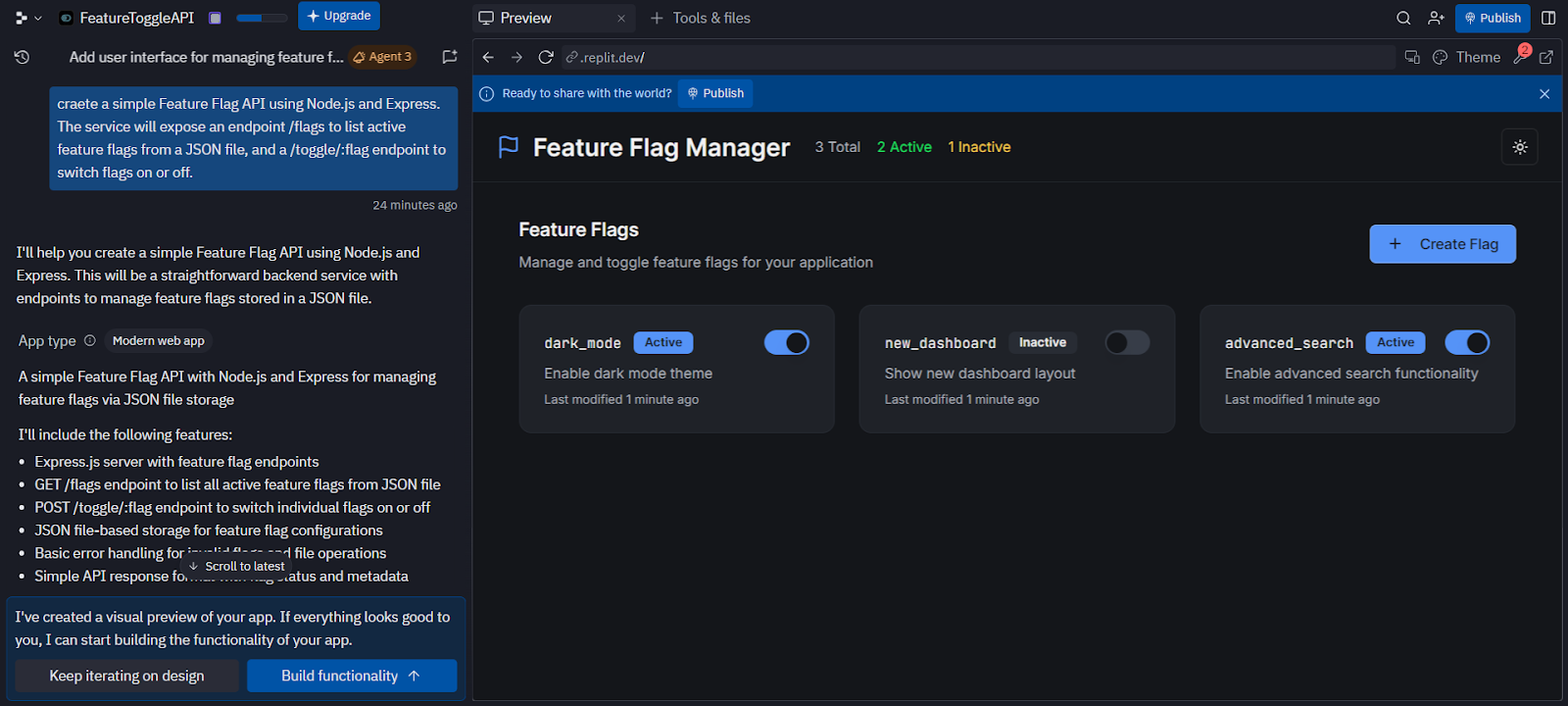
Interestingly, Replit’s assistant responded differently than expected. Instead of scaffolding the requested API, it interpreted the task as building a React + Tailwind UI for an AI assistant. The generated plan outlined features such as a centered chat window with an “AI Assistant” header, a scrollable message area with user/assistant distinction, a send button with simulated responses, and a light/dark mode toggle. Alongside this, it scaffolded an entire project structure with files like chat-window.tsx, message.tsx, input-bar.tsx, and theme-provider.tsx, while also setting up dependencies, configuration scripts, and a replit.md file for instructions.
While this wasn’t aligned with the original feature flag API request, what stood out was how Replit’s assistant proactively scaffolded a complete application with consistent theming, interaction flow, and environment setup. It demonstrated strong defaults for modern React + Tailwind development, handling boilerplate like CSS setup, component organization, and dark mode support without further prompting.
The workflow highlighted an important aspect of AI-assisted coding: sometimes the assistant interprets prompts broadly, offering a solution it deems relevant rather than exactly what was asked. In this case, instead of a minimal Express API, it provided a fully scaffolded UI project with ready-to-use components and startup scripts.
Pricing
Offers a free version; Paid plans start at $15/month for individuals.
Review: “Fantastic tool for non-coders.” – G2 Review
4. OpenAI Codex
Codex CLI is an open-source, Rust-based coding agent that runs directly from the terminal. It can read and modify your local code, execute commands, and interact with your repository in an isolated environment. Official support covers macOS and Linux; Windows works via WSL. You can install it with npm install -g @openai/codex or brew install codex, then authenticate using a ChatGPT plan or API key.
Key Features
- Terminal-native agent: Runs as a local CLI tool, editing files and executing commands in your working directory.
- Flexible install: Available via npm or Homebrew; easy to upgrade with the package manager.
- Model selection: Defaults to GPT-5, but you can switch to gpt-5-codex or other models with the –model flag.
- Approval modes:
- Auto: Directly edits and executes in your repo.
- Read Only: Safe, no file changes.
- Full Access: Includes network access (use carefully).
- Image inputs: Supports screenshots for debugging or diagram interpretation via the –image flag.
- Batch/one-shot mode: Run codex exec “…” for single commands without launching the TUI.
Hands-on example
I prompted Codex with: “Add a button to export the current table data (services + statuses + timestamps) as a CSV file, and another to import CSV back.”
Codex started by scanning the repo as shown in the snapshot below:
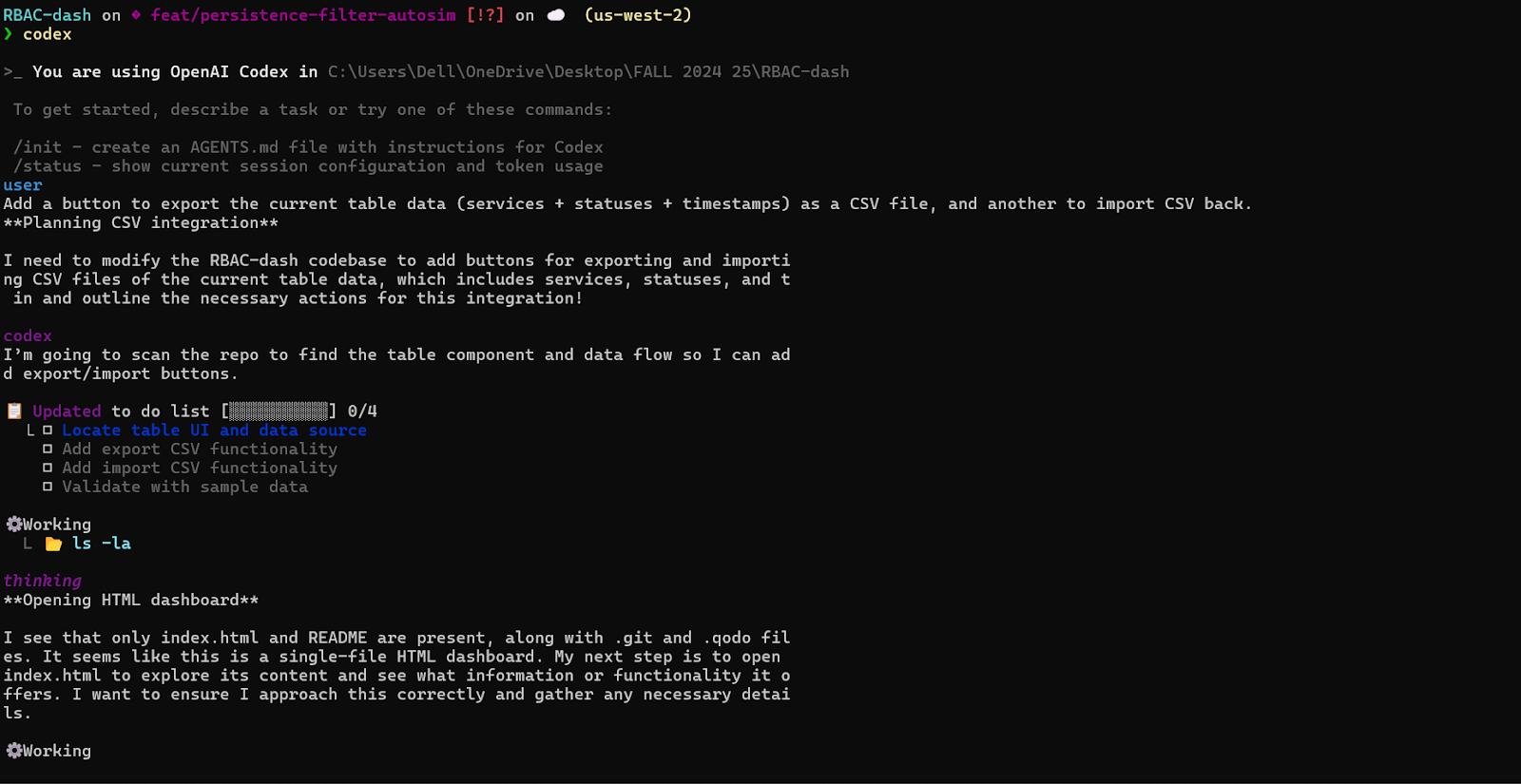
It found this was a single-page app with just index.html and README, so it opened up the HTML file and broke the task into four items: find the table/data flow, add export, add import, and validate.
It then updated the UI by adding two buttons in the header, #exportCsvBtn and #importCsvBtn, along with a hidden file input #importCsvInput for uploads.
For the export path, it generated an exportCsv() function that pulls the current view from getFilteredServices(). The function outputs a CSV with the headers service_name,status,last_updated, formats timestamps into ISO strings, and triggers a download directly in the browser.
For the import path, it wrote importCsvFile() and importCsvText(). These functions parse CSV with quoted-field handling, enforce the three required columns, and accept statuses in any case (Healthy, Degraded, Down). Each valid row is parsed, assigned a fresh ID, persisted into services, saved to localStorage, and re-rendered across the table, KPIs, and chart. Invalid rows are skipped with warnings.
After this, the workflow looked clean:
- Filter the table and click Export CSV; you will get a file containing only the visible rows.
- Hit Import CSV with a file containing service_name, status, and last_updated, the table reloads with that data, metrics update, and the state survives a reload because of localStorage.
The next logical improvements would be a merge option for imports (instead of full replace) and a couple of automated tests to check round-trip export/import and status normalization.
Pricing
- Included with ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Team, Edu, and Enterprise subscriptions.
- No separate pricing tier for Codex Cloud itself; access depends on your plan.
Review: Codex Cloud behaves less like a “typing assistant” and more like a delegated junior developer that can propose diffs, run tests, and handle refactors.
5. Sourcegraph Cody
Sourcegraph Cody combines powerful code search capabilities with AI-driven assistance. It’s particularly beneficial for navigating large codebases and improving code comprehension.
Key Features:
- Advanced code search with AI suggestions.
- Integration with major IDEs and Git repositories.
- Supports multiple programming languages.
- Excellent for improving codebase navigation and understanding.
Hands-on section
In VS Code, Cody can be invoked directly from the editor to generate documentation or explanations for existing code.
The screenshot below shows a Rust program that creates a file called example.txt and writes “Hello, world!” 100,000 times into it.
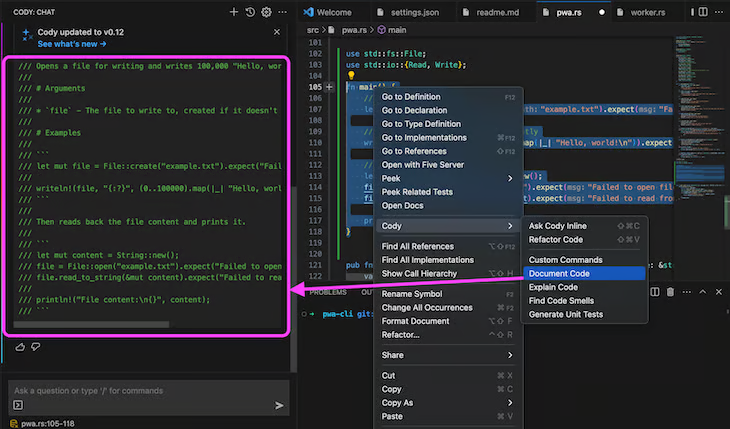
By right-clicking the function and selecting Cody, then going to Document Code, Cody automatically generates structured Rustdoc comments in the left-hand panel.
The documentation it produces explains the function’s purpose, describes the arguments, and even includes an example of how the file is created and written to. This transforms raw source code into something production-ready with clear usage notes and examples.
From the same context menu, choosing Explain Code opens a plain-English summary that describes what the function is doing: creating the file, looping 100,000 times, and writing “Hello, world!” on each iteration. This is useful for quickly understanding unfamiliar code without manually tracing every line.
Cody also goes beyond explanation and documentation. When prompted to refactor the same function to use idiomatic Rust error handling with the ? operator, it suggested a cleaner implementation that removes .expect() calls and returns a proper Result. This makes the program more robust and better aligned with Rust best practices.
The flow visible in the snapshot above highlights Cody’s strength: working directly alongside code to document, explain, and improve functions in real time without leaving the editor. Developers can move seamlessly from raw implementation to documented, reviewed, and refactored code, all within VS Code.
Pricing: Free for basic use; premium plans start at $9/month.
Review: “Save time and avoid errors in your code” – G2 Review
6. Zencoder
Zencoder is an AI-powered coding assistant designed to help developers write, analyze, and optimize code directly in their IDEs. By integrating with popular platforms like VS Code, JetBrains IDEs, and Android Studio, Zencoder automates repetitive coding tasks, resolves issues, and improves code quality. Unlike general-purpose AI assistants, Zencoder tailors its suggestions based on your project’s structure, dependencies, and coding patterns, offering contextual solutions specific to your codebase.
Key Features:
- Repo Grokking: Analyzes your entire codebase to understand its structure and logic, allowing Zencoder to offer more relevant, context-aware suggestions.
- Agentic Pipeline: Runs generated code through verification and repair steps, refining solutions until they’re fully optimized for your repo.
- Coding Agent: Provides contextual suggestions based on your code, helping you write and optimize code directly in the IDE.
- Unit Testing Agent: Automatically generates unit test cases based on your implementation, including appropriate mocks and assertions.
- Integrations: Seamlessly integrates with over 20 tools, including Jira, and supports Model Context Protocol (MCP) for better workflow integration.
Hands-on Section:
I prompted Zencoder with: “Generate repo.md file with information from my repo.”
Zencoder began by analyzing the structure of the repository as visible in the snapshot below:
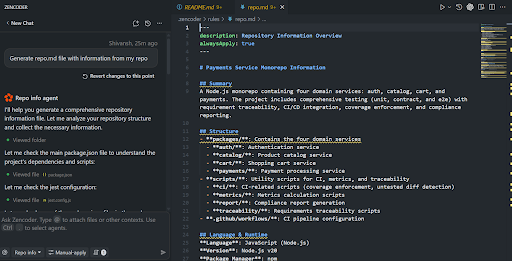
It started by collecting key information from various files to generate a comprehensive repo.md. It began by checking essential files, such as the main package.json for dependencies and scripts, the Jest configuration for testing setups, and other relevant project files.
The tool went step-by-step, analyzing the following:
- Main package.json: Zencoder reviewed the file to understand the project’s dependencies, scripts, and configuration settings.
- Jest Configuration: It examined the Jest configuration to understand the testing framework setup and test-related scripts.
- Other package.json files: It looked into other package.json files in the project, particularly those in the packages directory, to gain insights into sub-package dependencies.
- CI Workflow: Zencoder checked the CI configuration (.github/workflows) to understand the automated pipeline setup for continuous integration.
- requirements.yaml: The tool analyzed the requirements.yaml file to capture the traceability information and ensure that project requirements were linked correctly to tests.
- Package Structure: Zencoder reviewed the structure of one of the packages to understand how the code was organized across the repo.
- Test Structure: Finally, Zencoder checked the test structure to capture how tests were organized (unit, contract, and E2E tests).
Once all necessary information was gathered, Zencoder created a detailed repo.md file with the following content:
- Repository Overview: It provided a summary of the project’s purpose and structure, explaining that it was a Node.js monorepo with four domain services: auth, catalog, cart, and payments.
- Project Structure: Zencoder detailed the directory structure, listing main directories such as packages/, scripts/, and .github/workflows/ with explanations of their contents.
- Dependencies and Dev Dependencies: It included information on both main and development dependencies, such as express, jest, ajv, and pdfkit.
- Build & Installation Instructions: The tool provided simple commands for installing dependencies and running tests.
- Testing: Zencoder included information about the testing framework (Jest), different types of tests (unit, contract, and E2E), and the relevant commands to run them.
- CI/CD Setup: It also captured the CI/CD configuration, highlighting jobs like build-test, pr-guardian, and quarantine for flaky tests.
Zencoder saved the repo.md file to a new directory (.zencoder/rules/repo.md), providing a clear, structured overview of the entire project.
Pricing:
- Free Tier: Includes core features such as Repo Grokking and basic integration with IDEs.
- Pro Plan: Custom pricing for teams and enterprise use, unlocking additional features like the Unit Testing Agent, enhanced integrations, and support for more advanced use cases.
Review: Zencoder has received positive feedback from users on G2, with an average rating of 4.9 out of 5.
7. Amazon Q Developer
Amazon Q Developer is the evolution of Amazon CodeWhisperer, offering enhanced AI-powered coding assistance that is tightly integrated with the AWS ecosystem. This tool empowers developers with intelligent code suggestions, security insights, and seamless IDE compatibility.
Key Features:
- Provides accurate and contextually relevant code completions, reducing development time.
- Identifies vulnerabilities and suggests fixes to enhance the security of your applications.
- Tailors code recommendations to align with your organization’s coding guidelines.
- Compatible with popular IDEs such as Visual Studio, IntelliJ, and VS Code for a smooth development experience.
Hands-on section
I prompted Amazon Q with: “Write a Python boto3 script that lists all S3 buckets and reports if encryption and public access block are enabled, output in table format.”
Amazon Q CLI generated a Python script that interacts with AWS S3 using the boto3 library as shown in the terminal below:
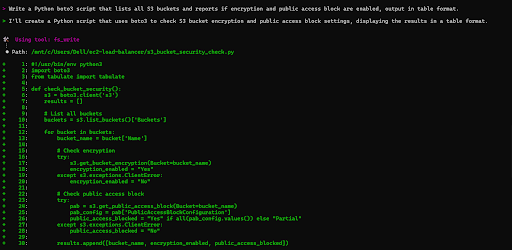
The script follows a simple process: it lists all S3 buckets, checks their encryption and public access block settings, and outputs the results in a table format.
- Listing all S3 Buckets
The script begins by retrieving all the S3 buckets in the AWS account:
buckets = s3.list_buckets()[‘Buckets’]
This command fetches all the bucket names, which are then iterated over to check their configurations.
- Checking Encryption and Public Access Block
For each bucket, the script checks whether encryption and public access block are enabled. If encryption is enabled, it returns “Yes”, otherwise “No”. Similarly, it checks the public access block settings and reports “Yes”, “Partial”, or “No” based on whether the settings are fully, partially, or not configured.
Here’s how it handles encryption and public access block:
try: s3.get_bucket_encryption(Bucket=bucket_name) encryption_enabled = "Yes" except s3.exceptions.ClientError: encryption_enabled = "No" try: pab = s3.get_public_access_block(Bucket=bucket_name) pab_config = pab['PublicAccessBlockConfiguration'] public_access_blocked = "Yes" if all(pab_config.values()) else "Partial" except s3.exceptions.ClientError: public_access_blocked = "No"
Explanation:
- If encryption is configured, it sets encryption_enabled to “Yes”. Otherwise, it handles the exception and sets it to “No”.
- The same logic applies to public access block settings, where it checks if all settings are applied (resulting in “Yes”), some settings are applied (“Partial”), or no settings are applied (“No”).
- Displaying Results in a Table
Finally, the results are displayed in a neat table format using the tabulate library:
print(tabulate(results, headers=["Bucket Name", "Encryption", "Public Access Block"], tablefmt="grid"))
This generates a grid-style table that shows each bucket’s name along with its encryption and public access block status. The script at the end successfully lists all S3 buckets, checks their encryption and public access block settings, and outputs the results in a clear table format.
This Python script allows AWS administrators to quickly audit the security settings of their S3 buckets. The next logical step would be adding error handling for various edge cases and setting up a schedule to run this script regularly using AWS Lambda.
Pricing:
- Free Tier: Includes basic features ideal for individual developers.
- Pro Plan: Advanced functionality for teams, including enhanced security and administrative controls. Pricing details are available on the Amazon Q Developer pricing page.
Review: “Thanks to Amazon Q, we have been able to reduce our time to deploy new features for our products by 25%.” – AWS Website
Quick Comparison Table
Below is a quick comparison of the top GitHub Copilot alternatives, each catering to different developer needs and preferences:
| Tool | Key Features | Languages Supported | IDE Compatibility | Pricing | Best For |
| Qodo Gen | Context-aware code generation, seamless IDE integration, unit test generation | Python, Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, Golang | Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, JetBrains | Free Tier; Paid plans start at $19/user/month | Developers looking for comprehensive, tailored code suggestions and unit testing |
| Tabnine | Contextual code completion, privacy-focused, on-premises option | Python, JavaScript, Go, C++, TypeScript | VS Code, IntelliJ, PyCharm, Sublime Text | Free version; Paid plans start at $9/month | Developers prioritizing privacy and multi-language support |
| Replit Ghostwriter | Real-time code completion, debugging, excellent for pair programming | Python, JavaScript, and more | Replit (online IDE) | Free version; Paid plans start at $15/month | Collaborative development, educational use |
| OpenAI Codex | Local terminal agent, runs directly in repo, model control | Multiple languages | Command-line interface (macOS, Linux, WSL) | Included with ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Team | Developers seeking command-line integration and local editing |
| Sourcegraph Cody | Code search, refactoring, and documentation generation | Rust, Go, Java, Python, TypeScript | VS Code, other Git-integrated IDEs | Free for basic use; Premium plans start at $9/month | Developers working with large codebases, needing documentation and refactoring |
| Zencoder | Repo Grokking, unit test generation, security-focused suggestions | Multiple languages | VS Code, JetBrains, Android Studio | Free version; Custom pricing for Pro plan | Developers looking for project-specific code suggestions, testing, and security insights |
| Amazon Q Developer | Contextual code completions, AWS-specific optimizations, security insights | Python, Java, JavaScript, AWS-specific languages | VS Code, IntelliJ, Visual Studio | Free Tier; Pro plans available | Developers working in the AWS ecosystem with a focus on security and context-aware code generation |
After analyzing the top GitHub Copilot alternatives, the next step is determining the most suitable tool for your specific development needs. As a senior developer, you’re likely to prioritize technical features that improve productivity, enhance code quality, and integrate seamlessly into your existing workflows.
How to Choose the Right GitHub Copilot Alternative
When selecting a GitHub Copilot alternative, looking for tools that cater to your unique development needs is essential. While different alternatives may have varying features, here are specific factors and features to consider when making your decision:
1. Language and Framework Support
- Look for tools that offer multi-language support if you work across different languages.
- Some AI tools provide specialized suggestions for popular frameworks such as React, Django, Flask, or Spring Boot. If you work with a particular framework, prioritize tools that offer deep knowledge and templates for that framework.
- The AI should be aware of syntax nuances in different languages and adapt its suggestions accordingly, which is crucial for writing clean, efficient code.
2. IDE and Editor Integration
- Check whether the AI assistant supports the IDEs and text editors you use.
- The AI should be able to deliver real-time, context-aware suggestions and auto-completions as you type, making the development process faster and more efficient.
- Look for IDEs with tight integration where suggestions are displayed inline within the code editor.
3. Code Quality and Security Features
- Tools with built-in security scanning can help identify vulnerabilities, suggest fixes for common security flaws, and ensure that the generated code adheres to security best practices.
- A solid alternative should provide code analysis and linting features, automatically identifying errors, inefficiencies, or code style issues as you type.
- Some tools go beyond simple suggestions and allow you to interactively review code changes, offer recommendations, and assist with refactoring.
4. Customization and Adaptability
- The tool should learn from your coding patterns and adapt over time. Look for options that offer personalized suggestions based on your past work and preferred coding style.
- In a team environment, it’s important to customize the AI’s suggestions to align with your team’s coding standards. This may include enforcing specific naming conventions, documentation styles, or architectural patterns.
- Some alternatives allow you to define reusable code snippets, templates, or boilerplate code for your team, which can streamline project setups and coding consistency.
5. Collaboration and Team Features
- The tool should support team workflows, allowing multiple developers to access shared suggestions, notes, or comments in real time.
- Look for integrations with Git or other version control systems, enabling the assistant to understand the history and context of the project. This helps provide suggestions that are relevant to the current stage of development.
- A collaborative tool should allow team members to share code snippets, provide feedback, and review each other’s work, improving the overall development process.
6. Cost and Licensing Flexibility
- If you’re an individual developer or just starting, look for free-tier options that provide enough functionality for small-scale development without requiring an upfront investment.
- If you’re part of a larger team, ensure that the tool offers flexible pricing plans that scale with the number of users. Enterprise-level plans often come with additional support, collaboration features, and administrative controls.
Conclusion
Choosing the right GitHub Copilot alternative ultimately depends on your specific needs as a developer or a team. Whether you prioritize language support, IDE integration, security features, or customization, there are several alternatives available that offer unique strengths and capabilities. By focusing on key factors such as compatibility, code quality, pricing, and performance, you can ensure that the tool you select will enhance your productivity, streamline your development processes, and maintain the quality of your code.
FAQs
1. What is the best GitHub Copilot alternative?
The “best” GitHub Copilot alternative depends on your specific needs. Tools like Tabnine and Amazon Q Developer are great for broad language support and real-time code suggestions. If you prioritize customization and team collaboration, Qodo offers excellent options for developers working in a team-oriented environment. Codex could be a solid free option with strong language support. Ultimately, it’s important to assess your development workflow and feature requirements when choosing the best alternative.
2. Which programming languages do these AI coding assistants support?
AI coding assistants support a wide range of programming languages, including but not limited to:
- Qodo covers languages including JavaScript, Python, Java, and TypeScript.
- Tabnine supports languages like Python, JavaScript, Java, Go, C++, and TypeScript.
- Amazon Q Developer provides strong support for AWS-specific languages and frameworks, along with other popular programming languages such as Python, Java, and JavaScript.
Most Copilot alternatives offer support for the most common languages in modern development, but it’s important to confirm that your preferred language is covered by the tool you choose.
3. Will these tools integrate seamlessly with popular IDEs?
Yes, most GitHub Copilot alternatives integrate with popular IDEs like Visual Studio Code, JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, and Sublime Text. Integration varies by tool, but most provide easy-to-install plugins or extensions that allow for smooth real-time coding suggestions within your preferred IDE. Some tools like Tabnine and Qodo offer broader IDE compatibility, ensuring seamless integration into diverse workflows.
4. How do these AI assistants ensure code security and privacy?
AI coding assistants generally follow industry-standard security protocols to ensure the privacy and integrity of your code. Here’s how they approach security:
- Data encryption: Most tools encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information.
- Local processing: Some assistants, like Tabnine, offer local processing options, ensuring your code doesn’t leave your machine and reducing potential security risks.
- Privacy policies: Many tools, such as Amazon Q Developer, comply with privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR) and restrict data sharing with third parties.
- On-premises deployment: For enterprise users, options like Tabnine and Codeium offer on-premises deployments, ensuring complete control over data and code.