20 Best AI Coding Assistant Tools [Updated Aug 2025]
AI coding assistants don’t replace developers but can significantly enhance their capabilities and efficiency. They can help with small and simple tasks from debugging and code formatting to more complex and sophisticated tasks like AI powered code review, suggesting architectural improvements or automating comprehensive test coverage. The most powerful assistants are those that understand your codebase, coding standards, and compliance requirements, making their recommendations truly context-aware.
The future of AI coding assistants is in multi-agent systems: specialized agents that communicate with each other, each handling distinct tasks under safe guardrails. Imagine one agent generating code, another performing reviews, a third creating documentation, and yet another ensuring tests are thorough. You go to sleep, and by morning, a significant portion of your workflow has already been completed, ready for your review.
It sounds amazing, but as a developer myself, I sometimes find it hard to navigate the world of AI with new tools coming out every week. Are they good? Are they secure? Are they going to help or create technical debt? And what about the code quality? To save you some time (a lot of time 😉 ) I have created this list of AI code assistants that I’ve tried and tested myself.
Best AI Coding Assistant Tools (Updated – August 2025)
How I Selected the Best AI Coding Tools in this List
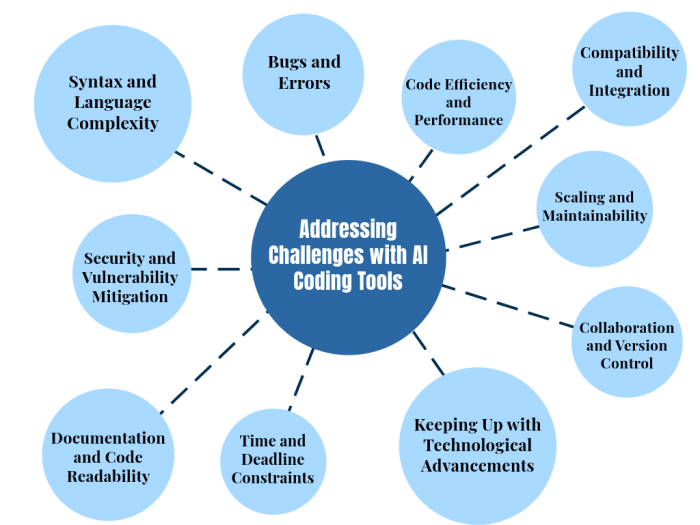
As a developer, I’ve explored many AI-assisted coding tools over the years, but not all of them make the cut. To ensure this list includes only the best AI for coding, I evaluated each AI code helper based on how effectively it addresses common challenges faced by developers. Here are the 10 things I considered:
- Syntax and language complexity: Navigating the intricate syntax of programming languages can be challenging, especially when trying out a new language. I’ve often struggled with minor errors like missing brackets or misplaced semicolons. The best AI tools in this list excel at offering real-time syntax suggestions and corrections, making coding faster and less frustrating.
- Debugging and error resolution: Debugging is a critical but time-consuming part of coding. Tools that made it to this list stood out for their ability to identify bugs in real time, analyze code behavior, and even suggest actionable fixes-saving hours of trial and error.
- Code efficiency and optimization: Writing efficient and clean code is a constant challenge, especially when considering algorithm complexity or resource constraints. I prioritized tools that assist with code refactoring, performance optimization, and alternative implementation suggestions.
- Seamless integration and compatibility: Compatibility issues often arise when integrating APIs or components into a project. The tools here shine in helping developers identify compatible libraries and APIs, streamlining the integration process.
- Scalability and maintainability: For growing projects, managing and scaling codebases can be daunting. The tools I’ve selected analyze existing codebases and recommend refactoring strategies, ensuring long-term maintainability and scalability.
- Collaboration and version control: Team projects often come with challenges like resolving merge conflicts and managing multiple contributors. Tools that integrate well with version control systems and enhance collaboration earned their place in this list.
- Meeting deadlines without compromising quality: Balancing speed and quality under tight deadlines is always stressful. The tools I’ve included excel at automating repetitive tasks, providing intelligent suggestions, and helping developers meet deadlines without sacrificing quality.
- Adapting to rapid technological advancements: The tech landscape evolves rapidly, with new frameworks, libraries, and techniques emerging constantly. I selected tools that act as learning companions, offering up-to-date documentation, examples, and tutorials on demand.
- Improving documentation and readability: Well-documented, readable code is essential for collaboration and future maintenance. The tools here help developers create better documentation through comment suggestions, templates, and intuitive naming conventions.
- Security and vulnerability mitigation: Security is paramount in software development. The tools I’ve chosen excel at identifying vulnerabilities and promoting secure coding practices, ensuring peace of mind for developers.
By focusing on how these tools address real-world challenges, I’ve narrowed the selection to the 15 Best AI Coding Assistant Tools that truly stand out for developers in 2025. Let’s dive in!
20 Best AI Coding Tools
1. Qodo
Qodo is an AI-powered code quality platform that helps teams ship reliable, compliant, and production-ready code fast. Instead of focusing solely on code generation, Qodo prioritizes agentic code review, test coverage, and code integrity at scale. It integrates directly into VS Code, JetBrains, the terminal, and CI pipelines, providing end-to-end visibility and control across the SDLC.
Its specialized agents – Qodo Merge, Qodo Gen, and Qodo Aware – collaborate through a shared codebase intelligence layer, ensuring every AI suggestion aligns with your organization’s standards and architecture.
Pros of Qodo
- Full SDLC coverage: Qodo includes purpose-built agents Gen for generating code and tests, Cover for improving test coverage, and Merge for PR summaries, risk diffing, and automated code review.
- Precise, context-aware suggestions Provides tailored suggestions, including docstrings, exception handling, and best practices, directly enhancing code quality. Helps developers maintain cleaner, more maintainable code.
- Context-aware: Powered by a RAG-based intelligence engine (Qodo Aware), it understands your codebase, conventions, and dependencies to provide precise, relevant suggestions.
- Code explanation: Breaks down source code or snippets with detailed descriptions. Includes insights and sample usage scenarios, improving code comprehension for both junior and senior developers.
- Automated test generation: Saves time and effort by generating accurate and reliable unit tests. Simplifies testing, especially for large and complex codebases.
- Code behavior coverage: Ensures thorough testing by covering all possible code behaviors. Generates test cases and applies related changes seamlessly to source code.
- Streamlined collaboration: Facilitates teamwork through Git integration, enabling code sharing and reviews. Promotes efficient workflows and overall code quality.
- Seamless implementation: Intelligent auto-completion agent integrates with task plans, simplifying the coding process from start to finish.
- Multiple language and IDE Support: Supports popular programming languages like Python, JavaScript, and TypeScript. Compatible with leading IDEs, including VSCode, WebStorm, IntelliJ IDEA, CLion, PyCharm, and JetBrains.
- Pull request review (Qodo Merge PR-Agent): The Qodo Merge Chrome extension enhances pull request management with AI-driven feedback and suggestions, reducing review time.
- Enterprise-grade readiness: SOC 2–compliant, supporting on-prem, SaaS, and air-gapped deployments with granular control over AI usage, governance, and compliance.
Cons of Qodo
- Premium paid features: Access to advanced features like SOC2 compliance and static code analysis within Qodo Merge Pro requires a paid plan. This may present a barrier for smaller teams or individual developers.
My Experience with Qodo:
I ran Qodo on a pull request against the GrapesJS repository, a large open-source web builder that deals heavily with dynamic HTML templates, external assets, and client-side rendering. This is exactly the kind of codebase where subtle security and quality issues tend to hide: HTML generation, CDN usage, long-running browser sessions, and user-supplied content.
Instead of leaving scattered inline comments, Qodo posted a single PR Compliance Guide as a structured comment on the pull request, as shown in the snapshot below:
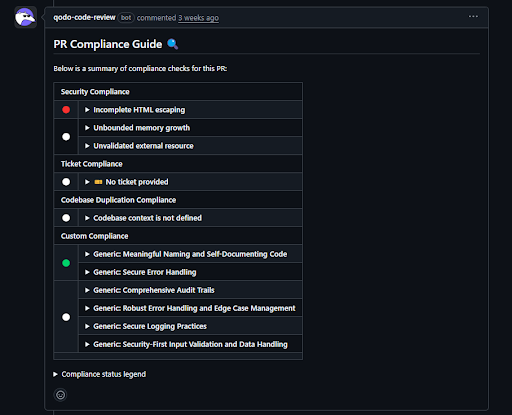
The framing is immediately different from that of typical AI reviewers. It’s not trying to “review code” line by line. It’s answering a higher-level question: is this change compliant with the standards we expect before it merges?
At the top of the comment, Qodo summarizes the PR across multiple compliance dimensions. Under Security Compliance, it flags incomplete HTML escaping as a failed check, as shown in the snapshot below:
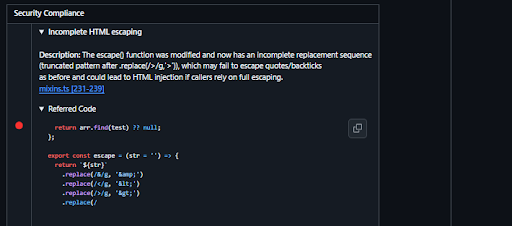
In the context of GrapesJS, this is a meaningful signal; the project renders HTML templates dynamically, and incomplete escaping is a real XSS risk, not a theoretical one. It also lists checks like unbounded memory growth and unvalidated external resources as unresolved rather than failed, which is an important distinction. Qodo isn’t asserting certainty where it doesn’t have enough context; it’s explicitly surfacing unknowns.
The next signal is Ticket Compliance, where Qodo flags that no ticket or issue is linked to the PR. This isn’t about code correctness at all; it’s a process check. The tool is enforcing traceability: every change should be tied back to some requirement or issue. For teams that care about audits, regressions, or accountability, this is exactly the kind of thing that usually slips through manual review.
Qodo then reports that codebase duplication compliance couldn’t be evaluated because the broader codebase context wasn’t defined. Again, this is notable not for what it catches, but for what it refuses to guess. Instead of quietly skipping the check or producing a low-confidence result, Qodo makes the lack of context explicit. That’s a recurring pattern in this output: it’s conservative about what it claims.
The final section covers custom compliance rules, things like secure error handling, audit trails, logging practices, edge-case handling, and security-first input validation. Some of these checks pass, others remain unresolved. What stands out is that these are not stylistic preferences or generic best practices. They’re policy-level expectations that teams usually document somewhere but rarely enforce consistently at PR time.
Taken together, the experience feels less like “AI code review” and more like an automated quality gate. Qodo isn’t trying to explain the code to you or suggest refactors. It’s surfacing risks, gaps, and missing process signals early, while the cost of fixing them is still low.
The trade-off is clear. Qodo needs upfront configuration and context to be most effective, and it won’t walk you through fixes inline. But that appears intentional. It’s designed to sit between fast AI-assisted coding and production readiness, catching the kinds of issues that usually only show up later in security reviews, audits, or incidents.
In a codebase like GrapesJS, where HTML rendering and external assets are core concerns, the signals Qodo surfaced are exactly the ones you’d want to see before a merge, not after a release.
Qodo’s pricing
- Developer (Free): 250 credits; code generation, reviews, autocomplete, docs, test creation; community support.
- Teams ($30/user/month, $38 monthly): 2,500 credits; PR descriptions, ticket compliance, best-practice learning; standard support, optional SSO.
- Enterprise (Custom): Full platform access; enterprise dashboard, SSO, flexible deployments (SaaS, on-prem, air-gapped); priority support.
Expert Summary:
Free is generous for individuals. Teams offers the best balance of features and cost. Enterprise suits organizations with strict security and deployment needs.
2. GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot is a tool widely used by developers to autocomplete code, making it an essential addition to my toolkit. Its ability to streamline the coding process and enhance productivity is why I’ve included it in this list. The generative AI model powering GitHub Copilot is the result of a groundbreaking collaboration between GitHub, OpenAI, and Microsoft. This partnership has truly revolutionized the coding experience by combining the power of AI and machine learning.
Pros of GitHub Copilot
- Code suggestions: GitHub Copilot provides code suggestions, completing lines or entire functions based on comments in your file.
- Chat functionality: It features a chatbot within the developer’s environment, allowing for questions, suggestions, debugging, and natural language queries.
- Easy auto-complete navigation: Cycle through multiple auto-complete suggestions with ease, allowing them to explore different options and select the most suitable suggestion for their code.
- Multiple language and IDE support: The tool seamlessly integrates with popular IDEs like Visual Studio, Neovim, Visual Studio Code, and JetBrains, supporting various programming languages, including TypeScript, Golang, Python, and JavaScript.
Cons of GitHub Copilot
- Code duplication: Since GitHub Copilot generates code based on learned patterns, it may inadvertently produce similar or identical code segments, leading to code duplication across projects.
- Inefficient code generation: At times, the tool may generate incorrect or inefficient code, posing challenges, particularly for less experienced developers who might struggle to identify and rectify errors.
- Limited test case generation: For larger codebases, maintaining test coverage is crucial. GitHub Copilot may lack the capability to generate an adequate number of test cases, making it harder to identify and debug issues and ensuring overall code quality.
- Paid features: Advanced features like GitHub Codespaces access and assigning multiple users or teams for pull request reviews are available only in the paid Team plan. This limits access to premium collaboration tools for individual developers or small teams on free plans.
My Experience with Github Copilot
In this example, GitHub Copilot is used inside Visual Studio Code to scaffold a Terraform configuration for a Google Cloud Storage bucket.
I opened a main.tf file and prompted: “create me Terraform config with a Google Cloud Storage bucket with versioning enabled and named as logs”
Copilot generated a working configuration that covers all the basics:
- Declares the Google provider and parameterizes the project_id and region.
- Defines a google_storage_bucket resource named logs.
- Enables object versioning through the versioning block.
- Adds variable blocks for project_id and region so the configuration isn’t tied to a single environment.
As shown in the snapshot below, the resulting file looked like this:
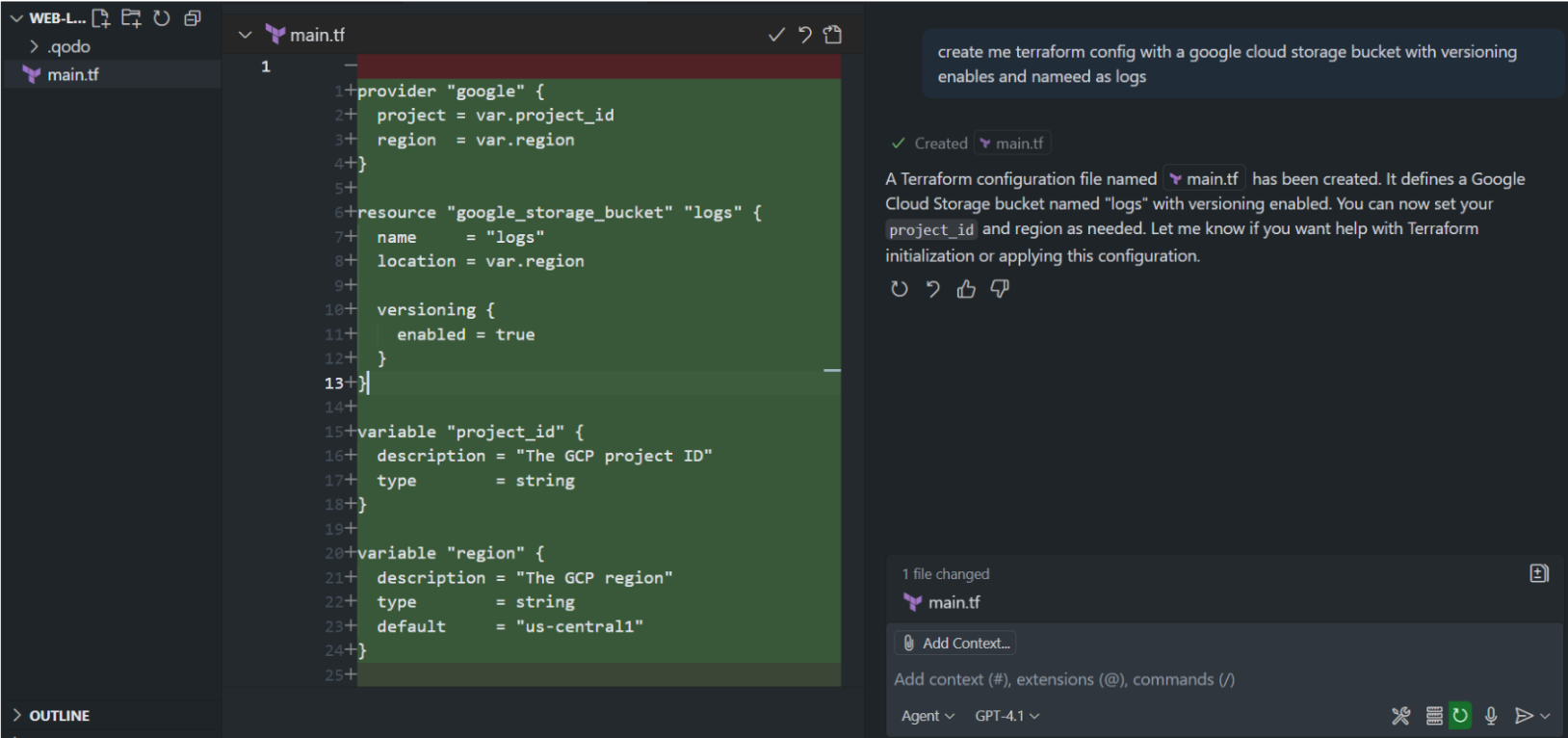
This configuration can be applied right away. The only step before running terraform init and terraform apply is to provide your project_id (and optionally override the region). This output is syntactically valid and can be applied as-is after supplying the required variable values.
Github Copilot’s Pricing:
- Free: $0 per user/month; basics for individuals and organizations.
- Team ($4/user/month): Adds advanced collaboration features.
- Enterprise (from $21/user/month): Security, compliance, and flexible deployment options.
Expert Summary:
Free works for casual or exploratory use. Pro is the best value for individuals, Pro+ is suited for heavy users, and Enterprise is designed for organizations with strict security and compliance requirements.
3. Tabnine
The reason I’m including Tabnine in this list is because of its incredible features that enhance the coding experience. With intelligent code completion, error detection and fixes, refactoring assistance, and automatic code documentation, Tabnine empowers you to write efficient, clean, and high-quality code.
Pros of Tabnine
- Code refactoring assistance: Tabnine offers excellent guidance and suggestions to help refactor code effectively, improving readability, efficiency, and maintainability.
- Code linting: Its code linting feature has been a lifesaver, identifying potential issues and suggesting fixes to ensure my code is error-free and polished.
- Automatic code documentation: One of my favorite features is how Tabnine automatically generates code documentation. This makes collaboration easier and ensures everyone on my team understands the codebase.
- Intelligent code completions: Tabnine leverages an extensive dataset of open-source code to provide me with intelligent and contextually relevant code completions, saving time and reducing errors.
- Privacy and security: The enterprise version ensures that your code remains on your local server, offering complete privacy and security.
- Customization: Can be tailored to match specific coding styles and project requirements.
Cons of Tabnine
- Limited features in free version: The free version is limited to essential code completion and lacks advanced features available in paid versions.
- Less intuitive suggestions for beginners: Since it doesn’t pull from public repositories, its suggestions may be less intuitive for beginners or those working with unfamiliar programming languages.
My Experience with Tabnine
My experience with Tabnine has been very positive, as it can assist with various coding tasks, such as generating tests, fixing code, and providing intelligent code suggestions, which significantly enhances my productivity and the quality of my code.
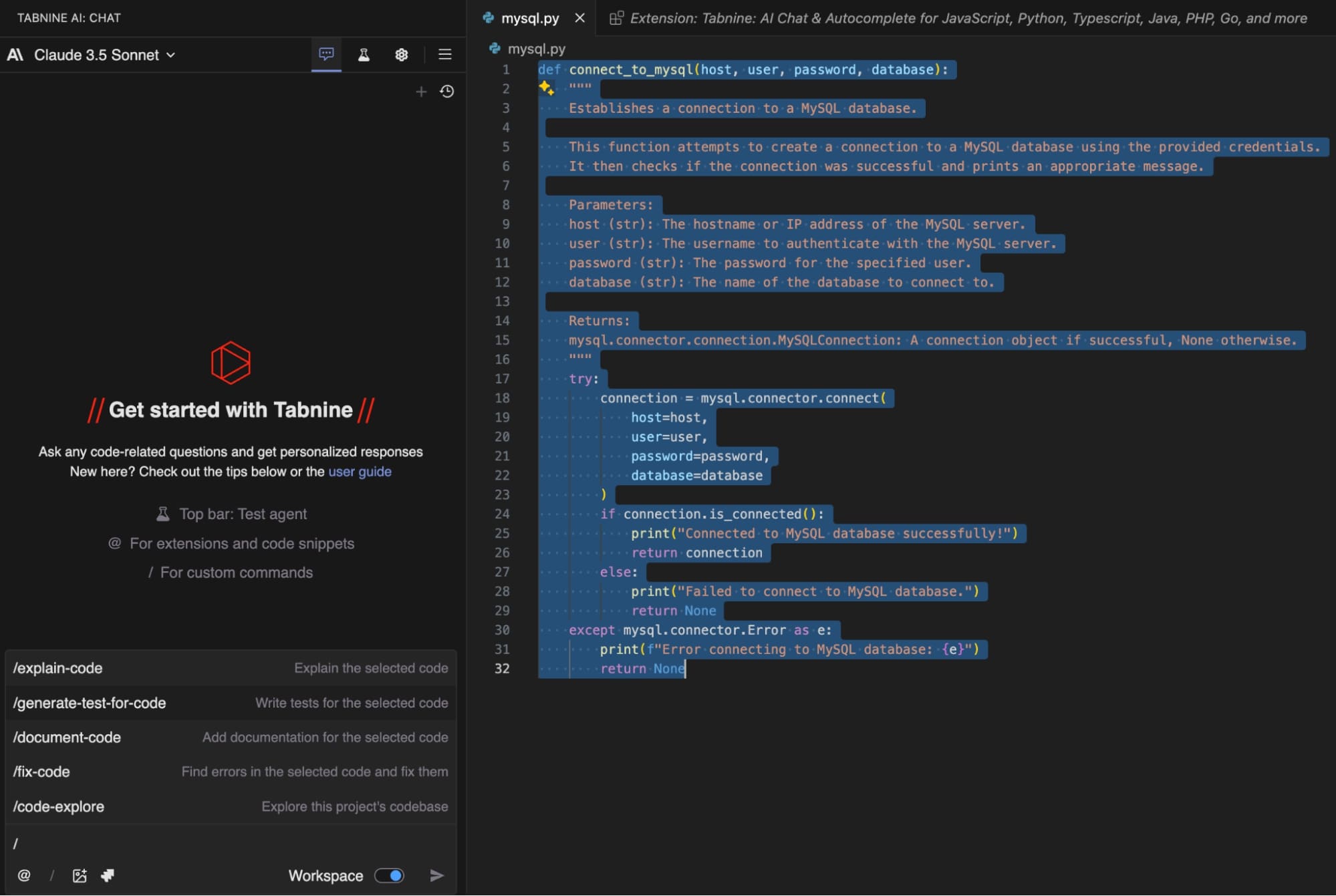
I had some initial code that established a connection to a MySQL database. I then used Tabnine to improve it by using its “document code” command. Tabnine suggested several enhancements, including the creation of a reusable function that encapsulates the core logic for establishing database connections and adds clear documentation. This not only made the code more readable and maintainable but also improved its overall structure and reusability.
Tabnine’s Pricing:
- Free ($0/user/month): Basic AI code completions.
- Dev ($9/user/month): Adds AI chat, contextual code generation, test and documentation creation, and Jira integration.
- Enterprise ($39/user/month): Advanced security, deployment options (on-prem/air-gapped), and customizable validation rules.
Expert Summary:
The Free plan suits individual developers, the Dev plan is a practical upgrade for daily coding, and the Enterprise plan is tailored for organizations with stricter security and deployment needs.
4. Bolt
Bolt is a browser-native, AI-powered coding tool built on StackBlitz WebContainers. It allows you to describe full-stack apps in plain English and instantly generates, runs, and deploys them all within the browser, with no local tooling required.
Pros
- Full-browser execution: Handles installs, terminal commands, code editing, and even deployments entirely in the browser, with zero local setup needed.
- Prompt-to-app generation: Accepts natural language input to scaffold frontend components, backend endpoints, and project structure.
- Integrated services: Offers built-in support for Netlify deployments, Supabase backend setup, Stripe integration, and GitHub collaboration.
- Optimized for prototyping: Ideal for quickly validating product ideas, spinning up MVPs, or teaching app architecture in a live environment.
Cons
- Editor lock-in: Only works inside the Bolt interface, with no support for external IDEs like VS Code or JetBrains.
- Not for production-scale code: Designed for demos and small apps; lacks the performance and structure needed for large monorepos.
- Beta-stage product: Still maturing; occasional prompt misfires or UI quirks may occur during complex interactions.
My Experience with Bolt:
I explored Bolt by building a basic version of a session-tracking app called FocusFlow. The goal was to log work blocks, categorize tasks, and store session data for later review. Bolt handled the initial setup by generating the project structure, installing dependencies, and scaffolding components like TaskForm.tsx and Timer.tsx.
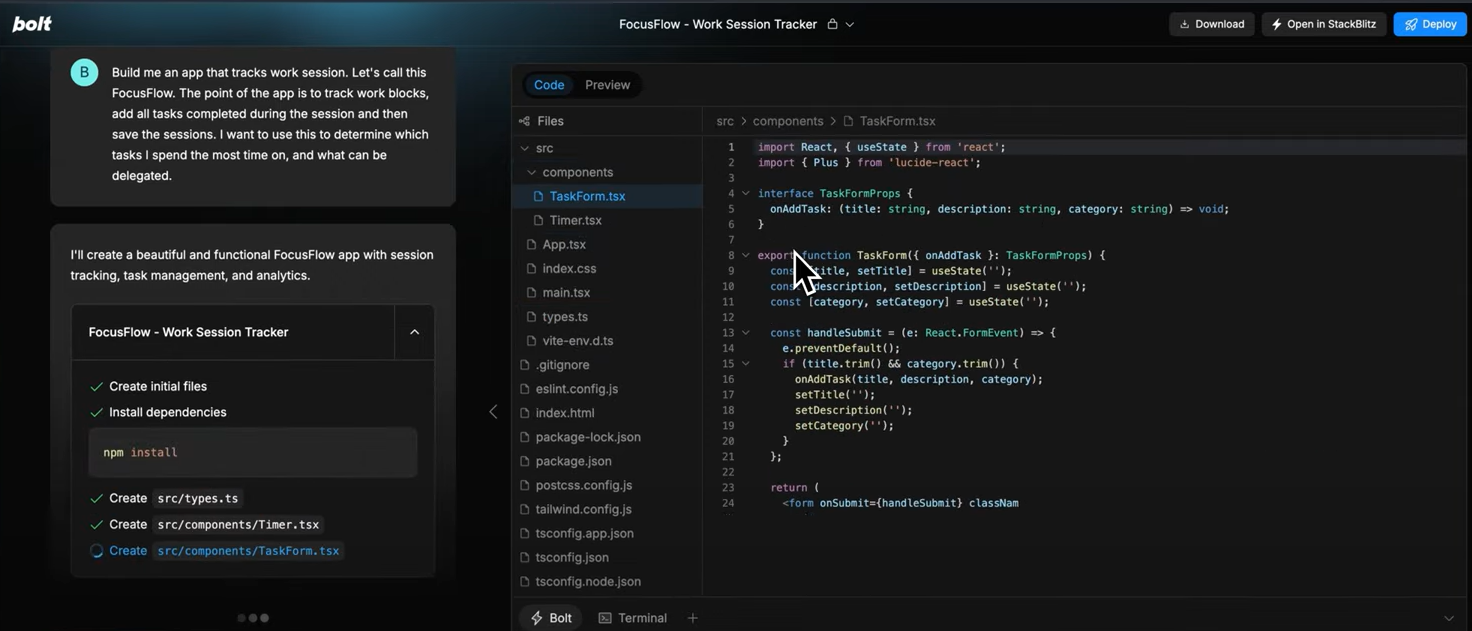
The prompt-driven workflow was efficient for quickly getting from concept to code. For example, the TaskForm.tsx component was generated with typed props, controlled input fields, and basic form validation logic. This helped reduce the usual boilerplate effort involved in setting up React + TypeScript projects. One observation: while the tool was useful for getting started, the quality and structure of the output were heavily influenced by how specific the prompt was. In some cases, I needed to manually adjust or extend the generated logic to align with my intended app behavior, especially around state management and UI flow. Overall, Bolt was useful for prototyping and bootstrapping, but I still needed to review and refine the generated code to meet production standards.
Bolt’s Pricing
- Free – $0
- Pro – $25/month
- Teams – $30 per member/month (billed monthly)
- Enterprise – Custom (quote)
Expert Summary:
Free suits basic individual use within daily/monthly token limits. Pro removes daily caps and adds higher monthly tokens and branding/domain features for regular usage. Teams adds management and admin controls for collaborative work. Enterprise targets organizations needing security, governance, support, and custom integrations at scale.
5. Amazon Q Developer
Amazon Q Developer is an AI coding assistant available in both CLI and IDEs (including VS Code). It focuses on AWS-native architectures, supporting automated code edits, testing, and security scans while respecting your organization’s IAM and access controls.
Pros
- Full IDE support: Integrates with VS Code, providing inline chat, multi-file edits, and step-by-step task execution.
- Agentic task handling: Executes bash commands, generates diffs, writes files, and interacts directly with AWS APIs.
- Security-first design: Respects AWS IAM roles and ensures code output remains customer-owned.
- MCP collaboration: Can process external artifacts and pull context from connected systems during execution.
Cons
- AWS-centric: Best suited for AWS stacks; less effective for cross-platform or non-AWS-heavy workflows.
- Mixed feedback: Some users report outputs are underwhelming when used outside AWS-specific contexts.
My Experience with Amazon Q:
I asked it to create a GitHub webhook listener from the ground up using its agentic workflow in Visual Studio Code.
I prompted Q to create a FastAPI microservice that listens to GitHub push events, validates the X-Hub-Signature-256 header using a shared secret, and logs the branch and commit message. Q parsed the request and immediately began writing files to my local workspace:
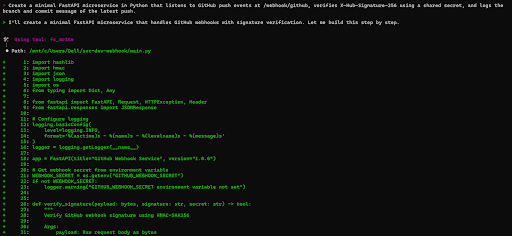
The generated main.py file implements a secure webhook endpoint at /webhook/github with HMAC-SHA256 signature verification using the X-Hub-Signature-256 header and hmac.compare_digest() to prevent timing attacks. It parses incoming push events to log the repository, branch, commit ID, author, and commit message, and exposes a /health endpoint for monitoring. Q also produced a .env example file for environment configuration (GITHUB_WEBHOOK_SECRET, PORT) and a requirements.txt with all dependencies (fastapi, uvicorn). The autogenerated README walks through setup, environment variables, webhook configuration in GitHub, and explains the microservice’s security controls and log format.
Amazon Q’s Pricing
- Free Tier ($0/user/month)
- Pro Tier ($19/user/month)
Expert Summary:
The Free tier offers essential development assistance with moderate usage limits, making it suitable for individual experimentation. The Pro tier expands those limits and adds organizational controls, customization, and legal protections, well-suited for teams or developers needing higher usage and governance support.
6. AskCodi
AskCodi made it to this list because it’s a practical and reliable AI coding assistant that simplifies the coding process. It’s a tool I’ve found helpful for both speeding up workflows and tackling coding challenges. AskCodi stands out for its versatility and ease of use. It’s not just about generating code it supports learning, debugging, and writing better code with minimal effort, all while integrating seamlessly into popular development environments.
Pros of AskCodi
- Code generation: AskCodi can generate code in several programming languages, including Python, Java, TypeScript, Rust, Ruby, Kotlin, and more.
- Answering programming questions: It answers coding-related queries in natural language, making it easier to understand new concepts or troubleshoot problems.
- Code suggestions: It analyzes your code and provides suggestions to improve or fix it, helping to avoid mistakes and save time.
- IDE integration: With support for IDEs like Visual Studio Code, PyCharm, and IntelliJ IDEA, you can use it directly within your development environment.
Cons of AskCodi
- Question structure: Structuring questions effectively can be difficult, potentially leading to inaccurate or incomplete results.
- Reliance on open-source code: The tool’s reliance on open-source code for training may limit its ability to address all use cases or scenarios.
- Paid plan: The monthly subscription required for full access to features might be costly for some users.
If you’re a developer looking for a practical tool to enhance your coding process, AskCodi is worth checking out.
My Experience with AskCodi
I used AskCodi primarily for its code suggestion feature, and it has been a great companion in refining my work. The tool analyzes my code and offers insightful recommendations to improve the structure, fix potential issues, and even optimize performance. It’s like having an extra pair of expert eyes on my code, saving me time and helping me catch mistakes early. That said, I’ve noticed that framing the right questions can be a bit tricky. If the query isn’t structured clearly, the suggestions or explanations can sometimes miss the mark. While this hasn’t been a dealbreaker for me, it’s a reminder to be precise when using natural language queries to get the most out of the tool.
AskCodi’s Pricing
- Premium – $149.99/year
- Ultimate – $349.99/year
Expert Summary:
Premium is positioned for individual professionals who need steady monthly credits and core integrations. Ultimate is aimed at teams or power users requiring more credits, broader model access, and additional code spaces for larger workflows.
7. Warp
Warp is a modern Rust-based terminal designed to improve developer productivity with an AI-powered agent, block-based UI, and collaborative workflows. Unlike traditional terminals, Warp treats commands and outputs as structured “Blocks,” integrates AI for command suggestions, and allows teams to share reusable workflows using Warp Drive.
Pros of Warp
- AI-powered commands: Natural language prompts are converted into accurate, context-aware shell commands.
- Block-based interface: Groups inputs and outputs into clean, editable, and shareable blocks.
- Warp Drive workflows: Save, parameterize, and share terminal workflows across teams.
- Cross-platform support: Built in Rust, optimized for macOS, Linux, and Windows.
Cons of Warp
- Learning curve: Adapting to the blocks-based UI can feel unfamiliar at first.
- Windows version still maturing: Occasional platform inconsistencies compared to macOS.
- AI usage limits: Free plan restricts AI requests; heavy users may need a paid plan.
- Higher resource usage: Requires more memory than lightweight terminals like iTerm or Alacritty.
My experience with Warp:
I asked Warp’s AI agent to scaffold and build a small C++ concurrency demo from the terminal.
As shown in the snapshot below, the prompt is: “Implement a thread-safe bounded queue in C++ using condition variables? It should support multiple producers and consumers without race conditions.”
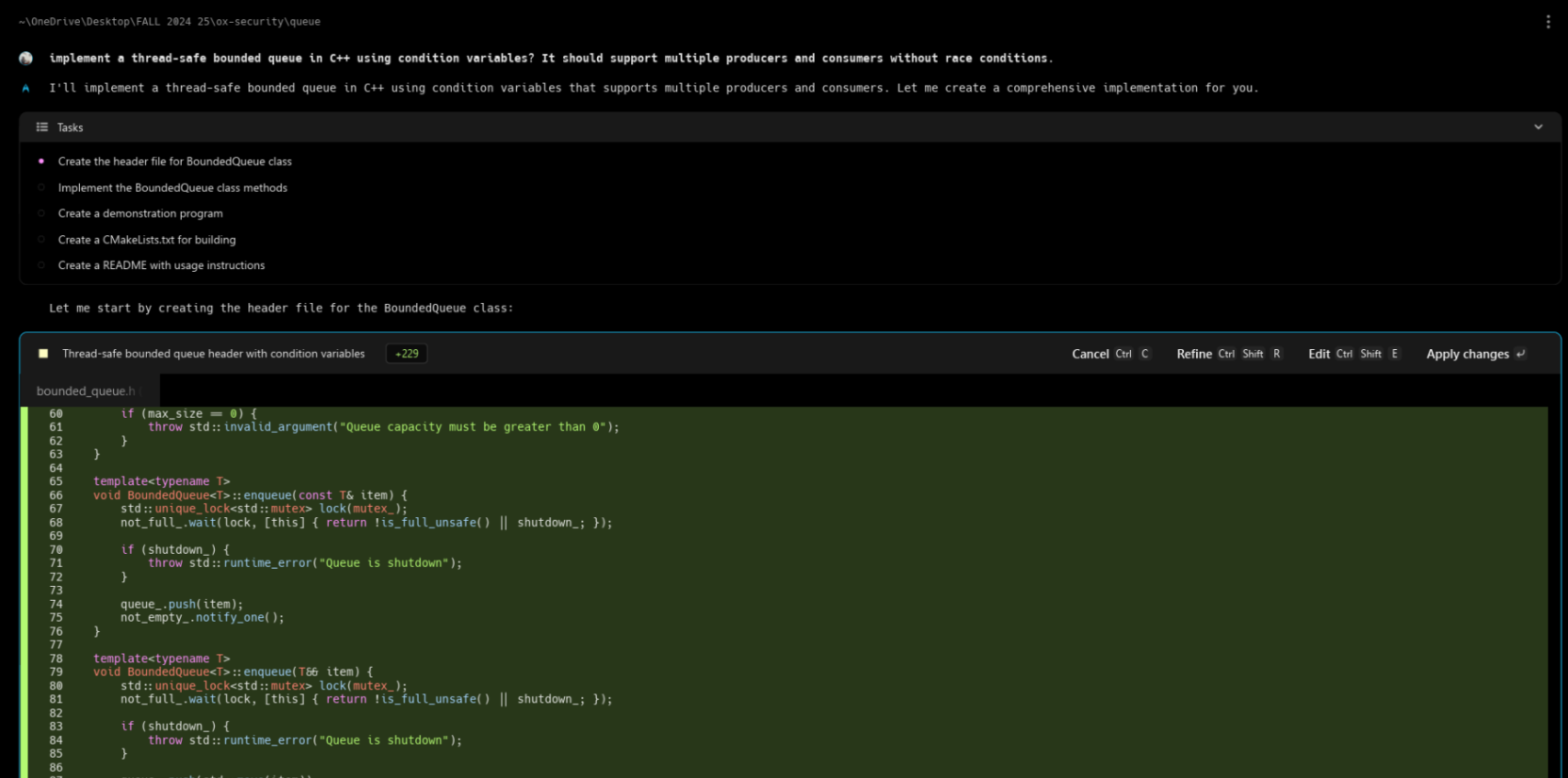
Warp parsed the intent and proposed a task plan in the terminal, then generated files directly in my working directory. The snapshot above also shows the task list and the newly created bounded_queue.h with a templated BoundedQueue<T> using one std::mutex and two std::condition_variables (cv_not_full_, cv_not_empty_) for multi-producer / multi-consumer coordination.
Warp’s Pricing
- Free – Core features, AI suggestions, and Warp Drive included.
- Pro – ~$15/month per user; higher AI quotas and priority support.
- Business – ~$55/month per user; adds admin controls and zero-data retention.
Expert summary:
The Free plan works well for individual developers experimenting with core terminal features, AI suggestions, and Warp Drive workflows. Pro is designed for power users or small teams, offering higher AI quotas, advanced features, and priority support. Business adds collaboration management, admin controls, and zero-data retention, making it suitable for enterprises that require stronger security, compliance, and centralized governance.
8. Replit
Replit is a coding platform that combines AI-powered assistance with an interactive development environment. I included it in this list for its balance of coding support and learning features that help developers write and understand code better.
Pros of Replit
- Advanced in-line suggestions: The real-time code suggestions help speed up the coding process and maintain consistent code quality
- Code explanation and comments: It breaks down code snippets with clear explanations and helps generate meaningful comments for better documentation
- Mistake detection and correction: Identifies coding errors and provides guidance for fixes, improving code accuracy
- Interactive learning environment: Offers an environment where you can learn while coding, making it valuable for both new and experienced developers
Cons of Replit
- Language limitations: While Replit supports various programming languages, it may have limited compatibility with certain niche languages.
- Dependency on internet connection: As an online tool, Replit requires a stable internet connection, which can be a drawback in offline scenarios.
My Experience with Replit
I asked Replit’s AI assistant to create a React + Tailwind-based chat UI for an AI assistant, complete with modular components and light/dark mode support.
Prompt:
“Create a simple React + Tailwind UI for an AI assistant with a centered chat window, scrollable messages, a text input box with a Send button, and mocked assistant responses. Keep components modular and add a theme toggle.”
Replit’s AI generated a task plan and scaffolded the project automatically. It created a clean file structure with separate ChatWindow, Message, and InputBar components, ensuring maintainable, modular code.
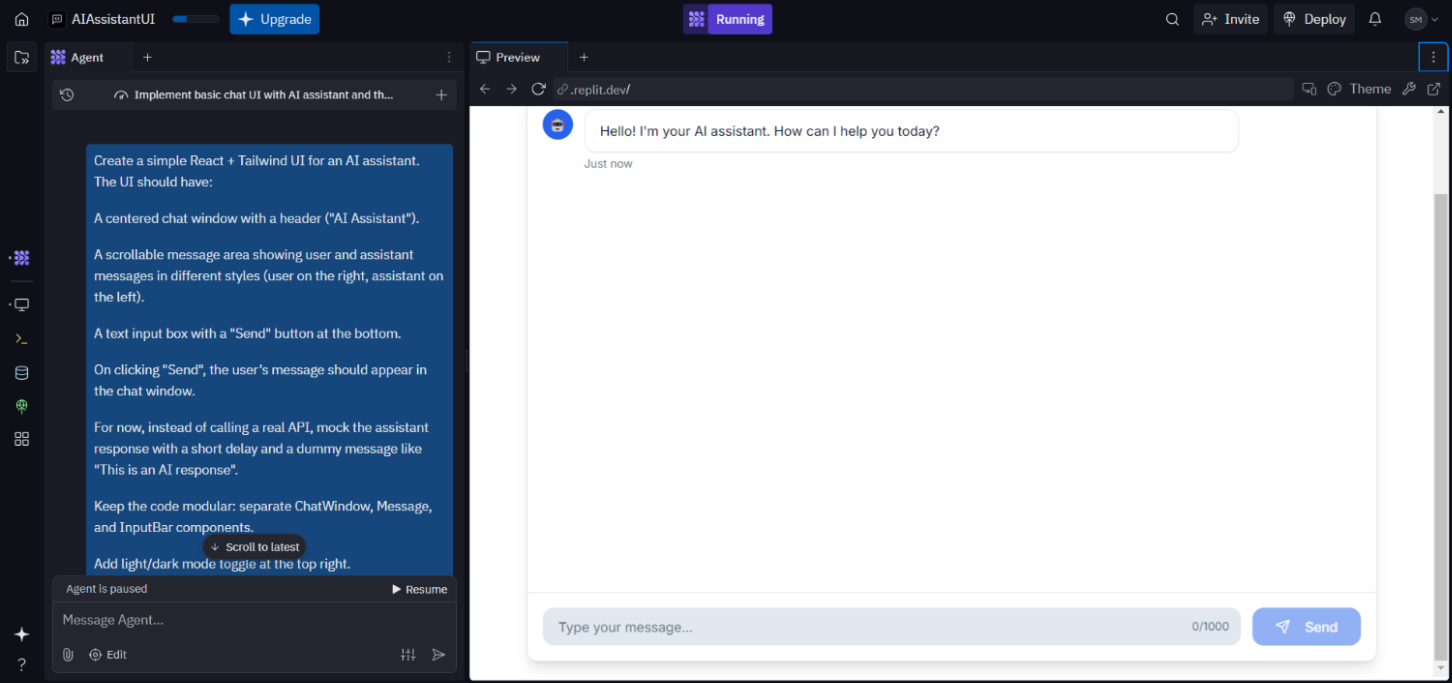
The above-generated UI includes:
- A centered chat window with a fixed header titled “AI Assistant”.
- A scrollable message area, styling user messages on the right and assistant responses on the left.
- A text input box with a functional Send button at the bottom.
- Mocked assistant responses triggered after a short delay, simulating real-time interaction.
- A light/dark mode toggle implemented with Tailwind classes and persisted via state.
Replit’s preview panel instantly reflected changes, and the mocked assistant generated responses like “This is an AI response” to validate message flow. The generated code was modular, readable, and easy to extend for API integration later.
Replit’s Pricing:
- Starter – Free
- Replit Agent trial included
- 10 development apps with temporary links
- Replit Core – $20/month (billed annually)
- Teams – $35/user/month (billed annually)
- Enterprise – Custom pricing
Expert Summary:
The Free plan works for experimenting with public projects. Core is designed for individuals building and deploying serious apps. Teams adds collaboration, management, and private deployments for group projects, while Enterprise is aimed at larger organizations needing security, compliance, and dedicated support.
9. Qwen3‑Coder (Unsloth)
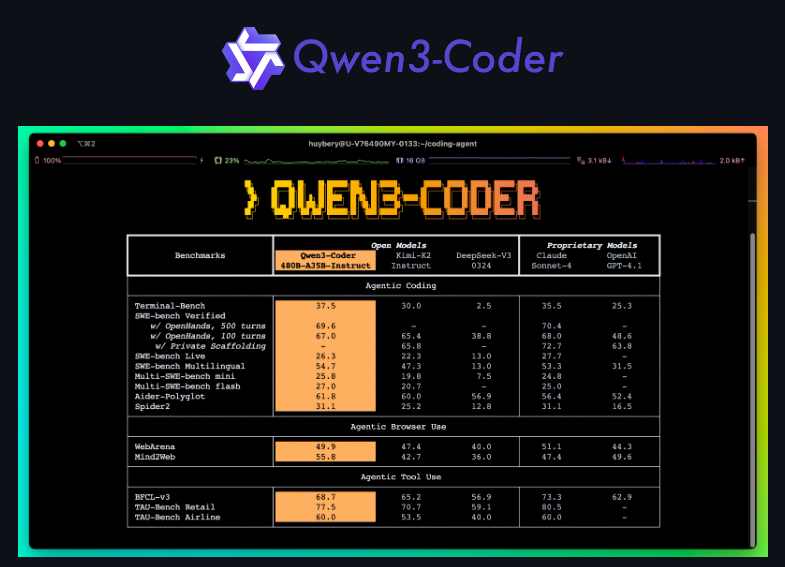
Qwen3‑Coder is Alibaba’s open-source agentic coding model, running up to 480B parameters, now deployable locally through Unsloth. It combines autonomous code generation with massive context windows designed for developers who want full offline control over high-performance LLM workflows.
Pros
- Agentic coding workflow: Qwen3 can read code, generate structured edits, write tests, and patch bugs via natural language or script prompts, useful for replacing multi-tool chains with a single model.
- 256K–1M token context support: Easily handles large monorepos, full-stack traces, or deeply nested logic without chunking. Dynamic context lets you reason across long sessions.
- Efficient quantization via Unsloth: Uses 2–8 bit dynamic quantization with GGUF to run locally on commodity GPUs and CPUs, balancing performance with memory usage.
- Local-first architecture: Fully runs via llama.cpp, Ollama, or other backends. No API calls, telemetry, or external dependencies, well-suited for secure, air-gapped, or regulated environments.
Cons
- High memory requirements: Full 480B variant needs ~150GB unified memory (VRAM+RAM). For local use, 32B or 110B variants are more realistic, especially without A100-class GPUs.
- Tuning overhead: Running optimally requires manual setup, quantization config, GGUF file selection, MoE tuning, and CPU/GPU flag optimization.
- No native IDE integration: Qwen is a base model only. To use it inside editors like VS Code or JetBrains, you’ll need to wrap it with tools like Continue.dev, Aider, or Cursor.
My Experience with Qwen:
I asked Qwen3-Coder via Unsloth to generate a Bash script that backs up a folder into a timestamped .zip file, complete with parameterized inputs and validations.
Prompt:
“Create a Bash script that backs up a given folder into a timestamped .zip file, with defaults to the current directory, optional destination paths, and proper error handling.”
As shown in the snapshot below Qwen3-Coder read the project context, checked the directory, and generated the script from scratch:
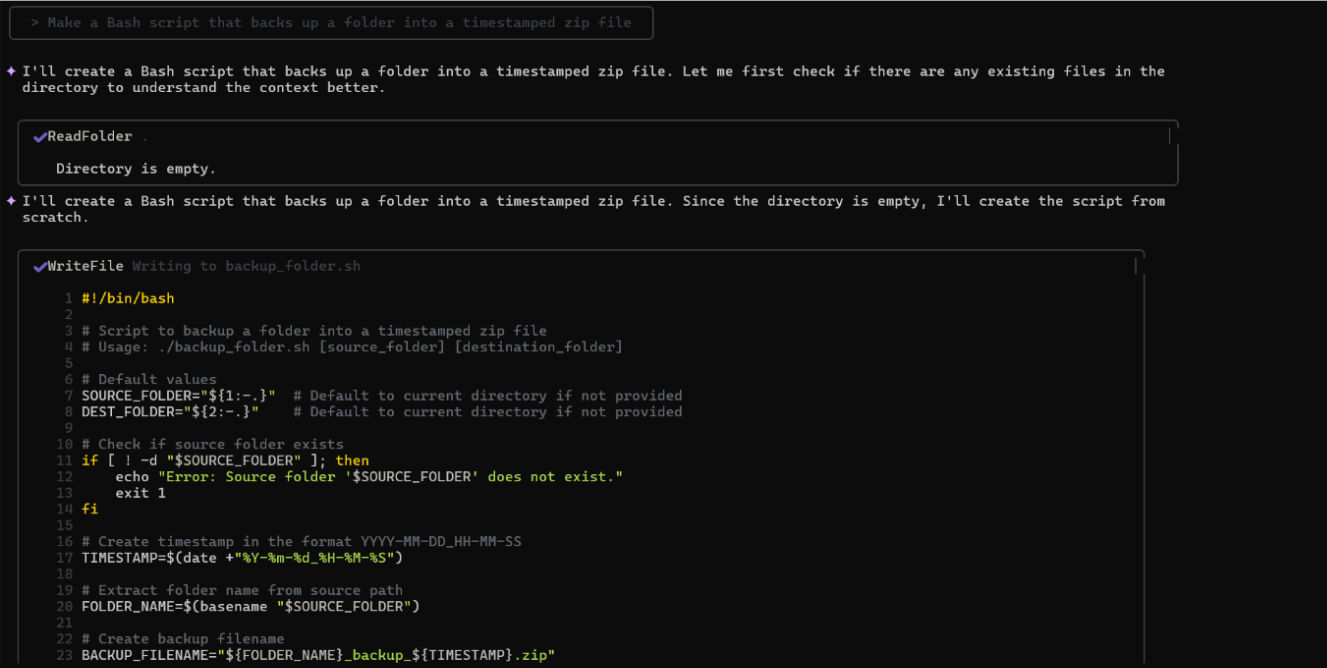
Generated script highlights (backup_folder.sh):
- Parameterized inputs: Accepts [source_folder] and [destination_folder] as arguments; defaults to current directory if omitted.
-
- Error handling: Validates if the source folder exists, exiting gracefully with informative messages.
- Timestamped naming: Uses date +”%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S” to append a timestamp to the .zip file.
- Portable design: Uses zip instead of hard dependencies like tar, ensuring compatibility across Linux/macOS.
Qwen3‑Coder’s Pricing
- Free and open-source. All model weights and deployment tooling (including Unsloth, llama.cpp quant formats, and configs) are available under Apache 2.0, with no licenses or usage fees.
Expert Summary:
Quen3Coder is entirely free and open-source, making it accessible for both individual developers and organizations without cost barriers, while also offering flexibility in deployment through widely supported tooling.
10. OpenAI Codex
OpenAI Codex is an advanced AI model that transforms natural language into functional code. I included it in this list because it excels at understanding natural language programming instructions and can work with an impressive range of programming languages, making it a versatile tool for developers of all backgrounds.
Pros of OpenAI Codex
- Quick setup: OpenAI Codex provides a user-friendly and efficient setup process, allowing developers to use the tool quickly and seamlessly.
- AI code completion tool: Codex offers advanced AI-powered code completion, providing accurate and contextually relevant suggestions to expedite the coding process and improve productivity.
- Natural language prompting: With natural language prompting, Codex enables developers to interact with the AI more intuitively, providing instructions and receiving code suggestions based on plain English descriptions.
- Supported languages: Proficiency in Python, JavaScript, Go, Perl, PHP, Ruby, Swift, TypeScript, Shell, and over a dozen other languages, making it versatile for diverse programming needs.
- Training dataset: Utilizes a training dataset containing both natural language and billions of lines of source code from publicly available repositories, including those on GitHub.
- Memory capacity: Memory capacity of 14KB for Python code, allowing it to consider over three times as much contextual information compared to GPT-3 during tasks.
- General-purpose programming model: It is applicable to various programming tasks such as transpilation, code explanation, and refactoring, with potential for further exploration.
Cons of OpenAI Codex
- Cost: OpenAI Codex can be costly for some users.
- Complexity: The setup and effective use of Codex may present challenges.
- Limited flexibility and interpretability: Codex might not always generate the most efficient or suitable code suggestions.
My Experience with OpenAI Codex
I’ve found OpenAI Codex particularly useful for its AI-powered code completion, which provides contextually relevant suggestions that speed up the coding process. The natural language prompting feature has also been a game-changer, as it allows me to describe what I need in plain English and get accurate code suggestions in return, making my workflow smoother and more intuitive. However, Codex does have a cost that might be prohibitive for some users, especially when working on personal projects or tight budgets. Additionally, while the tool is powerful, I’ve noticed it can be challenging to set up and use effectively at times, and it doesn’t always provide the most efficient or relevant code suggestions, which can be a bit of a setback.
Codex’s Pricing:
- Token-based pricingStarter – Free
- Billed per 1,000 tokens (≈750 words) or per 1M tokens for higher usage volumes
- Rates vary depending on the specific Codex model selected
- Costs scale with the number of tokens processed (input + output)
Expert Summary:
OpenAI Codex uses a flexible, usage-based pricing model. Developers pay according to the number of tokens consumed, with different rates for different Codex variants. This makes it cost-efficient for light use cases, while heavy users or enterprises can estimate costs more accurately at the million-token scale. For exact rates, OpenAI’s pricing page should be referenced, as prices may change over time.
11. Sourcegraph Cody
I included Sourcegraph Cody in this list because of its seamless integration with Sourcegraph’s search capabilities. What makes it stand out is how it understands my codebase, offering suggestions based on my repositories, documentation, and comments.
Pros of Cody
- Faster code generation: Cody can generate code on demand, either small code snippets or complete functions in any programming language.
- Code insights: The tool can explain individual code segments or entire repositories, where developers can easily understand new or complex projects.
- Quick unit test generation: It can generate unit tests in seconds, which helps developers save time and focus more on writing new features.
- Code smell detection and optimization: Cody can identify potential issues or bad practices in the code, helping users refactor and optimize their code for better performance.
- Custom prompts: Developers can define their custom prompts so the tool can adapt to specific workflows and coding styles.
- AI-powered autocompletion: The tool offers autocompletion that can generate single-line codes for entire functions, enabling faster coding and reduced syntax errors.
- Contextual awareness: With its AI capabilities, Cody offers context-aware suggestions, explanations, and edits, which provides developers with more accurate autocompletion and better guidance.
- Support for multiple LLMs: Cody is compatible with multiple large language models (LLMs), such as Claude 3.5, GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5, and Mixtral-8x7B. Users can also bring their LLMs through Amazon Bedrock and Azure OpenAI services.
Cons of Cody
- Limited language support: Cody may not cover all programming languages.
- Subscription cost: The subscription fee may be too expensive for some users.
My Experience with Cody
I tried out Cody’s VS Code extension to analyze and review a piece of code. The experience was straightforward, and generating results took just a single click. Below is the Sourcegraph Cody interface in VS Code, along with a coding example:
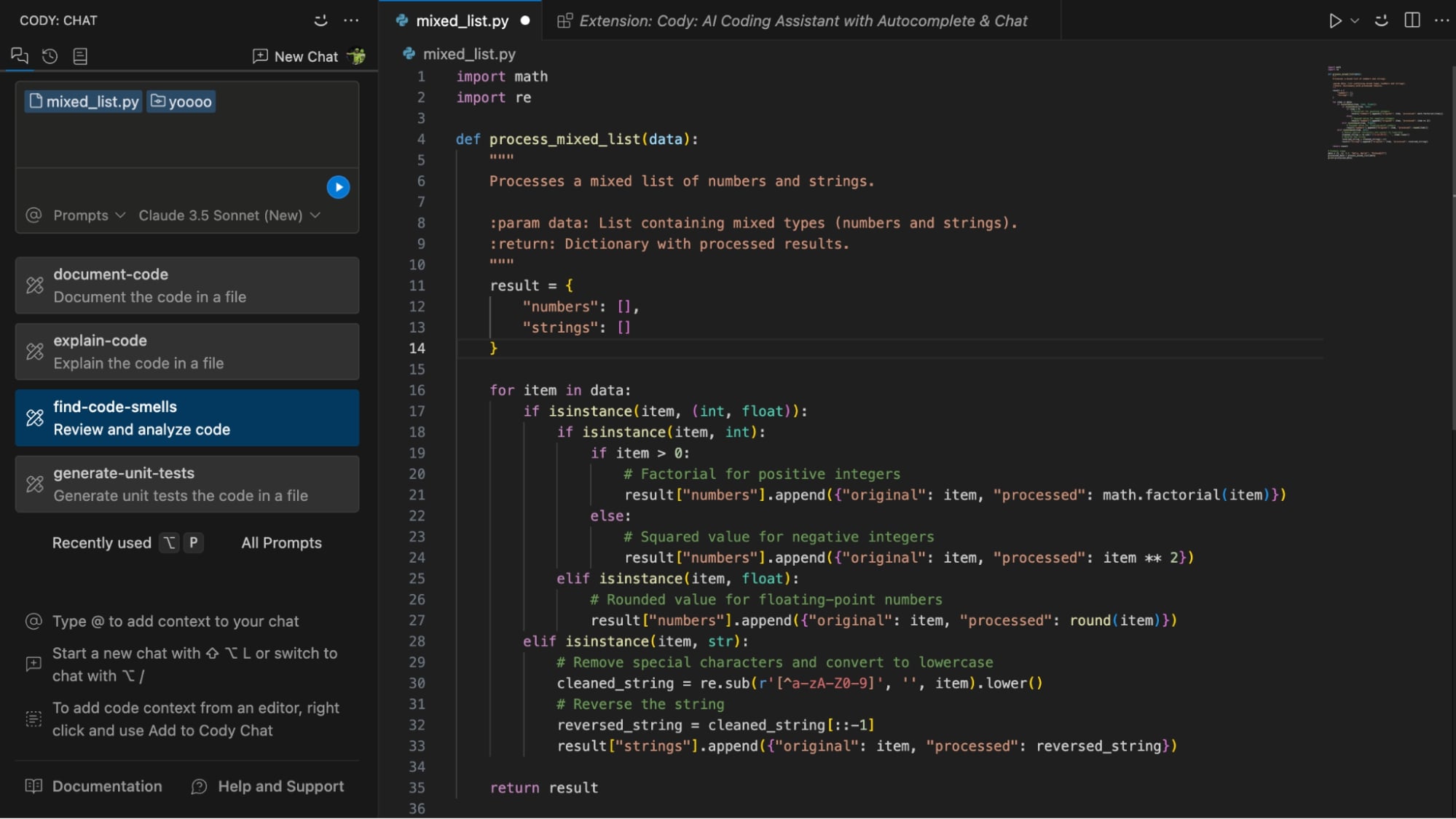
Here is the screenshot showcasing code smell detection for analysis and review, where Cody provided five constructive suggestions, such as input validation and type hints, along with corresponding code examples and their benefits.
Cody’s Pricing:
- Enterprise Starter – $19/user/month (up to 50 devs)
- Enterprise Search – $49/user/month (25+ devs)
Expert Summary:
Enterprise Starter is aimed at smaller teams wanting private code search with GitHub-only integration at a lower cost. Enterprise Search adds advanced search, insights, monitoring, and broader compatibility with enhanced security, making it more suitable for larger teams with complex codebases and compliance needs.
12. DeepCode AI
I included DeepCode AI by Snyk in this list because of its unique focus on security-first code analysis. What caught my attention is its hybrid approach – instead of relying on a single AI model, it combines symbolic AI with generative AI, trained specifically on security data from Snyk’s researchers.
Pros of DeepCode
- Hybrid AI: DeepCode AI uses symbolic and generative AI models trained on security-specific data, minimizing hallucinations and ensuring high accuracy.
- AI-powered quick fixes: The tool provides in-line quick fixes and automatically scans them to ensure they don’t introduce new issues. These fixes include a higher accuracy with an average success rate of 80%.
- Customized rule creation: Users can write their queries using DeepCode AI logic with autocomplete functionality, making it easier to create, test, run, and save custom rules.
- CodeReduce technology: Reduces the processing time and amount of code that the LLM (Large Language Model) needs to handle and also improves the quality of generated fixes, reducing hallucinations and enhancing overall accuracy.
Cons of DeepCode
- Restricted language compatibility: Snyk may not offer support for all programming languages.
- Pricing: The subscription fee for the team plan with advanced features may be too high for some users.
My Experience with DeepCode
I’ve found DeepCode AI to be a valuable tool, especially for identifying and fixing security vulnerabilities in my code. It seamlessly integrates with popular platforms like GitHub and code editors like Visual Studio Code, making it a smooth addition to my existing workflow. One of its standout features is continuous monitoring, ensuring my code stays secure as I work. However, there are some limitations. It doesn’t support every programming language, which can be an issue depending on the project. Additionally, the subscription cost might be too steep for some users, particularly those on tight budgets.
DeepCode’s Pricing:
- Open Source – Free
- For open source repositories
- Personal – $5.99/user/month
- For private repositories (1 user)
- Enterprise – Custom pricing
Expert Summary:
DeepCode is free for open source projects. The Personal plan provides affordable private repo support for individuals. The Enterprise option is designed for organizations needing on-premise deployment and tailored integrations.
13. Figstack
I included Figstack in this list because it solves multiple common development challenges in one tool. What stands out is its ability to explain complex code, translate between languages, and analyze code performance – features I find myself using regularly during development.
Pros of Figstack
- Code explanation in natural language: This feature helps users easily understand the code written in any language by translating it into clear, natural language descriptions.
- Cross-language code translation: Developers can easily convert code from one programming language to another. This simplifies the process of porting applications across different technology stacks.
- Automated function documentation: Figstack automatically generates detailed docstrings that describe the function’s purpose, parameters, and return values, ensuring that your code is always readable, maintainable, and well-documented.
- Time complexity analysis: The tool helps developers assess the efficiency of their code in Big O notation, pinpoint bottlenecks, and optimize their code for better performance by identifying the time complexity of a program.
Cons of Figstack
- Limited free credits: Figstack’s free plan offers a solid starting point, but the limited credits may not be sufficient for users with larger or more complex project requirements.
- Requires internet access: To make full use of Figstack’s features, a stable internet connection is necessary, which might not always be practical in certain situations.
- Paid features: Many of Figstack’s more advanced capabilities are locked behind paid plans, which could restrict access for users who prefer or are unable to pay for the premium options.
- Learning curve for new users: Although the platform is relatively easy to navigate, beginners may require some time to fully master its advanced features and integrations.
My Experience with FigStack
Let me show you how Figstack’s language translation feature works in real time. For example, I used it to convert a simple Python function to Go. This feature effortlessly bridges the gap between programming languages, saving time and making transitions between languages smooth and efficient. It’s a powerful tool for developers who need to work across different coding environments. 
Figstack’s Pricing:
-
Free – $0
-
Starter – $9/month
Expert Summary:
Free suits occasional use and quick explanations. Starter fits individual developers who need more credits and file/GitHub features. Unlimited targets for heavier usage; confirm exact entitlements on the official page.
14. Intellicode
I included Microsoft IntelliCode in this list because it seamlessly integrates with Visual Studio and VS Code, providing intelligent code suggestions right where I need them. What makes it valuable is how it learns from thousands of open-source GitHub projects to provide relevant code completions.
Pros of IntelliCode
- Autocompletion: IntelliCode offers whole-line autocompletion by analyzing the code context, significantly speeding up the coding process.
- Improved privacy: IntelliCode runs locally on the developer’s machine, ensuring the privacy of the code while offering precise and context-aware suggestions.
- Contextual IntelliSense: IntelliCode places the most relevant suggestions in the developer’s code based on analyzing thousands of open-source projects on GitHub.
- Repeated edits detection: The tool detects repetitive edits, where developers can apply changes consistently across their codebase.
- Quick actions: IntelliCode can recognize common coding patterns and tasks and suggest quick actions to simplify them, such as automatically generating constructors, adding parameters to constructors, etc.
Cons of IntelliCode
- IntelliCode suggestions may not be effective when working with complex code repositories that involve large codebases and multiple programming languages.
- The IDE can experience performance issues, particularly when dealing with large codebases and projects, leading to slower load times.
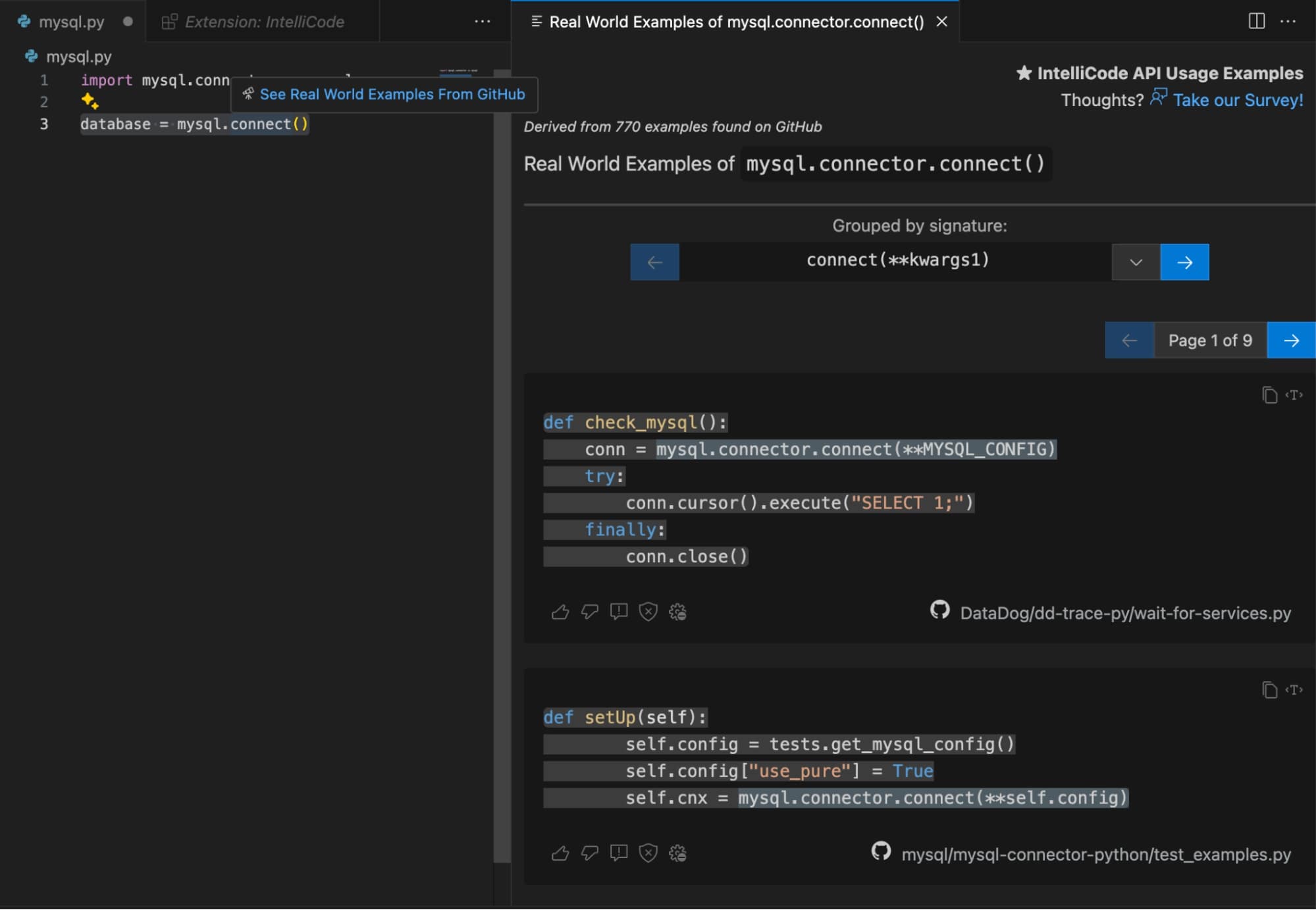
My Experience with IntelliCode
I installed IntelliCode as a VS Code extension and tested it while working with MySQL connections. When I hovered over the ‘connect’ function in the line “database = mysql.connect()”, IntelliCode displayed real-world usage examples from GitHub. By selecting a suggestion, I could access more detailed examples from GitHub repositories and easily integrate them into my code. Overall, IntelliCode has been a valuable tool, enhancing my coding efficiency by offering relevant, real-world examples directly within the IDE. It saved me time by eliminating the need to search for documentation or look up examples online.
Intellicode’s Pricing
- Free: Available at no cost for all Visual Studio users
Expert Summary:
IntelliCode is included free with Visual Studio, giving developers AI-assisted code completions and recommendations without requiring a separate subscription.
15. CodeGeeX
During my exploration of AI coding tools, I included CodeGeeX for its practical approach to code assistance. What makes it valuable is its straightforward functionality and useful features, which I’ve found helpful for developers. Its code generation works well for basic tasks, and the code translation feature has proven useful when working across different programming languages. The built-in AI chatbot helps answer quick technical questions, keeping me focused within my development environment.
Pros of CodeGeeX
- Code generation and completion: CodeGeeX offers accurate code generation capabilities based on natural language descriptions. Also, it can complete the current line or multiple lines ahead, making the development process faster.
- Code translation: Developers can effortlessly convert their code from one programming language to another.
- Automated comment generation: The tool saves time by automatically generating line-level comments, which helps improve code readability and maintainability.
- AI chatbot: The AI chatbot in CodeGeeX provides quick answers to technical questions directly within the development environment instead of having developers find solutions on the internet.
- Wide IDE and language support: CodeGeeX supports various popular IDEs, including Visual Studio Code, JetBrains IDEs, and multiple programming languages, such as Python, C++, JavaScript, and Go.
Cons of CodeGeeX
- Paid advanced features: Some of CodeGeeX’s advanced features are only available through the paid plan, which may limit access for users who prefer not to subscribe or are on a budget.
My Experience with CodeGeeX
Let me show you how I use CodeGeeX in practice. I was working on a simple time printing function in Python, and CodeGeeX helped me generate an explanation for the code. It provided a clear, concise breakdown of what the function was doing, which was incredibly helpful for understanding the logic behind the code. Overall, CodeGeeX has been a great tool for quickly generating explanations for my code. It helps clarify complex logic and is particularly useful when I need to document or explain my code to others.
CodeGeeX’s Pricing
- Free: Access to core multilingual code generation features across 15+ programming languages.
- Paid Plans – from $9/month: Unlocks advanced features and higher usage limits.
Expert Summary:
CodeGeeX offers free access for general use, while the paid plans starting at $9/month are intended for users who need extended capacity and advanced functionality across multiple languages.
16. Cline
Cline is a local-first coding agent for VS Code that acts as a task-based assistant rather than an autocomplete tool. You give it a goal, it plans the steps, shows you exactly what it intends to do, and executes only after approval. It’s designed for developers who want structured automation with full control and transparency.
Pros
- Plan and Act workflow: Reviews planned changes before execution.
- File and terminal control: Reads/modifies files, runs commands, and opens test sessions within a prompt flow.
- Snapshot checkpoints: Saves workspace states for easy diffing and rollback.
- Flexible model support: Works with Claude, DeepSeek, Gemini, or local models like Ollama.
- No telemetry: Fully local by default and open source for auditability.
Cons
- No inline autocomplete: Requires explicit task instructions; not a Copilot replacement.
- Manual setup: Needs user-supplied models or API keys.
- Best for scoped tasks: Can stall on large files or deeply nested repos.
My Experience with Cline:
In this example, Cline is asked to create a distributed event-driven system in Go for a microservices architecture, including error utilities, an event broker, and event handlers.
Prompt:
“Implement a distributed event-driven architecture in Go with an event bus, error handling utilities, and service-specific event handlers.”
Cline parsed the request, created a multi-step plan, and presented each action for approval before making any changes.
The plan included:
- Creating error handling utilities inside microservices/common/utils/errors.go.
- Implementing an event broker in eventbus.go to handle event publishing and subscription.
- Generating event handlers for individual microservices.
- Updating services to integrate with the event-driven architecture.
Cline displayed a detailed preview of file writes and modifications before applying them. For example, the event bus implementation as shown in the snapshot below used sync.RWMutex to coordinate access and sync.WaitGroup to manage concurrent event handler executions:
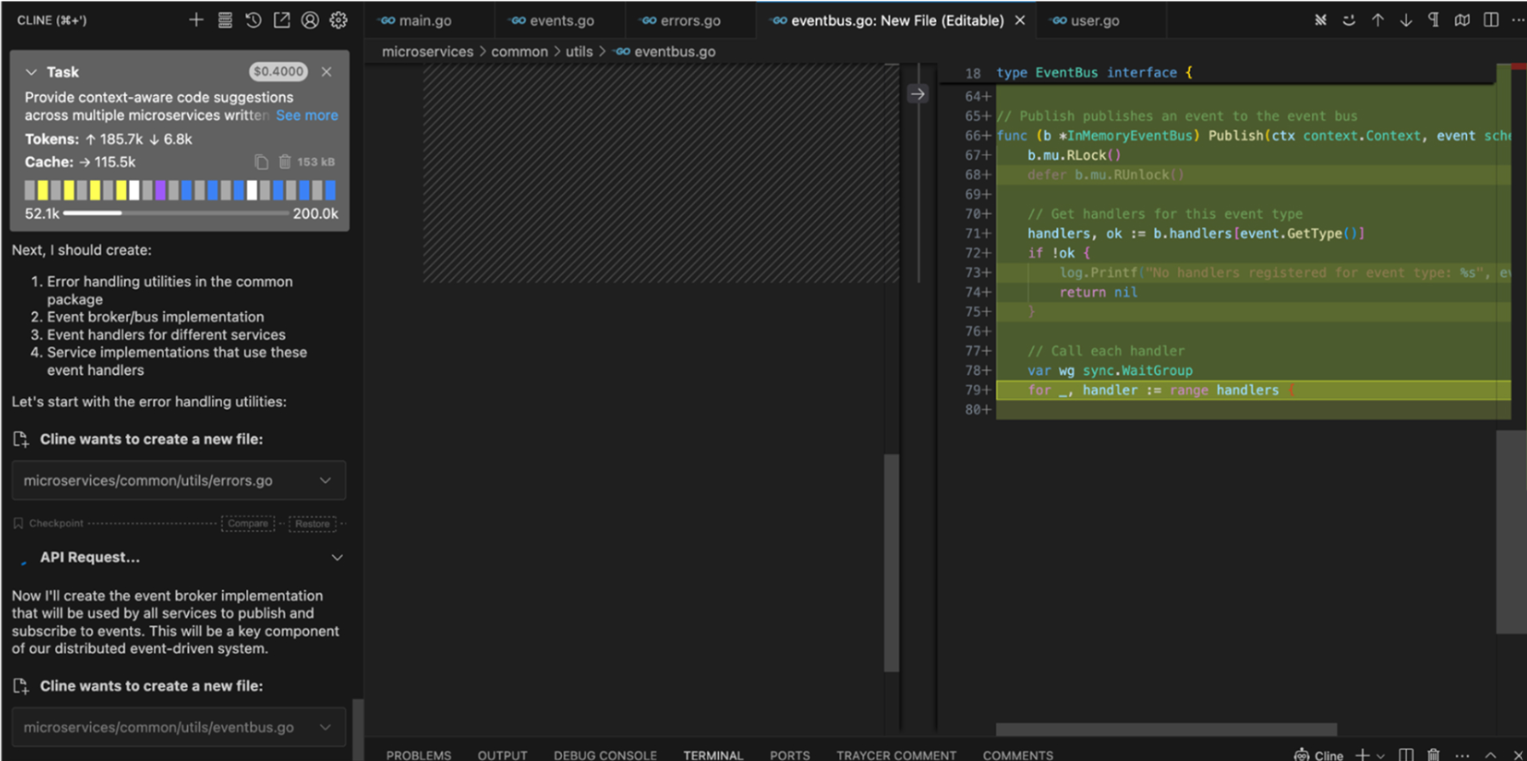
Because Cline is local-first, it gave complete control over every step:
- Approved each file creation and diff before writing.
- Watched the agent open terminals, run commands, and execute tests.
- Reverted changes at any point using snapshot checkpoints.
This approach allows for bootstrapping an event-driven microservices system quickly, while retaining auditability, safety, and control over the codebase.
Cline’s Pricing
- Open Source – Free (single users)
- Cline Teams – $30/user/month or $300/user/year
Expert Summary:
Open Source and Open Source Teams plans cover individuals and small groups at no cost, with charges only for inference usage. The paid Teams plan at $30 per user adds advanced admin controls, security features, and priority support, making it suitable for larger or more structured teams.
17. Augment Code
Augment Code is a developer AI platform that deeply indexes your codebase to power code completions, natural-language instructions, and autonomous agents. It integrates with VS Code, JetBrains, and Vim/Neovim, allowing the AI to interact with your workspace contextually, run terminal commands, and apply multi-file edits with awareness of your project structure.
Pros
- Context-aware indexing: Ingests your full workspace (code, docs, dependencies) for relevant, intelligent suggestions.
- Rich editor integrations: Supports chat, inline instructions, and step-by-step “Next Edit” workflows across major editors.
- Agent-driven execution: Can plan tasks, run commands, modify files, and review changes with checkpoint-based rollback.
- Guidelines and memory: Supports workspace rules, shared coding standards, and retains project-specific preferences.
- Enterprise compliance: Holds ISO/IEC 42001 and SOC 2 Type II certifications with options for customer-managed keys and no training on your code.
Cons
- Setup complexity: Requires indexing, rule configuration, and clear prompt structuring to leverage agents effectively.
- Cost: Enterprise compliance and advanced features are gated behind paid tiers, though a free trial is available.
- Occasional noise: Users report cases where agents merge test files incorrectly or introduce extra features if prompts lack precision.
My Experience with Augment Code:
Augment Code was used to enhance a TypeScript-based RingBuffer implementation by adding a method to remove a specific item. The developer simply requested, “Add a function to remove a specific item from the RingBuffer,” and Augment instantly generated the removeItem() method with well-structured logic. The newly added method:
- Iterates through the buffer’s items using modular arithmetic to account for wraparound
- Checks for the first occurrence of the item
- Removes it and returns true if found, or false otherwise
The tool didn’t just stop at code generation—it also integrated the new method into the corresponding test file (ring-buffer.test.ts). The generated test cases handled both successful and failed removal scenarios, ensuring thorough validation. With features like inline previews, context-aware suggestions, and a seamless way to apply or reject changes, Augment streamlined the entire enhancement process. All changes were scoped to the selected repository, file, and framework (Jest), maintaining precision and relevance. Overall, Augment Code provided a clean and intuitive workflow to evolve existing code with minimal effort while keeping full developer control intact.
Augment’s Pricing
- Community – Free
- Up to 10 user messages
- Context Engine, MCP & Native Tools
- Developer – $50/month
- Up to 600 user messages
- Team management (up to 100 users)
- Enterprise – Custom pricing
Expert Summary:
The Community plan is suited for individuals testing the platform with limited usage. The Developer plan expands capacity and adds compliance and team features for production use. The Enterprise plan is designed for larger organizations with advanced security, integration, and support requirements.
18. Gemini CLI
Gemini CLI is Google’s open-source AI agent for the terminal, bringing Gemini directly into your shell workflows. It operates in a ReAct-style loop, reasoning about your request before taking action using built-in tools. While it excels at coding-related tasks, it can also handle documentation, code search, and even multimedia generation through integrations like Imagen and MCP (Model Context Protocol).
Pros
- Large context window: Runs on Gemini 2.5 Pro with a 1 million token context, making it practical for large codebase analysis and multi-file reasoning.
- Generous free quota: Individual users get up to 60 requests per minute and 1,000 per day, one of the most liberal free tiers available.
- Rich tooling: Includes native grep, terminal execution, file read/write, Google Search grounding, and MCP integration.
- Open source: Licensed under Apache-2.0, allowing full inspection, extension, and self-hosting.
Cons
- Preview status: Still in public preview; APIs and feature stability are evolving.
- No deep IDE integration: Primarily terminal-based; while Gemini Code Assist offers some VS Code support, tight IDE hooks are still rolling out.
- Mixed user feedback: Some developers report occasional slow responses, context mismatches, or incorrect file edits.
My Experience with Gemini CLI:
Gemini CLI was used to analyze the src/routes/transactions.js file in a Node.js Express project. It provided a concise summary of the file’s functionality and flagged critical issues with remarkable clarity. The route in question handles a POST /transactions request that expects amount and cardNumber in the request body. Beyond summarization, Gemini CLI surfaced three key security concerns:
- Unused fs module: Identified as imported but unused, potentially hinting at dead code or a latent attack vector.
- Hardcoded internalToken: Flagged for being embedded directly in the source code, exposing sensitive data instead of utilizing process.env and a .env file.
- Use of eval(): Marked as a severe injection vulnerability, with a clear explanation that eval() could be exploited to run arbitrary code from a crafted request.
Gemini CLI didn’t just highlight problems—it explained the why behind each one, turning static analysis into actionable insights. With automatic file parsing and targeted feedback, it proved to be a valuable tool for securing Node.js APIs and enforcing clean code practices.
Gemini CLI’s Pricing:
- Standard – $22.80/user/month (monthly) or $19/user/month (annual)
- Enterprise – $54/user/month (monthly) or $45/user/month (annual)
Expert Summary:
Standard suits individual developers and small teams using IDEs and Google Cloud tools. Enterprise adds customization, broader integrations, and higher usage, targeting larger teams with advanced security and scalability needs.
19. Lovable
Lovable is a browser-native AI app builder that translates plain-English project specs into working full-stack applications. It automates frontend layout, backend logic, database wiring, and deployment, all without requiring a local IDE or manual infrastructure setup.
Pros
- End-to-end prompt-based generation: Type natural commands like “Build a blog with login and comments”, and Lovable scaffolds React + Tailwind UIs, backend handlers, and database schema.
- Native integrations: Supports out-of-the-box connectivity with GitHub, Supabase (data/auth), Clerk/Stripe (auth/payments), and LLM APIs (OpenAI, Claude, DeepSeek), with zero backend boilerplate.
- Visual editing + version control: Offers click-to-edit UI components, visual diffs, and version history useful for quick iterations without touching code.
- Export-friendly: Full codebase can be pushed to GitHub or downloaded locally, allowing further development in your IDE of choice.
Cons
- Token burn during debugging: AI-driven fix loops can burn through credits quickly, especially during backend error resolution.
- Prompt-debug friction: Some users hit repetitive edit–retry cycles when trying to fix logic bugs, which leads to inefficiencies at scale.
- Not IDE-integrated: Lovable runs entirely in-browser; it doesn’t support VS Code or JetBrains plugins for inline editing or debugging.
My Experience with Lovable
I used Lovable to generate a landing page for a platform focused on code generation and testing. The prompt was intentionally minimal to see how well it could infer layout, design, and messaging. Once the generation began, Lovable designed a modern, developer-facing UI with a dark theme, bold typography, and component breakdowns. It scaffolded elements like the CTA.tsx file and included design tokens for gradients, buttons, and layout structure. Here’s how the UI looked after generation:
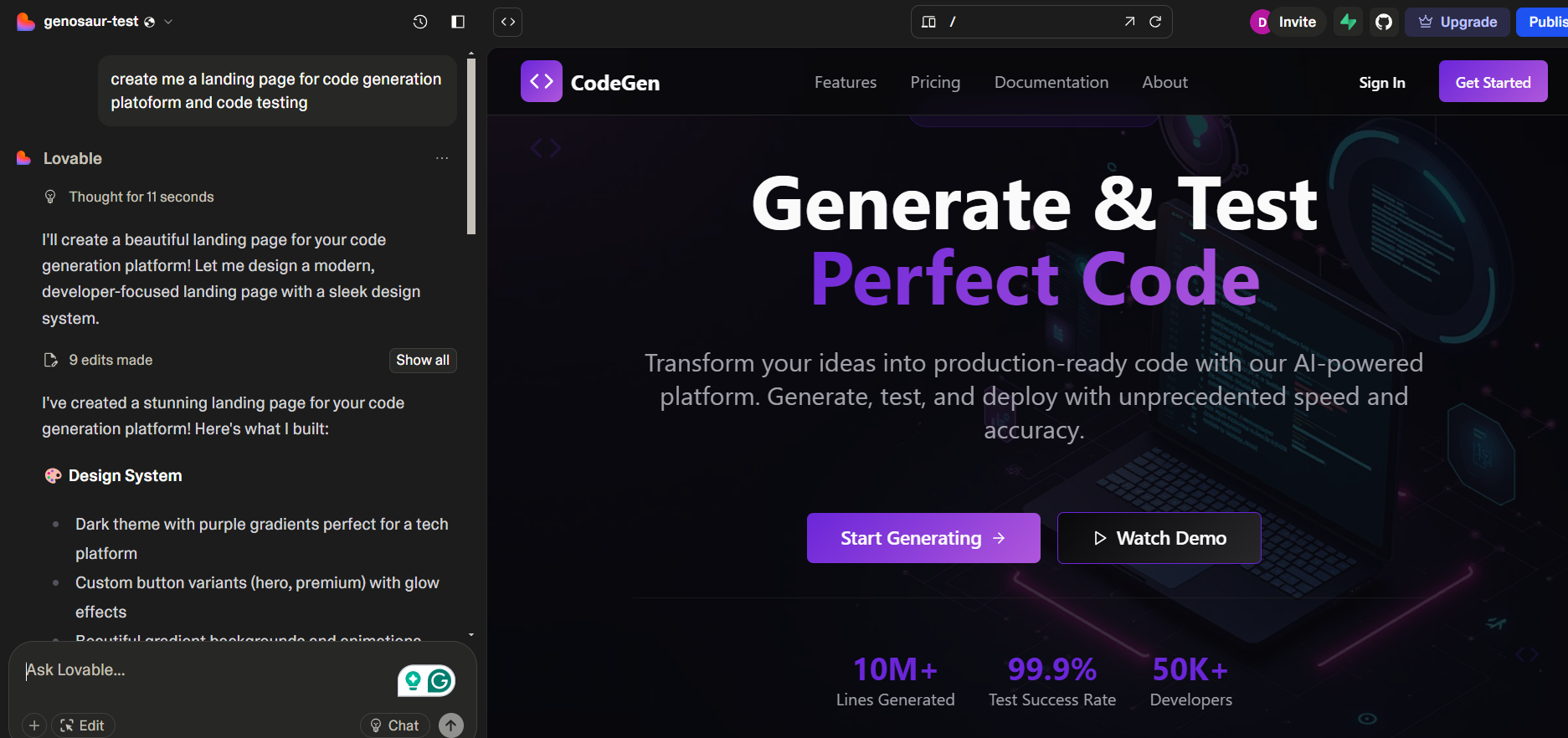
The layout it produced featured key landing page elements: a prominent headline, call-to-action buttons, and metrics to establish credibility. While visually polished, the actual structure followed a generic pattern, so customizing for product-specific flows (e.g., dynamic demos, API sections, signup logic) still required manual edits. Overall, Lovable was effective in quickly generating a presentable front-end structure. It’s best suited for prototyping or iterating on landing pages, though deeper customization and refinement are necessary before production use.
Lovable’s Pricing
- Free – $0
- Pro – $25/month (annual billing)
- Business – $50/month (annual billing)
- Enterprise – Custom pricing
Expert Summary:
Free is suitable for individuals experimenting with public projects. Pro adds private projects and collaboration tools for small teams. Business introduces SSO, personal projects, and compliance features for growing departments. Enterprise is tailored for large organizations needing governance, integrations, and dedicated support.
20. CodeGPT
CodeGPT is an AI coding agent platform that integrates into IDEs like VS Code, JetBrains, and Cursor. It provides repository-wide context, multi-model backend support, and customizable agents for automated development tasks. It’s designed for engineers who want deeper code understanding and automation without leaving their editor.
Pros
- Repo-wide code understanding: Builds an internal knowledge graph of your codebase, including symbols, dependencies, and call trees to provide relevant, scoped suggestions.
- Supports multiple LLMs: Compatible with OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Mistral, and local models via Ollamaenabling flexible or self-hosted deployments.
- Agent ecosystem: Offers prebuilt agents for code review using AI code review tools, test generation, documentation, and framework-specific helpers (Laravel, Supabase, Next.js, etc.).
- Privacy and local execution: Supports self-hosted setups and offline inference with local models, ideal for sensitive or private repositories.
- Cross-editor and web support: Runs inside VS Code, JetBrains IDEs, Cursor, and a standalone browser-based studio.
Cons
- Initial setup overhead: Requires installing the extension, setting up API keys, and (optionally) configuring local model servers, more involved than simple autocomplete plugins.
- Freemium limitations: The Free plan has restricted quotas and limited agent capabilities; access to private repos and advanced workflows requires a paid plan.
- Learning curve: Custom agent development and tuning prompts may require time and familiarity with the agent architecture and model behaviors.
My Experience with CodeGPT:
Example of CodeGPT to assist in building a basic agent-based interaction system using a fictional Swarm API. The task involved setting up a message loop that filters out empty messages and formats valid ones for console output. The prompt was centered around explaining logic inside a message processing loop. CodeGPT immediately broke down the use of if message[“content”] is None: and explained how the continue statement skips irrelevant entries. It also showed the correct use of f-strings to log sender and message content. While the user was editing the app_swarm.py file, CodeGPT actively explained:
- The structure of conditionals within loops
- Why skipping None values avoids unnecessary processing
- How the log output maintains sender attribution
Here’s the interface during the explanation and code interaction:
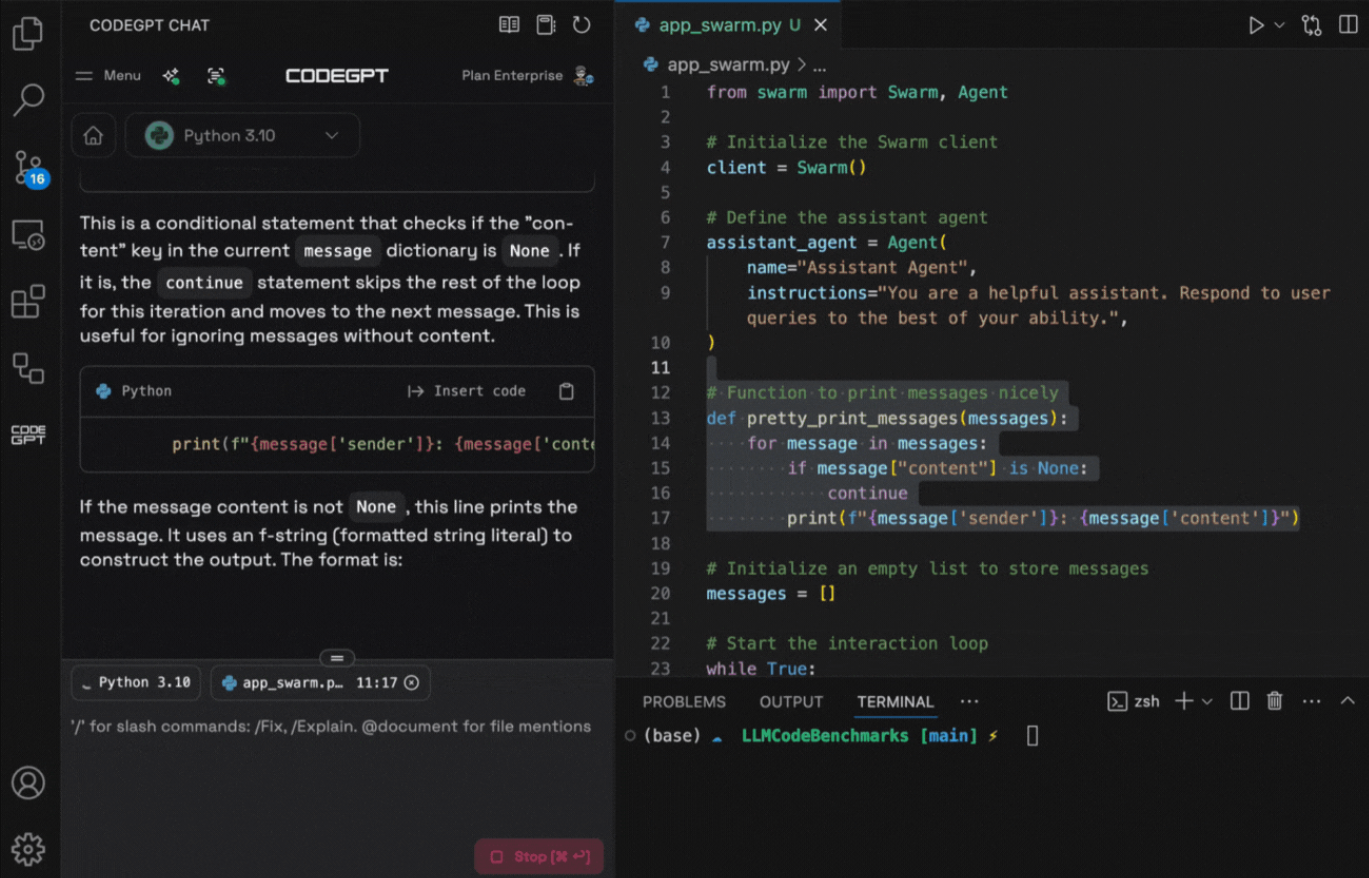
CodeGPT’s inline explanation sat adjacent to the IDE, allowing context-aware understanding of the surrounding logic. The assistant wasn’t just suggesting syntax but actively interpreting intent, useful for onboarding developers or validating reasoning in shared codebases. Works well for scenarios where understanding intent behind logic is as important as writing it. Particularly valuable in debugging or reviewing unfamiliar code by augmenting the editor with interactive, targeted documentation.
CodeGPT’s Pricing
- Free – $0/seat/month
- BYOK – $7.20/seat/month (billed annually)
- Teams – $30/seat/month (billed annually)
- For Business – Custom pricing
Expert Summary:
The Free plan works for beginners with light usage. Bring your own key (BYOK) removes daily limits and adds planning features, making it a good step up for individuals. Teams expands capacity, storage, and collaboration for organizations. The Business plan is fully customizable, offering enterprise security, flexible deployment, and tailored AI solutions.
Evaluating AI Code Review Platforms for Enterprise Teams
1. Integration at Enterprise Scale
Enterprise code review platforms must integrate seamlessly. At scale, success depends less on flashy features and more on how well the platform fits into existing workflows. Many tools create friction by forcing developers into browser-based IDEs or CLIs, which slows teams down.
Enterprise-ready solutions need to connect directly with GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, integrate with CI/CD pipelines, and surface quality checks inside IDEs, as well as pull requests. Integration with task managers such as Jira or Linear further improves traceability. Qodo addresses this by embedding its agents directly into IDEs, pull requests, and pipelines without requiring workflow changes.
2. Codebase Complexity and Context Modeling
Complex codebases demand deep context. Enterprises often maintain monorepos or multi-repo architectures spanning many frameworks, languages, and services. Lightweight tools usually fail in these environments because their context windows are limited and their understanding of service dependencies is shallow.
A robust solution must recognize internal libraries, track historical commit patterns, and reason across repositories as a native capability. Qodo solves this with an organization-wide context model that combines multiple indexing strategies. Its agents use this model to analyze repositories holistically, which reduces regressions in dependent components during reviews.
3. Enforcing Consistent Code Quality
Consistent code quality requires automated enforcement. Large, distributed teams often face uneven reviews where outcomes vary by reviewer. An effective platform enforces coding standards, security requirements, and testing policies automatically, while providing structured fixes with clear explanations.
Test generation and validation are equally important to sustain healthy coverage. Qodo extends these capabilities with a multi-agent architecture: one agent generates code, another manages testing, another enforces compliance, and another performs structured reviews. By embedding quality checks throughout the SDLC, Qodo eliminates reliance on disconnected tools and ensures consistent, policy-driven reviews at scale.
Best Coding AI: Summary
In my experience, AI coding assistants have been game-changers for boosting productivity. They offer features like code suggestions, explanations, test generation, and collaboration tools. Some even go a step further by providing real-world code examples from platforms like GitHub, making it easier to learn and implement best practices. These tools support a wide range of programming languages and IDEs, catering to both individuals and teams with pricing options ranging from free to subscription-based plans. Let me summarize the tools we’ve discussed in a concise table for easy comparison.
| Tool | Pricing | Key Features |
| Qodo | Free for individual use; $19/user/month for teams | Precise code suggestions, code explanation, automated test generation, code behavior coverage, streamlined collaboration, seamless implementation, multi-language and IDE support |
| GitHub Copilot | Free for individual use; $4/user/month for teams | Code suggestions, chat functionality, easy auto-complete navigation, multi-language and IDE support |
| Tabnine | Free for basic AI code completions; Pro: $9/user/month | Code refactoring assistance, code linting, automatic code documentation, intelligent code completions |
| Bolt | Free tier; Paid plans unlock more resources and integrations | Browser-based full-stack development environment with instant preview, rapid prototyping, collaborative editing, and integrated deployment |
| Amazon Q Developer | Included with AWS subscription plans; pricing varies by usage | AI-powered coding in AWS ecosystem, context-aware code generation, natural language queries for code and cloud resources, integrates with IDEs and AWS Console |
| AskCodi | $9.99/month membership; Free for personal use | Code generation, answering programming questions, providing code suggestions, IDE integration |
| Codiga | Free for individual; Paid subscription starts at $14/month | Static code analysis, code completion, code linting, code refactoring, code reviews, language and IDE support |
| Replit | Free for individual use; Hacker: $7/month; Pro: $20/month | Advanced in-line suggestions, code explanation and comments, mistake detection and correction, interactive learning environment |
| Qwen3-Coder (Unsloth) | Free and open source; costs depend on model usage | Large language model optimized for coding, reasoning, debugging, multi-language support, and efficient local or cloud deployment |
| OpenAI Codex | Price based on API usage | Quick setup, AI code completion, natural language prompting, supported languages, memory capacity, general-purpose programming model |
| Sourcegraph Cody | Free for individual; Paid starts at $9/month | Code generation, insights, test generation, custom prompts |
| DeepCode AI | Free plan; Paid starts at $25/month | AI-powered quick fixes, customized rule creation, code reduction technology |
| FigStack | Free | Code explanation, automated documentation, time complexity analysis |
| Intellicode | Free | Real-world usage examples from GitHub, improved privacy |
| CodeGeeX | Free plugin version | Code generation, code translation, AI chatbot |
| Cline | Free and open source; Costs depend on model used (local or API calls) | Local-first task-based coding agent for VS Code, Plan-and-Act workflow with approval steps, file/terminal control, snapshot checkpoints, flexible model support, no telemetry |
| Augment Code | Free trial; Paid tiers for compliance & advanced features | Context-aware code indexing, multi-editor integration (VS Code, JetBrains, Vim), agent-driven execution, workspace rules/memory, enterprise compliance |
| Gemini CLI | Free for individuals; Advanced tiers via Google Cloud | Terminal-based AI agent with 1M token context window, generous free quota, native tools (grep, file I/O, search), MCP integration, open source |
| Lovable | Free tier; Paid plans unlock advanced templates & integrations | Browser-native full-stack app builder, prompt-based generation, integrations with Supabase/Clerk/Stripe, visual editing, GitHub export |
| CodeGPT | Free tier; Plus/Pro unlock premium agents, private repos, and advanced API routing | IDE-integrated coding agent with repo-wide context, multi-model support (OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, local), customizable agents, privacy-friendly local execution |
Conclusion
As technology advances, I see AI coding assistants playing a bigger role in software development. With LLMs’ ability to keep learning and improving, these AI tools have the potential to completely change how developers code, helping them innovate, collaborate, and write better-quality code. By embracing the power of these tools, developers can tackle coding challenges more easily, enhance their skills, and build high-quality software in this fast-changing digital world.
FAQs
What is an AI coding assistant?
Have you ever spent hours writing repetitive code or struggling to find the perfect function? AI coding assistants are here to help! These sophisticated software tools harness the capabilities of powerful AI, such as large language models (LLMs), to streamline your development workflow.They act as your virtual coding partner, offering intelligent suggestions for completing code lines, fixing errors, and even recommending alternative approaches to achieve your goals. This translates to faster development, cleaner code, and a significant boost in your overall productivity.
What is the best AI tool for generating code?
Several AI coding assistant tools are on the market, and finding the best one for you depends on your needs. Users should consider several key factors when choosing an AI code-generation tool. Typically, you will want tools that offer intelligent code completion and suggestions, debugging assistance, code refactoring recommendations, automatic tests, documentation generation, integration with your preferred IDE, and support for your favorite programming languages. We are biased, but take a look at Qodo; we think you will love it!
Is there a free AI coding assistant?
Yes, several AI coding assistants offer a free version. Qodo offers a free plan for individual developers. To get started, just download our free VS Code extension or JetBrains plugin. As part of the free plan, you get test generation, the coding agent, code review, and auto-documentation, among other tools.
Who can benefit from AI coding assistant tools?
AI coding assistants can benefit a wide range of users, from experienced programmers looking to fast-track their development to newer developers seeking guidance and learning opportunities. These tools can also help organizations simplify processes and boost team productivity through collaboration.
What are common use cases for coding assistant tools?
Common use cases for coding assistant tools include:
- Code completion and generation
- Code refactoring
- Test case generation
- Documentation creation
- Error and security findings detection
- Debugging assistance
- Optimizing code reviews
- Enhancing productivity in workflows
How do you generate code using AI?
AI code generation promises a quick boost of productivity for programmers. To generate code using AI, first choose an AI-powered coding assistant tool. Then, provide a natural language description of your expected code. The AI coding assistant tool will suggest code snippets that you can review, refine, or accept as is. Finally, integrate the code into your project. Never forget to test and validate the AI-generated code thoroughly.
What is the best AI for coding?
There’s no single “best” tool for everyone, but if you want something precise, collaborative, and versatile, Qodo is a standout. It offers sharp code suggestions, clear explanations, and even automated test generation, all while working smoothly across multiple languages and IDEs. It’s especially handy for teams that want built-in collaboration. That said, GitHub Copilot is great for quick inline completions, Qwen3-Coder (Unsloth) is perfect for those who value open-source control, and CodeGPT is ideal if you want to tap into multiple AI models from one place.
What tool is used for writing and running a model’s code?
Most developers stick with familiar environments like VS Code or JetBrains to write and run code for AI models. If you’re experimenting with AI or machine learning, tools like Jupyter Notebook or Google Colab let you code and see results instantly. For command-line fans, there are also CLI tools like Gemini CLI or Hugging Face CLI that work great for running models directly.
What’s the difference between black box and white box testing?
Black box testing is all about checking what the software does from the outside, not peeking at the code like pressing buttons on a remote to see if it works. White box testing means looking inside the code and testing every branch and function, more like inspecting the wiring inside the remote to make sure everything is connected properly.
Which AI is best for coding?
The answer depends on factors like the programming languages you use, the size of your codebase, and the type of tasks you need help with. For example, Qodo is often chosen by developers who want a single tool that can handle code generation, automated testing, and pull request reviews within popular IDEs such as VS Code and JetBrains. Its multi-language support and ability to integrate into existing workflows make it a practical option for teams and individual developers alike.
What is the best AI model for coding?
The best AI model for coding depends on your requirements, such as speed, accuracy, offline capability, and cost. Popular options include OpenAI’s Codex, Anthropic’s Claude, Google’s Gemini, and open-source models like Qwen3-Coder. Some tools, such as Qodo, can work with multiple models, allowing developers to choose the one that best fits their workflow and project needs.